This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by BSCK I Nguyen Hong Phuc - Emergency Department - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital.Edema is defined as an increase in extracellular and extravascular fluid. The disease is caused by many different causes. Manifestations of edema are also divided into several types based on the characteristics and nature of edema.
1. What is edema?
Edema is an excess of fluid in the buffers and natural cavities of the human body. The disease may be localized in only a few organs and organs of the body or may be edematous all over the body. Focal edema can include cerebral edema, pulmonary edema, and periorbital edema.2. Properties of edema fluid
The edema fluid is viscous, transparent, pale yellow, similar to plasma, but contains less albumin. Medically divided edema fluid into 2 types are exudate and seepage.2.1 Leakage
An edematous fluid containing a lot of protein and blood cells, often seen in inflammatory cases, when there is large endothelial damage, causing albumin to escape, sometimes accompanied by red blood cells.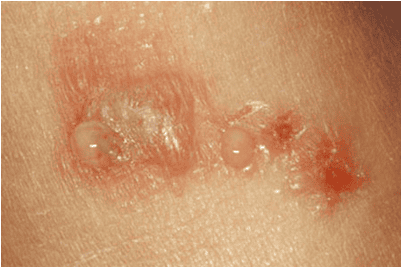
2.2 Permeation
The seepage is an edematous fluid containing less protein and fewer cells than the exudate. The essence of this fluid is the ultrafiltration of the plasma, because the endothelial damage is so small that large albumin molecules cannot pass. Therefore, the edema fluid contains little albumin, which is usually located in the tissues.3. What is the cause of edema?
Each cause of edema will have a different mechanism of causing edema. Classification of causes of edema based on the following mechanism:3.1 Edema due to increased hydrostatic pressure
3.1.1 Inflammatory edema
Inflammatory fluid leaks through the vessel wall due to the phenomenon of increased vascular permeability from many factors: the effect of chemical mediators, lack of oxygen due to slow blood flow causing damage to endothelial cells, adhesion of white blood cells. platelets and platelets enter the vessel wall, increasing the hydrostatic pressure of the peripheral blood vessels (this is the most important cause of increased fluid transport from the lumen to the stroma and causing edema).3.1.2 Edema due to high blood pressure
High blood pressure increases the pressure in the arteries, causing more gastric juice to move out and cause edema.
3.1.3 Edema due to heart failure
Edema due to heart failure is also known as edema due to blood stasis. Heart failure increases the pressure of the vena cava to the peripheral veins, damaging the vessel wall leading to increased vascular permeability causing edema (passive congestive edema).3.2 Edema due to decreased colloidal pressure
Hepatic edema: Due to lack of albumin, protein synthesis is reduced. Renal edema: Lack of albumin due to excessive excretion of protein in the urine, seen in chronic kidney diseases.3.3 Lymphatic Obstruction Edema
Edema due to lymphatic obstruction is rare.Lymphedema-induced edema is common in tumour-induced lymphatic embolism or chronic inflammatory embolism. In African countries, parasitic infections such as filariasis will cause lymphatic obstruction of the lower extremities, causing the patient's feet to swell to the size of an elephant's foot.
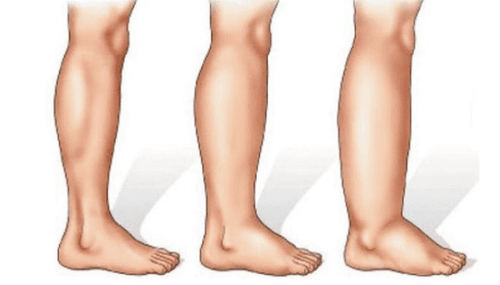
3.4 Edema due to increased blood volume due to salt and water retention
The excretion of salt and water depends on a complex regulatory system, based on the action of renin, angiotensin, and aldosterone. Patients with kidney disease will increase renin secretion, stimulate the formation of angiotensin, act on the adrenal cortex to release aldosterone, increase salt and water retention, causing edema.4. Manifestations of edema disease
The first sign of edema is recognized by pressing the skin with the thumb on the medial side of the tibia for 10-20 seconds, if the indentation appears and persists for a long time, edema is present.4.1 Manifestations of focal edema disease
Edema in one extremity is the result of thrombophlebitis, venous compression, or lymphedema. Edema of this type is often accompanied by skin lesions (skin ulcers, dermatitis...). Edema due to inflammation: Edema is often accompanied by heat and redness. Transient swelling of the face or sometimes spreading to the tongue and nasopharyngeal mucosa is a typical sign of allergic edema (also known as Quincke's edema). "Room" edema: common in superior vena cava compression, when compressing the inferior vena cava, it will cause edema in the lower extremities.4.2 Manifestations of systemic edema disease
Cardiac edema: Accompanied by shortness of breath, if breathing is difficult when lying down, it may be due to blood stasis in the lungs and stasis in the veins. Renal edema: Symptoms of edema are usually most pronounced in the morning on the face and eyelids. Facial edema in constrictive pericarditis Edema due to cirrhosis is often accompanied by ascites, edema in the lower extremities, and effusion in the testicles.
5. Edema characteristics of edema
Newly acquired edema is often characterized by soft edema, which can be concave. Chronic edema often becomes solid and difficult to press. Edema due to lymphatic occlusion is characterized by non-concave and can be very solid. Edema associated with local cyanotic symptoms is usually venous occlusion. Cardiac edema often presents with systemic cyanosis. Edema in nephrotic syndrome or edema due to low blood protein levels is characterized by soft, white edema. Myxedema is common in hypothyroidism, this is not true edema, but essentially the entire skin is thickened, the skin is cold, rough and drier than usual. BSCK I Nguyen Hong Phuc has nearly 20 years of experience in Emergency Resuscitation. Before being an Emergency Medicine Doctor at Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital, Dr. Phuc worked at hospitals: Bac Ninh Lung Hospital, Cu Chi Regional General Hospital - Ho Chi Minh City Bright.Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.