This is an automatically translated article.
Magnesium plays an important role in the health of the body and brain. However, the body can lack magnesium even if you eat a healthy diet. It is necessary to supplement magnesium with magnesium-rich foods or supplements. Here are 10 science-based health benefits of magnesium.1. Magnesium participates in hundreds of biochemical reactions in the body
Magnesium is a mineral found in the earth, sea, plants, animals and humans. About 60% of the magnesium in your body is found in your bones, with the rest in your muscles, soft tissues, and fluids, including blood. In fact, every cell in your body contains magnesium and needs it to maintain normal functions.
One of the main roles of magnesium in the body is that they act as an aid in the ongoing biochemical reactions carried out by enzymes. It is involved in more than 600 reactions in your body, including:
Energy generation: Helps convert food into energy Protein formation: Helps make new proteins from amino acids Gene maintenance: Helps create and repair repair DNA and RNA Muscle movement: As part of muscle contraction and relaxation Nervous system regulation: Helps regulate neurotransmitters, sending messages throughout the brain and nervous system
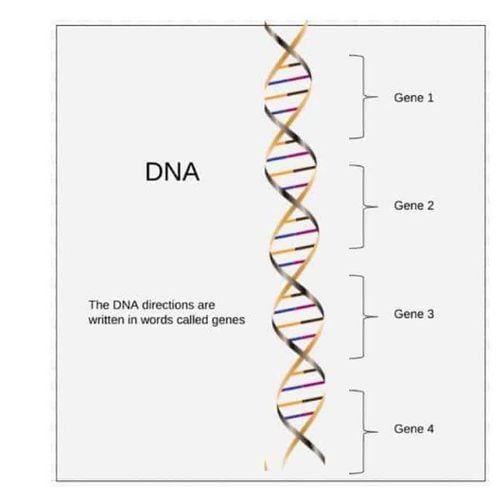
Magie giúp tạo và sửa chữa DNA và RNA
2. Increase exercise performance
When exercising, you may need 10-20% more magnesium than you would at rest, depending on the exercise. Magnesium helps move blood sugar into your muscles and get rid of fat that is created during exercise and causes fatigue.
Studies have shown that magnesium supplementation improves exercise performance in athletes, the elderly, and people with chronic conditions. In a recent study, athletes who took magnesium supplements for four weeks performed faster in running, cycling, and swimming in a triathlon. Insulin and stress hormone levels were also lower in these athletes than in the control group.
3. Magnesium helps fight depression
Magnesium plays an important role in mood and brain function. They are also associated with an increased risk of low-grade depression. An analysis of more than 8,800 subjects found that those under the age of 65 with the lowest magnesium intake had a 22% higher risk of depression.
Some experts believe that the low magnesium content of modern foods may be causing more cases of depression and mental illness. However, more studies are needed to confirm this result. Magnesium supplements have been shown to reduce symptoms of depression and in many cases are very effective. In a randomized controlled trial in older adults with depression, a daily dose of 450 mg of magnesium improved mood as effectively as an antidepressant.

Bổ sung 450 mg magie hàng ngày giúp cải thiện tâm trạng hiệu quả tương đương một loại thuốc chống trầm cảm ở người già
4. Magnesium helps fight type 2 diabetes
Studies show that about 48% of people with type 2 diabetes have low blood magnesium levels. This can decrease the effectiveness of insulin in controlling blood sugar. In addition, research indicates that people with low magnesium intake have a higher risk of diabetes. A study that followed more than 4,000 people for 20 years found that those with the highest magnesium intake had a 47 percent lower risk of developing diabetes.
Another study found that people with type 2 diabetes who took high doses of magnesium every day significantly improved blood sugar and hemoglobin A1c compared to a control group.
However, the research results are also inconsistent. In another study, magnesium supplements did not improve blood sugar or insulin levels in people who were not deficient.
5. Magnesium helps lower blood pressure
In a recent study, people with high blood pressure who took 450 mg of magnesium per day experienced significant reductions in systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Another study found that magnesium supplements may help lower blood pressure in people with high blood pressure but did not cause hypotension in people with normal blood pressure.
6. Magnesium helps fight inflammation
Low magnesium intake can promote chronic inflammation, which is one of the causes of aging, obesity and chronic disease. In a study that was conducted, children with the lowest blood magnesium levels had the highest levels of inflammatory CRP. They also have higher blood sugar, insulin, and triglycerides.
Magnesium supplementation may reduce CRP and other inflammatory markers in the elderly, overweight, and people with diabetes. Similarly, foods high in magnesium — like fatty fish and dark chocolate — can reduce inflammation.
7. Magnesium May Help Prevent Migraines
Migraine is painful, debilitating, nausea, vomiting, sensitive to light and noise. In fact, a few studies show that magnesium can prevent and even help treat migraines.
Just 1 gram of magnesium provides faster and more effective relief of acute migraines than some common medications. In addition, magnesium-rich foods can also help reduce migraine symptoms.
8. Magnesium reduces insulin resistance
Magie làm giảm kháng insulin
Insulin resistance is one of the leading causes of metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes, due to the impaired ability of muscle and liver cells to absorb blood sugar.
Magnesium plays an important role in this process. In fact, many people with metabolic syndrome show signs of severe magnesium deficiency. In addition, high insulin levels associated with insulin resistance lead to loss of magnesium in the urine, further increasing the body's level of deficiency.
Fortunately, magnesium supplementation can remedy the situation mentioned above. One study found that magnesium supplementation helped reduce insulin resistance and blood sugar levels, even in people with normal blood counts.
9. Magnesium helps improve premenstrual syndrome
Premenstrual syndrome is one of the most common disorders in women of childbearing age. Its symptoms include fluid retention, cramps, fatigue, and irritability. Magnesium has been shown to improve mood, reduce water retention, and other symptoms in women with PMS.
10. Magnesium is very safe and easy to supplement
Magnesium is absolutely essential for a good health. The recommended daily intake of magnesium is 400 - 420 mg for men and 310 - 320 mg for women. You can get magnesium from both food and supplements. Magnesium can be obtained through foods:
Pumpkin seeds: 46% of the recommended dose in a quarter cup (16 grams) Boiled spinach: 39% of the recommended dose in a cup (180 grams) Swiss chard: 38% of the recommended dose in a cup (175 grams) Dark chocolate (70 - 85% cocoa): 33% of the recommended dose (100 grams) Black beans: 30% of the recommended dose in a cup (172 grams) Cooked quinoa : 33% of the recommended dose in a cup (185 grams) Almonds: 25% of the recommended dose in a quarter cup (24 grams) Cashews: 25% of the recommended dose in a quarter cup (30 grams) Mackerel: 19% of the recommended dose (100 grams) Avocado: 15% of the recommended dose in a medium avocado (200 grams) Salmon: 9% of the recommended dose (100 grams)

Magie rất an toàn và dễ bổ sung
11. Magnesium supplements
If you have a medical condition, you should discuss it with your doctor before taking magnesium supplements. While these drugs are generally well tolerated, they may not be safe for people who are taking diuretics, heart medications, or certain antibiotics. You should also pay attention to the recommended daily dose of magnesium. Supplements that are well absorbed include magnesium citrate, glycinate, orotate, and carbonate.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. examination and treatment at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: healthline.comSEE MORE
Guide to magnesium supplements properly and safely Magnesium test: What you need to know How does the body feel when it's magnesium excess - deficiency?













