This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Tran Cong Trinh - Radiologist - Radiology Department - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital. The doctor has many years of experience in the field of diagnostic imaging.A stroke is a life-threatening condition if not treated quickly. The best way to prevent disease and serious complications is to control associated conditions and improve knowledge of primary self-care in the event of a stroke.
1. What is a stroke?
A stroke occurs when blood flow to part of the brain is interrupted due to a ruptured or compressed blood vessel in the brain. At that time, brain cells will die from lack of a constant supply of oxygen, causing permanent damage to the brain.Stroke has two types: ischemic stroke (also known as cerebral embolism) and hemorrhagic (also known as cerebral hemorrhage). A stroke caused by a hemorrhagic stroke causes blood to leak out of the arteries and into the brain.
An embolic stroke occurs when the blood vessels that carry blood to the brain are blocked or narrowed by the impact of a blood clot or narrowing of an artery.
Clogged arteries: Fat, cholesterol and other substances have the ability to build up on the walls of blood vessels. Over time, they harden and form a structure known as plaque. This causes an artery blockage, narrowing the flow of blood vessels. Blood clots: Blood clots that form in already very narrow blood vessels in the brain are the cause of a thrombotic stroke. In addition, a stroke can also be caused by blood clots that form elsewhere in the body and travel to a blood vessel in the brain, known as an embolic stroke. A stroke can also happen because air bubbles or other foreign substances in the blood move into a blood vessel in the brain. Symptoms that are similar to a stroke but last for a short time are called a transient ischemic attack (TIA). It usually leaves no lifelong complications but is a warning sign of an actual stroke. Symptoms of a TIA can last from a few minutes to 24 hours.
Stroke symptoms depend on the part of the brain affected. They happen suddenly, without warning. Among them, common symptoms include:
Severe unexplained headache Paralysis or weakness in the face, arm or leg (especially on one side of the body) Drowsiness and difficulty speaking or understanding speech Decreased vision in one or both eyes Dizziness, loss of balance, or a combination of both.

Đau đầu dữ dội không rõ nguyên do là triệu chứng cảnh báo đột quỵ
2. Measures to diagnose stroke
To diagnose a stroke, CT and MRI are the first steps used. The aim is to identify the type of stroke acquired (cerebral hemorrhage or cerebral embolism). From there, it helps to determine the right treatment.2.1. Computerized tomography (CT) of the brain CT scans combine special X-ray equipment with computers to help view images of organs in the body. It is used to differentiate between hemorrhagic stroke and cerebrovascular occlusion. In addition, CT angiography (CTA) may be combined to detect and characterize stroke. Then, the patient will have a CT scan with contrast injection to evaluate the cerebral blood vessels, observe the blood vessels supplying the injured area. CT perfusion (CTP) helps to observe cerebral blood flow. The combination of CT, CTA, and CTP helps determine the best therapy to treat stroke patients.
2.2. Brain MRI An MRI uses a strong magnetic field, electrical pulses, and a computer to create detailed images of organs, soft tissues, bones, and almost all other structures inside the body. Cerebral angiography (MRA) is also used to visualize the detailed structure of cerebral blood vessels. Cerebral blood flow was recorded by perfusion MRI (MRP). Brain MRI is used to assess the extent of brain damage caused by a stroke.
In order to confirm the type, location and cause of stroke and rule out other conditions, the following tests should be added:
2.3. Blood tests Indications for blood tests include many different types (blood cell analysis, blood biochemistry, coagulation,...). They are useful in assessing stroke status and provide additional information before prescribing treatment, especially before performing procedures and prescribing anticoagulants. In addition, biochemical indicators such as cholesterol, triglycerides, blood glucose, ... also help determine the causes of blood clots and blockage of blood vessels.
2.4. Electrocardiogram (ECG, EKG) An electrocardiogram records electrical signals as they travel through the heart. It helps identify heart conditions that are at risk for stroke.
Điện tâm đồ (ECG, EKG) giúp bác sĩ chẩn đoán đột quỵ
2.6. Cerebral Angiography A cerebral angiogram is a test done with one of three imaging techniques X-ray, CT, or MRI, or in some cases contrast medium to create images of the major blood vessels in the brain. Brain. It helps detect abnormalities such as blood clots or narrowing of the arteries.
3. How is a stroke treated?
Stroke is a medical emergency, the faster it is treated, the higher the survival rate and the reduction of complications. Treatment depends on the severity and type of stroke. Typically, it focuses on restoring blood flow for stroke due to cerebral embolism and controlling bleeding and reducing flow pressure for hemorrhagic stroke.
If the cause of the stroke is a blood clot, the patient is usually prescribed a thrombolytic drug such as tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA). This drug is prescribed within the first few hours after the onset of a stroke. In addition, other drugs such as aspirin or warfarin (coumadin), heparin, or clopidogrel (plavix) also work to dissolve blood clots.
A stroke is a medical emergency, and the quicker it is treated, the higher the survival rate and the lower the complications. Treatment depends on the severity and type of stroke. Typically, it focuses on restoring blood flow for stroke due to cerebral embolism and controlling bleeding and reducing flow pressure for hemorrhagic stroke.
If the cause of the stroke is a blood clot, the patient is usually prescribed a thrombolytic drug such as tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA). This drug is prescribed within the first few hours after the onset of a stroke. In addition, other drugs such as aspirin or warfarin (coumadin), heparin, or clopidogrel (plavix) also work to dissolve blood clots.
Other stroke treatments include:
Surgery to drain blood from a blood vessel due to a brain hemorrhage and repair broken blood vessels. Endovascular treatment: Endovascular intervention is a minimally invasive procedure used to improve blood flow in the arteries and veins of the brain. In endovascular therapy, a catheter is inserted into the site of a ruptured or narrowed blood vessel to deliver: Thrombolytic drugs. Mechanical thrombectomy Angioplasty balloons are used to widen narrowed blood vessels, and stents and small tubes are used to keep blood vessels open for extended periods of time. This procedure is done to improve blood flow in the carotid arteries that supply the brain. Small metal coils to mend broken brain arteries.
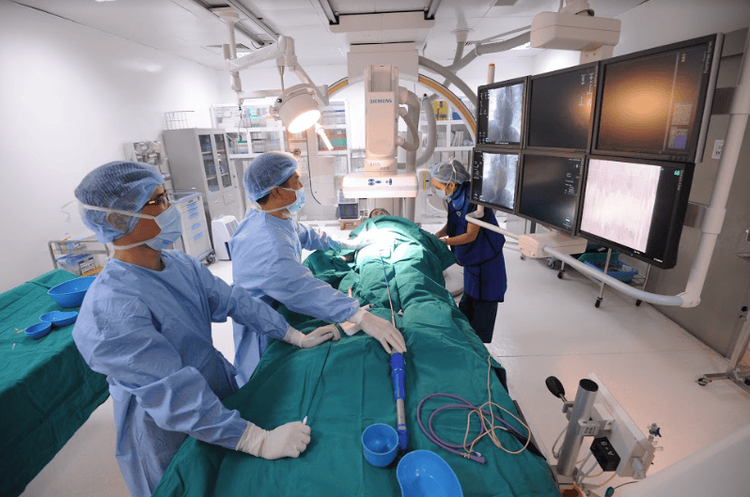
Sử dụng phương pháp can thiệp nội mạch trong điều trị đột quỵ
In order to serve the accurate examination and diagnosis of cerebral strokes, the Department of Diagnostic Imaging of Vinmec International General Hospital is now fully equipped with modern medical equipment such as: ultrasound, CT, MRI, electrocardiogram,...
Currently, Magnetic Resonance Imaging - MRI/MRA is considered a "golden" tool for brain stroke screening. MRI is used to check the condition of most organs in the body, especially valuable in detailed imaging of the brain or spinal nerves. Due to the good contrast and resolution, MRI images allow to detect abnormalities hidden behind bone layers that are difficult to recognize with other imaging methods. MRI can give more accurate results than X-ray techniques (except for DSA angiography) in diagnosing brain diseases, cardiovascular diseases, strokes,... Moreover, the process MRI scans do not cause side effects like X-rays or computed tomography (CT) scans.\
Vinmec International General Hospital currently owns a 3.0 Tesla MRI system equipped with state-of-the-art equipment by GE. Healthcare (USA) with high image quality, allows comprehensive assessment, does not miss the injury but reduces the time taken to take pictures. Silent technology helps to reduce noise, create comfort and reduce stress for the client during the shooting process, resulting in better image quality and shorter imaging time. With the state-of-the-art MRI system With the application of modern methods of cerebral vascular intervention, a team of experienced and well-trained neurologists and radiologists, Vinmec is a prestigious address for stroke risk screening and screening. reliable goods.
In the past time; Vinmec has successfully treated many cases of stroke in a timely manner, leaving no sequelae: saving the life of a patient suffering from 2 consecutive strokes; Responding to foreign female tourists to escape the "death door" of a stroke;...
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: radiologyinfo.org