Foban Cream is indicated for cases of Penicillin resistance such as abscesses, infections of bones and joints, … This article will provide a better understanding of the uses of Foban Cream and precautions when using it to ensure a safe and effective treatment.
1. What is Foban Cream?
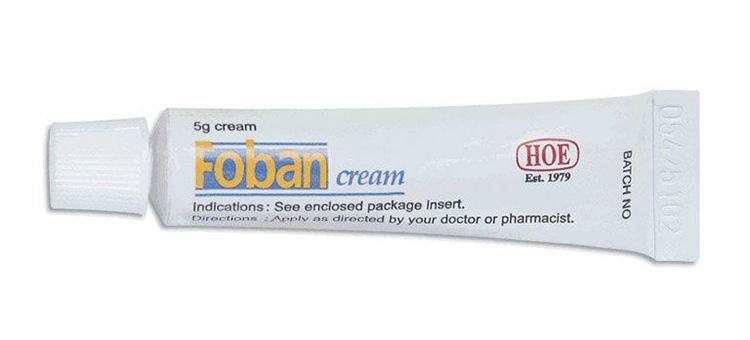
Foban Cream contains the key ingredient Fusidic Acid and is produced in the form of 5g, 15g, and 20g tube for topical application. Fusidic Acid is prescribed for bacterial skin infections (impetigo, cuts, dermatitis). It functions by inhibiting the growth of bacteria which cause infection.
Foban Cream is an antibacterial preparation that often sterilizes skin infections quickly, especially when the infection covers only a small area. If the infection is more widespread, oral or injectable antibiotics may be needed.
In case of skin infections, doctors may prescribe a creamy combination of fusidic acid with an anti-inflammatory agent, such as hydrocortisone or betamethasone.
2. What are the uses of Foban Cream?
2.1. Mechanism of action of Foban Cream
Fusidic acid disrupts the translocation of peptide subunits and prolongs the peptide chain of susceptible bacteria, thus inhibiting protein synthesis. The mechanism of action of Foban Cream is as follows:
- Absorption: Absorption is faster in children than in adults. At achievable serum concentrations, the post-antibiotic effect is 0.8 - 1.75 hours for S. aureus and 1 hour for Streptococcus pyogenes.
- Distribution: Widely distributed to tissues and body fluids, including bone, pus and synovial fluid, crosses the placenta, and enters breast milk.
- Metabolism: Metabolism in the liver with biliary excretion is the most likely route of elimination. Examination of the metabolites of fusidic acid in bile shows that it is a glucuronide conjugator and a carboxylic acid derivative. A series of minor metabolites are produced, including hydroxy, 3-keto, and 3 other unidentified metabolites.
- Biliary excretion (mainly as metabolites), feces (2% as unchanged drug), and urine. The half-life is 5 to 6 hours.
The pharmacokinetics of fusidic acid in patients with severe renal impairment requiring dialysis is basically no different from that in patients with normal renal function, as expected for a drug with minimal renal clearance. This medication is not removed by hemodialysis and concentrations in peritoneal dialysis fluid are low (<2.3 mg/l). Accumulation of metabolites has not been proved in these patients.
The pharmacokinetics of fusidic acid is varied in patients with celiac disease with AUC and Cmax increased by 60-70% compared to normal individuals. Low albumin levels and increased clearance in some patients are possibly due to decreased protein binding leading to increased drug metabolism. Conversely, decreased clearance occurs with severe cholestasis, the suggested mechanism of this condition is the competition of excess bilirubin for glucuronidation.
2.2. Indications of Foban Cream
Foban Cream is indicated in case of:
- Topical use for patients with lesions caused by primary or secondary Staphylococcus or Streptococcus infections;
- Treatment of cases resistant to Penicillin such as abscesses, bone and joint infections, Staphylococcus infections in patients with cystic fibrosis, and Staphylococcus endocarditis. Used in combination with other antibiotics;
- Topical drug, indicated for cases of eye and skin infections such as diaper rash, impetigo;
- Treatment of skin infections caused by Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, and bacteria that respond to Fusidic acid.
2.3. Contraindications of Foban Cream
Do not use Foban Cream in the following cases:
- Viral, tuberculous, or fungal skin infections;
- Ulcerated areas of the skin;
- Patients who are allergic or hypersensitive to any component of Foban Cream;
- Contraindicated for the use of Corticosteroids in cases of viral, tuberculous, or fungal skin infections, rosacea, perioral dermatitis, ulcerated skin conditions, and hypersensitivity to any component of Foban Cream.
You should consult your doctor if you intend to use this drug for children to control the smallest possible risks.
3. Side effects of Foban Cream
A small number of cases of unwanted reactions have been reported with the use of Foban Cream. In some special cases, reactions may include:
- Redness, itching at the applied area
- Headache, dizziness
- Nausea
- Rapid heart rate
You should notify your doctor immediately if you experience any problems after applying the cream.

4. Drug interactions
Inform your doctor about all the medications you are taking, including over-the-counter, herbal, or dietary supplements before starting treatment with Foban Cream.
Some drug interactions that may occur include:
- Generally, Fusidic acid should not be used with cholesterol-lowering medications, such as Atorvastatin and Simvastatin, as it may increase the risk of affecting the muscles (myopathy). If you are taking statins and your doctor asks you to use Foban Cream concurrently, monitor and report to your doctor any unexplained muscle symptoms, such as pain, cramps, or weakness.
- Fusidic acid can increase anticoagulant concentration. As this can increase the risk of bleeding, people using Foban Cream with anticoagulants should have their clotting time (INR) monitored regularly.
- If Foban cream is used in combination with protease inhibitors for the prevention of HIV, such as Ritonavir or Saquinavir, the blood levels of both drugs may increase. This increases the likelihood of side effects from either drug.
- The typhoid vaccine should not be taken for at least 3 days after you have finished a course of treatment, as Foban Cream may make the vaccine less effective.
- Previously, women using hormonal contraceptives such as pills or patches were advised to use an additional contraceptive method (e.g., condoms) while taking fusidic acid and for 7 days after the end of the course. However, you may no longer need to use an additional contraceptive method while taking a course of Foban Cream as there is currently insufficient evidence to support this.
5. Instruction of using Foban Cream
Foban Cream 5g or 15g is formulated as a tube of cream for topical application, so patients should apply the cream directly to the skin.
This is how to use Foban Cream:
- Wash your hands and clean the affected area, then pat dry with a clean towel.
- After contacting Foban Cream, you should wash your hands with soap again.
- The treated area should only be bandaged only if directed by your doctor.
- Avoid letting affected skin contact with other people's.
- Wear loose clothing to avoid rubbing against the treated area.
Use the cream with an average frequency of 2 to 3 times/day, for a continuous treatment period of about 7 days. For acne treatment, the duration may be longer than for other conditions.
In summary, Foban Cream is indicated for cases of primary or secondary Staphylococcus and Streptococcus skin lesions. By using Foban Cream, you may experience adverse reactions (ADRs). Therefore, you should use the drug as directed by your doctor to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.