This is an automatically translated article.
Benzocaine contains the active ingredient Benzocaine, belongs to the group of local anesthetics used in the relief of pain and discomfort caused by sore throat, mild skin irritation, hemorrhoids, bee stings, insect bites, toothache, otitis media. , acute otitis externa... Let's learn about the uses and notes when using Benzocaine through the article below.1. Benzocaine drug use
1.1. Indications "What are the effects of Benzocaine?". Benzocaine medicine contains the active ingredient Benzocaine, belongs to the group of local anesthetics indicated in the following cases:
Pain relief and discomfort relief in pathologies: Sore throat, mild skin irritation, ingrown nails, irritation vaginal or rectal, bee stings, hemorrhoids, insect bites, toothache, mouth and gum irritation, acute otitis externa, otitis media; Inhibits premature ejaculation during sex; Anesthetize the mucous membranes of the mouth, throat, nose, vagina, rectum, or numb the skin to relieve pain when medical instruments are needed to be examined. 1.2. Pharmacodynamics Benzocaine belongs to the group of local anesthetics with ester structure. The mechanism of action of the drug is to reversibly inhibit the depolarization of the neuronal membrane as well as the ion exchange, thereby preventing the depolarization of the cell membrane and reducing the transmission of nerve impulses. sensation near the injection site.
1.3. Pharmacokinetics Absorption: Benzocaine is rapidly absorbed through damaged skin and mucous membranes. Distribution: Benzocaine binds to both alpha-1-acid glycoprotein and serum albumin. Metabolism: Benzocaine is metabolized through 3 reactions including acetylation to acetylbenzocaine, ester hydrolysis to 4-aminobenzoic acid and N - hydroxylation to benzocaine hydroxide. 4-aminobenzoic acid is then acetylated to form 4-acetaminobenzoic acid, which is also the product of the hydrolysis of the acetybenzocaine ester. Elimination: The drug is eliminated as metabolites in the urine.
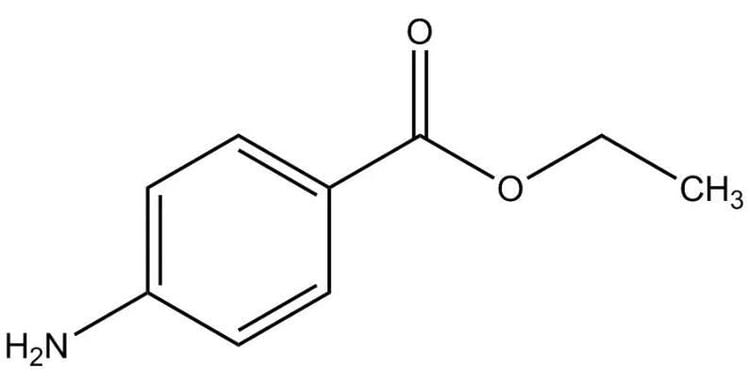
Thuốc Benzocaine thuộc nhóm chất gây tê cục bộ có cấu trúc ester
2. Dosage
2.1. Indicated dose Benzocaine dose depends on the age and condition of the patient, specifically as follows:
Adults:
Mild burns, bee stings, insect bites, sunburn: Apply a sufficient amount of Benzocaine. 5 - 20% on the affected area every 6-8 hours; Sore throat: Suck on one Benzocaine tablet, repeat the dose every 2 hours, and take it for up to 2 days. Or use an oral spray 4 times a day (for this form, spit the medicine out after 1 minute of spraying); Hemorrhoids: Use topical medication 5 - 20%, apply to the lesion and repeat every 4 hours; Toothache: Use Benzocaine 2.5 - 20% solution as needed; Pimples: Apply a sufficient amount of Benzocaine 20% to the affected area, repeat every 12 hours; Premature ejaculation: Use Benzocaine 7.5% to apply a small amount to the penis about 15-20 minutes before sex and need to wash it off after sex; Acute otitis externa, otitis media: Put about 4-5 drops of Benzocaine 20% solution, then use cotton swabs to insert into the ear to prevent the solution from flowing out. Repeat dose after 1-2 hours if necessary. Children:
Benzocaine for toothache due to newly erupting: Do not use in children under 4 years old. Children 4 years of age and older apply a sufficient amount of Benzocaine 7.5 - 10% to the painful gum area and repeat every 6 hours; Pimples, bee stings, minor burns, insect bites, sunburn, gums and mouth irritation: For children over 2 years of age only, the dosage is the same as for adults; Irritation of gums and mouth: For children over 2 years old, the dose is the same as for adults; Sore throat: Only use in children over 5 years old, the dose is the same as that of adults; Hemorrhoids: Use only in children over 12 years old, the dose is the same as that of adults. 2.2. Overdose and treatment Overdose: Overdosage of Benzocaine may appear systemic toxic symptoms such as central nervous system depression, cardiovascular function decline, bradycardia, cardiac arrest. , arrhythmias, hypotension, convulsions and syncope. In addition, drug overdose can lead to methemoglobinemia leading to cyanosis, respiratory failure.
Treatment in case of overdose: Symptomatic treatment of overdose and supportive treatment such as control of seizures, maintenance of airways. Patients with hypermethaemoglobinemia should be treated with intravenous methylene blue.
3. Benzocaine side effects
Some possible effects when using Benzocaine are as follows:
Hypersensitivity reactions on the skin such as inflammation, itching, burning, stinging, rash, edema, erythema, contact dermatitis and methaemoglobin; Applying benzocaine in the throat or mouth can cause confusion, headache, fast heart rate, shortness of breath, dizziness; Pale, gray, or blue lips, skin or fingernails; swelling of the lips, face, throat, or tongue; High fever, dark urine, vomiting, nausea, unusual tiredness or weakness, unusual bleeding or bruising, pain, redness, or worsening irritation around the mouth.
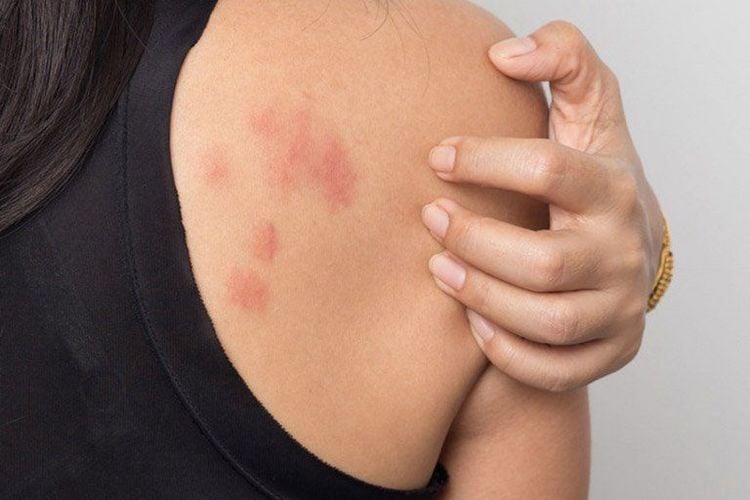

Thuốc Benzocaine có thể gây phát ban cho một số người bệnh khi sử dụng
4. Notes when using Benzocaine
4.1. Contraindications Contraindicated to use Benzocaine in the following cases:
People who are sensitive to Benzocaine or to local anesthetics of the caine group such as butacaine, procaine; Patients with anemia, laryngitis (contraindicated to use oral spray); Patients with suspected or history of methaemoglobinemia; Patients who are taking cholinesterase inhibitors concurrently or are being treated with drugs of the sulfonamide group; Benzocaine is contraindicated for use on blisters, large areas of skin, open wounds, infections or sunburn. Use caution when using the drug in the following subjects:
Patients with bronchitis, bronchial asthma, emphysema; People with heart disease; The patient smokes; Children; Pregnant and lactating women; Monitor for signs and symptoms of anemia in patients being treated with benzocaine. 4.2. Notes when using Benzocaine The notes when using Benzocaine are as follows:
Do not treat with Benzocaine for a long time (recommended not more than 7 days); Use of drugs that may mask symptoms related to the condition; Do not exceed the recommended dose of the drug; Do not use the drug in patients with complete heart block; In case of drug use on gingival or oral mucosa, do not eat food for 1 hour after taking the drug; For pregnant women, Benzocaine belongs to group C. Therefore, it should only be used in this population when the benefits outweigh the risks; For lactating women: There are no studies on the excretion of the drug in breast milk. Therefore, benzocaine should not be used in nursing women; For drivers, operating machines: The drug has no effect.
5. Benzocaine drug interactions
Some possible drug interactions with Benzocaine are as follows:
Sulfonamide: The metabolite of Benzocaine is para-aminobenzoic acid which can antagonize the effects of Sulfonamide. Cholinesterase inhibitors inhibit the metabolism of Benzacone. Hyaluronidase increases the absorption of Benzacoine, leading to increased serum drug concentrations and exacerbation of adverse effects. Technetium Tc - 99m tilmanocept: Benzocaine may decrease the effectiveness of the drug when taken together. Butalbital, Dapsone, Phenytoine, Valproic Acid, Sulfadiazine, Nitroprusside, Nitric Oxide, Quinine taking with Benzocaine may increase the risk or severity of methemoglobinemia. The information about Benzocaine will help you understand how to use it to get the best results.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.