This is an automatically translated article.
Tuberculosis can affect all parts of the body, of which pulmonary tuberculosis is the most common form of tuberculosis and the main source of infection for those around. Indicating a sputum culture for TB bacteria not only supports the diagnosis of tuberculosis, but also helps doctors devise the most appropriate treatment for each patient.
1. What is TB bacteria?
Mycobacterium tuberculosis, also known as tubercle bacillus, has the scientific name of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis bacteria are about 0.4 x 3-5mm in size. They have no hairs, no shells, and no spores. This is an aerobic bacteria that cannot be cultured in normal media but rich in nutrients. Mycobacteria grow slowly with a division time of about 18 hours per division. Due to the lipid-rich cell wall structure, TB bacteria are resistant to alcohol and acids.Tuberculosis mainly affects the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body such as pulmonary tuberculosis, bone tuberculosis, lymph node tuberculosis, peritoneal tuberculosis,... Thanks to its high resistance to factors Chemicals used to kill TB bacteria need to have high concentrations and long enough contact time to be effective.
2. When is a sputum culture test for TB bacteria indicated?
Sputum is a secretion of the respiratory tract consisting of mucus, red blood cells, white blood cells, ... accumulated in the lower parts of the lungs and bronchi. Your doctor may order a sputum culture test for TB bacteria when you have symptoms suggestive of TB such as cough, fatigue, fever in the afternoon, unexplained weight loss, ... to confirm the diagnosis. . After identifying TB bacteria present in the patient sample, technicians will continue to test the bacteria's sensitivity to anti-TB drugs (antibiotics). This allows doctors to choose the most suitable anti-TB drug for each patient.
Not only has the value of supporting the diagnosis of tuberculosis, the sputum culture test also helps to support the diagnosis of other respiratory diseases. Your doctor may order a sputum culture test when you have symptoms including cough, fever or chills, fatigue, muscle aches, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. Test results can reveal the cause of the above symptoms such as bronchitis, lung abscess, pneumonia, tuberculosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease,...
3. Principle of sputum culture technique to find tuberculosis bacteria
TB sputum culture technique uses nutrient-rich agar plates to culture and isolate pathogenic bacteria. Pathogenic bacteria will be identified based on morphological characteristics, culture characteristics and some metabolic properties. This is a technique that helps to definitively identify TB bacteria. The advantage of this technique is that it is possible to isolate and identify TB bacteria and can make antibiograms with anti-tuberculosis drugs. However, the disadvantage of this technique is that it takes a long time to get results, is expensive, and requires more complicated equipment than conventional tests.
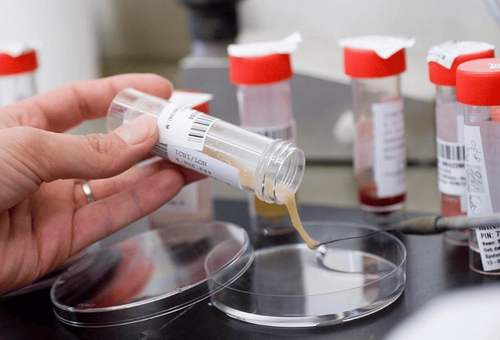
Xét nghiệm nuôi cấy đờm có giá trị hỗ trợ chẩn đoán bệnh lao
4. Sputum culture techniques for TB bacteria
Culture in solid medium: Nutrient rich media such as Ogawa, Lowenstein-Jensen, Middlebrook. Lowenstein Jensen medium is the commonly used medium (potato, egg yolk, Glycerol, Asparagine...). The time for TB bacteria to grow is after 3 - 6 weeks, after 2 months if the bacteria do not grow, the conclusion is negative. The technician will do the Niacin test and the nitrate reduction test to identify TB bacteria.
Culture in liquid medium: The advantage of this technique is that the growth time of TB bacteria is faster, usually 10-14 days on average. However, this technique is expensive and requires more complex equipment. In which, the BACTEC TB 460 culture system has the principle of determining the metabolism of TB bacteria by measuring the concentration of CO2 released when TB bacteria grow in C14-affixed medium. The average growth time of TB bacteria is 8-14 days. The MGIT culture system has the same principle as the BACTEC system, but instead of attaching C14 to the culture medium, TB bacteria are detected by UV light fluorescence technique.
5. Instructions on how to take a sputum sample for culture
5.1 Sampling time
The most suitable time to diagnose TB is to collect sputum in the morning after the patient wakes up or when the patient comes to the doctor. To facilitate sputum collection, the patient should drink plenty of fluids to help loosen the secretions and make it easier to expectorate.
5.2 Sputum collection technique
Patients should rinse their mouth with sterile physiological saline and not rinse with water containing antiseptic agents. The patient will sit on a bed or chair, legs relaxed, back straight, comfortable position, and shoulders relaxed. The patient will be asked to sputum into a small vial. This is a sterile plastic bottle with a screw cap. The container is labeled with the correct patient information, date and time of collection. To cough up sputum, take three deep breaths and then cough vigorously to spit out the sputum. If the patient is having trouble spitting up sputum, the doctor may pat the patient on the back to make it easier for the patient to spit. In addition, in case the patient is unable to produce sputum, the doctor can use the following methods to help collect the sputum sample: Bronchoscopy: The bronchoscope is inserted through the mouth or nose through the airways to the lungs. The patient is usually given an anesthetic that does not feel pain or discomfort, but in some cases an anesthetic may be prescribed. Aspiration: A nasogastric tube is inserted through the nose and down the throat. This technique usually takes about 15 seconds to collect a sputum sample. This technique is also commonly used for patients who have difficulty producing sputum such as children, patients who are unconscious, or those who are seriously ill. The volume of sputum sample should be 2ml or more: Medical staff check the quantity and quality of sputum, avoid mixing saliva. If the sputum sample is not of good quality, ask the patient to repeat the above steps. The sputum sample after collection will be sent immediately to the laboratory as soon as possible. If the sputum sample cannot be sent immediately, it should be stored at 2 - 4oC but not more than 4 hours.
Bạn có thể cảm thấy khó chịu ở ngực sau khi lấy mẫu đờm
6. Some risks of TB sputum culture test
You may feel chest discomfort after a sputum sample is taken to diagnose tuberculosis. After a bronchoscopy or sputum sampling with a nasogastric tube, your throat may feel sore You may also feel short of breath while taking a sputum sample with a nasopharynx if you have asthma or bronchitis manage .
7. Factors that may affect sputum culture results
Patient has recently used antibiotics. Because the use of antibiotics can affect the growth of TB bacteria in the specimen and may cause false negatives. Sputum sample taken with incorrect technique or contaminated with other impurities Insufficient amount of sputum to diagnose TB is not obtained. The time from taking the sample until reaching the laboratory is too long. Sputum samples are stored improperly. The patient uses mouthwash before taking the sputum sample. In summary, sputum culture technique will help confirm the presence of TB bacteria. The advantage of this technique of TB diagnosis is that it is possible to isolate and identify TB bacteria and can make antibiograms with anti-tuberculosis drugs. However, the main disadvantage is that it is time consuming, expensive and requires a lot of complicated equipment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.