This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Ho Viet Le Diem - General Internal Medicine - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Blood contains white blood cells, platelets and plasma. Plasma plays an important role in supplying and nourishing the body. The composition of plasma is not much, mainly water, so it can be diffused through the walls of small blood vessels such as capillaries.
1. What is plasma?
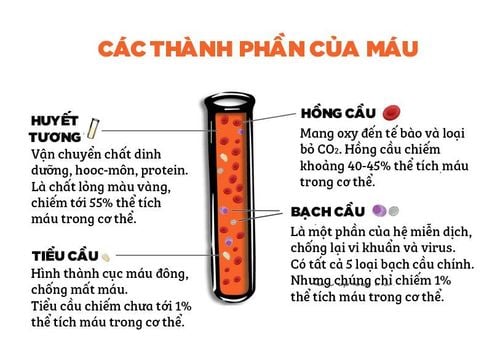
Plasma is a clear, pale yellow liquid, and plasma is also one of the most important components of blood. Plasma makes up 55 - 65% of the total blood volume in the body.Plasma physiology changes frequently according to the physiological state of the body. After a meal, the blood plasma is cloudy and a few hours after eating it becomes clearer and has a lemon yellow color. If the blood unit has cloudy plasma, it will not be used because it can cause shock and allergy to the patient.
>> See more: The role of plasma in the body - Article written by Specialist Doctor II Le Thi Na - Laboratory Department - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
2. Composition of plasma
Plasma contains 90% water by volume, the remaining 10% are solutes such as plasma proteins, organic components and inorganic salts,...Plasma proteins: Plasma contains a lot of soluble proteins. and accounts for 7% by volume, of which the most important proteins are: Albumin: The most abundant plasma protein (3.5-5g/dL blood) and a major factor causing osmotic pressure (osmotic pressure). pressure) of blood. Substances that are only partially soluble or will be insoluble in water are transported in plasma by binding to albumin. Globulins: Alpha, beta, and gamma are plasma-soluble globular proteins. Gamma proteins have antibodies or immunoglobulins that are synthesized by plasma cells. Fibrinogen: Converted to fibrin by enzymes that bind to the blood during hemostasis. Fibrinogen is synthesized and secreted in the liver. Other organic compounds: Other organic compounds in plasma include: amino acids, vitamins, glucose and some lipid-regulating peptides and steroid hormones.
There are also mineral salts: mineral salts occupy 0.9 g/o in volume, including electrolyte salts such as Na, Ca, K,....
3. Function of plasma
Huyết tương giàu tiểu cầu có nhiều tác dụng trong làm đẹp và chữa bệnh
This compound is divided into two main categories: albumin and globulin:
Albumin: Provides mid-osmotic pressure to the liquid portion of blood inside the blood vessels, preventing blood from overflowing into tissues and then into cells . Albumin can be seen as a kind of water-absorbing sponge, keeping the necessary amount of water in the blood stream. Globulins: Act as antibodies against infection. In addition, plasma is also conducted to separate blood components for transfusion according to the principle of "whatever is lacking". And with the development of science and technology in modern medicine today, instead of a whole blood transfusion, the basic principle of modern blood transfusion is to use only the type of blood product that the patient needs to develop. Maximize efficiency and minimize blood transfusion complications.
In blood products used in blood transfusion, plasma products are used quite commonly, mainly platelet-rich plasma and fresh frozen plasma.
4. In what case is plasma transfusion indicated?
The patient has a congenital decrease in a clotting factor in the absence of a specific preparation for infusion. The patient developed thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura) during plasma exchange. The patient had a massive blood transfusion and had symptoms of a disorder and was bleeding. The patient is antithrombine III deficient in the absence of antithrombine III concentrate for infusion. Acute bleeding with decreased total coagulation factor. Consumption-induced coagulopathy with severe reduction in coagulation factors.Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.