This is an automatically translated article.
Dehydration is one of the common clinical conditions, common in many different diseases. The loss of water in the body is closely related to blood osmolality. Either a decrease or an increase in blood osmolality can cause dehydration.
1. How does dehydration affect health?
Water makes up 50-60% of body weight. Water is everywhere. Water plays an extremely important role in participating in the structure of cells, the structure of organ tissues, participating in metabolic activities and maintaining the vital activities of the body.
Water is the solvent for all biological systems of the body in particular and of the external environment in general. Therefore, dehydration has a huge effect on the body. If the body loses 10% of its water, it will suffer from medical conditions. If we lose 20-25% of our water, we can die.
Water is supplied to the body through food or through endogenous sources in the body's metabolic processes.
In the body, the water regulation mechanism is ensured by many different factors including blood osmolality.
Blood osmolality or effective blood osmolality, which is the number of osmolarally active solute molecules in the plasma.
Normal blood osmolality is 280 - 290 mosmol/kg. Increased blood osmolality is when this concentration is above 290 mosmol/kg. Decreased blood osmolality is when this concentration is below 280 mosmol/l.

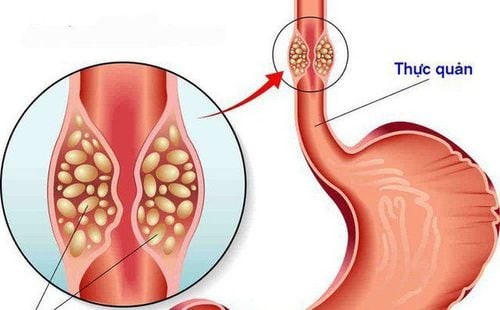
Nồng độ thẩm thấu máu góp phần điều hòa nước trong cơ thể
In essence, the transmembrane transport of water molecules in the body is based on the difference in osmotic pressure between the inside and outside of the cell membrane.
When blood osmolality decreases, water molecules will be pulled into the cell, causing extracellular water loss leading to edema and ascites. Conversely, if serum osmolality is high, water molecules will be pulled out of the cell causing intracellular dehydration.
In general, in order to maintain the water balance inside and outside the cell, blood osmolality must also be maintained at a certain threshold. When this concentration is changed, dehydration will occur.
2. Types of dehydration
From the fact that clinical cases show, most of the water disorders in the body are accompanied by electrolyte disturbances. Based on the concentration of extracellular Na+, it is divided into the following types of dehydration:
Hypertonic dehydration (loss of water due to increased blood osmolality):
Both intracellular and extracellular dehydration. A state where water loss is more than sodium ion loss, the extracellular volume is reduced. Increase in blood osmolality, leading to water in the cell being transported outside causing intracellular dehydration. Causes are not enough water for the body, excessive sweating leading to dehydration, using osmotic diuresis therapy, patients with chronic kidney disease, acute renal failure syndrome, diabetes insipidus or due to hyperventilation. Clinical manifestations: thirst accompanied by fever, apathy, even coma, delirium. Treatment: Treat the cause in combination with infusion of ringer lactate solution.
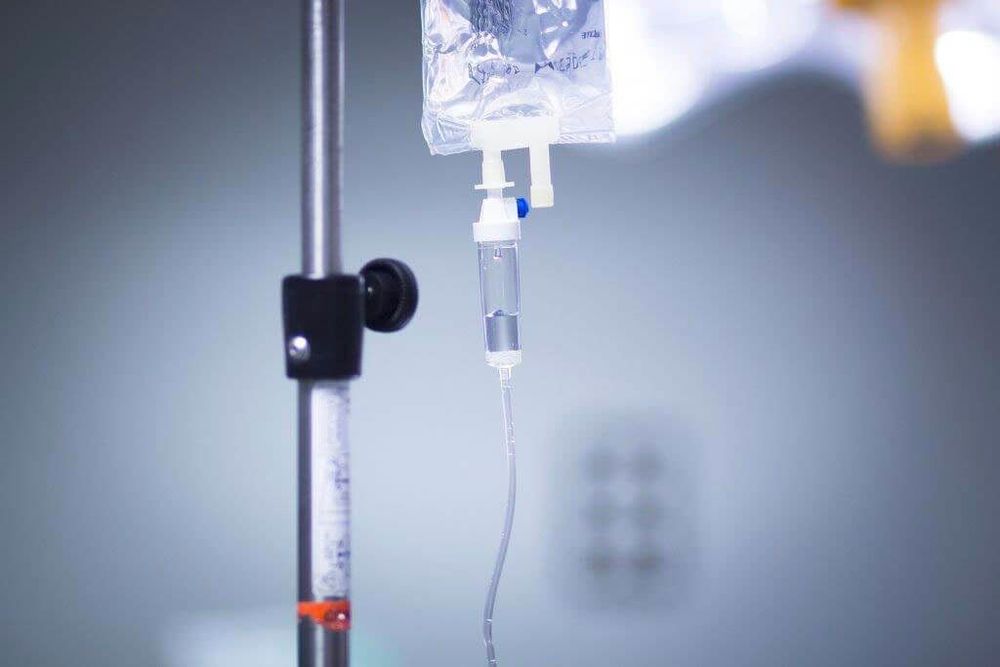
Truyền dung dịch ringer lactat để điều trị mất nước ưu trương
Isotonic dehydration:
Extracellular water volume decreases, intracellular water volume does not change. Water loss and sodium ion loss occur equally. Serum osmolality is normal. Common causes are vomiting, diarrhea, prolonged use of diuretics, peritonitis, patients with burns, heatstroke or sleeping pills poisoning... Clinical manifestations: excessive thirst, fatigue. fatigue, vomiting, pulse collapse, loss of consciousness, tachycardia, muscle twitching. Treatment: Treat the cause in combination with infusion of ringer lactate solution. Hypotonic dehydration:
Extracellular dehydration, increased intracellular water volume. Sodium ion loss occurs more often than dehydration. With low serum osmolality, extracellular water molecules are drawn into the cell, causing extracellular water loss. Common causes are due to sodium deficiency, after vomiting, diarrhea, excessive sweating or loss of sodium due to adrenal insufficiency, after adrenalectomy, prolonged use of diuretics, gastrointestinal disease. .. Clinical manifestations: fatigue, fever, nausea and vomiting, decreased muscle tone, pulse collapse, loss of consciousness, rapid pulse, muscle twitching and nervous depression may occur. Treatment: treat the cause in combination with 0.9% or 10% sodium chloride infusion depending on the condition and dehydration. Clinically, depending on the condition of each person and the causes of dehydration, patients have different clinical manifestations.

Người bệnh có biểu hiện lâm sàng mất nước khác nhau
Is dehydration when the amount of water is not more than 1-2 liters. Clinical symptoms: thirst, dry mouth, tachycardia, decreased 24-hour urine output. Moderate dehydration:
Loss of water from 3 to 5 liters. Clinical manifestations: excessive thirst, dry tongue, weak pulse, tachycardia, low blood pressure, oliguria accompanied by symptoms of peripheral circulatory disorders. Severe dehydration :
Lack of urine more than 8 liters. Clinical manifestations include hypovolemic shock, hyperosmolar coma, hallucinations, delirium, anuria, hypotension, tachycardia, and possibly psychomotor agitation. Water plays a very important role in the body to ensure the maintenance of life and stable development of the body. Dehydration causes many health effects, even death. Go to the doctor immediately if you see any abnormal changes in your body to promptly detect and treat, to avoid affecting your health.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of test results.
If there is a need for consultation and examination at the Hospitals of the National Health System, please book an appointment on the website to be served.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.