High liver enzymes in children are becoming increasingly common and tend to rise in number. However, many parents are still unaware of the causes, symptoms, and prevention methods for high liver enzymes in children.
1. What Are High Liver Enzymes?
Liver enzymes, also known as catalytic enzymes in the liver, include four main types:
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
- Aspartate transaminase (AST)
- Alanine transaminase (ALT)
- Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT)
When liver cells are damaged for any reason, the levels of these catalytic enzymes increase and dissolve into the blood, creating a certain concentration of liver enzymes that exceed the standard limit. Normally, liver enzyme levels should be within:
- ALT < 40U/L for men and < 37 U/L for women
- AST < 40U/L for both men and women
- GGT < 60U/L for men and 07 - 32U/L for women
- ALP 30 - 115U/L for both men and women
When liver enzyme levels exceed these standards, it is called high liver enzymes. High liver enzymes indicate that there are ongoing liver problems. If not controlled in time, high liver enzymes can progress to more dangerous diseases such as cirrhosis, hepatitis, and liver cancer.
2. Why Do Children Have High Liver Enzymes?
The condition of high liver enzymes in children is increasing in number and age. While the causes of high liver enzymes in adults stem from dietary habits, lifestyle habits, and certain diseases, high liver enzymes in children are mainly due to congenital factors, metabolic disorders, or inherited from the mother during pregnancy.
2.1. Congenital Causes
High liver enzymes in children can be congenital or inherited if family members, especially the parents, have high liver enzymes or liver diseases such as hepatitis, fatty liver, etc.
2.2. Polluted Environment
A polluted environment and food contaminated with harmful chemicals make the liver work harder to eliminate these toxins from the body. This is a cause of high liver enzymes in children due to the liver working excessively.

2.3. High Liver Enzymes in Children Due to Hepatitis
If the mother is infected with hepatitis A, B, or C during pregnancy, the risk of transmitting hepatitis to the fetus and newborn is very high. If the baby is not vaccinated against hepatitis in time, they will contract hepatitis from the mother, leading to high liver enzymes.
Therefore, if a pregnant woman has hepatitis A, B, or C during pregnancy, she needs regular check-ups to prevent transmission to the fetus. After birth, the baby should be vaccinated against hepatitis within the first 24 hours to prevent transmission from mother to child.
2.4. Antibiotics
Some antibiotics used to treat diseases in children can have side effects that affect the liver, causing liver enzymes to rise above normal levels.
2.5. High Liver Enzymes in Obese Children
Children with a diet high in protein and fat are prone to obesity, which can lead to fatty liver and increased liver enzymes.
2.6. Due to Formula Milk
Formula milk does not provide antitrypsin, so the child's liver cannot metabolize all the substances in the milk. This can be dangerous for the liver, leading to high liver enzymes in children.
3. Symptoms
In the early stages, it is difficult to detect high liver enzymes in children due to the lack of clear symptoms. However, testing and early detection of high liver enzymes in children greatly aid the treatment process. Therefore, parents should pay attention to even the smallest signs in their children, especially the following abnormal signs:
- Jaundice: High liver enzymes in children can make the skin yellowish, sometimes with a mucous layer in the mouth. Parents should take their children to medical facilities for timely examination.
- Pale yellow stools: Normally, the liver secretes bile into the small intestine to aid digestion. High liver enzymes in children can occur after liver damage, causing bile to flow back into the blood, leading to bloating, indigestion, or pale stools (due to lack of bile pigment).
- Itchy skin: When liver function is disrupted, high liver enzymes due to overwork can lead to toxins not being eliminated from the body, causing whole-body or localized itching.
- Swelling: This is a typical sign of high liver enzymes in children, often seen in areas such as the ankles and feet.
- Other symptoms: Children with high liver enzymes may also experience nausea, abdominal pain, fatigue, and weakness.
If parents notice any of the above abnormal signs in their child, they should promptly take them to the hospital for early diagnosis and timely treatment. Additional tests may include identifying the cause (such as detecting hepatitis viruses) and a general abdominal ultrasound to assess the liver's overall condition.
Symptoms of high liver enzymes in children tend to worsen at night, causing discomfort and seriously affecting the quality of life. If this condition persists without appropriate intervention, it can lead to more dangerous complications such as liver failure and liver cancer.
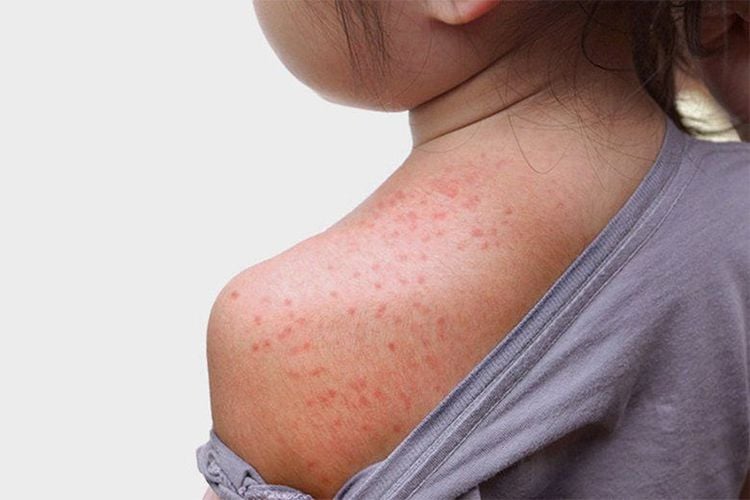
4. Prevention of High Liver Enzymes in Children
- For mothers with a history of hepatitis, they should be examined by specialists before and during pregnancy to prevent transmission to the child. Especially within the first 24 hours after birth, the child should be vaccinated against hepatitis B.
- Pregnant women should build a reasonable diet and lifestyle, and rest appropriately to support the healthy development of the fetus.
- Children should be exclusively breastfed for at least the first 6 months and can continue up to 2 years old. Breast milk has long been considered a safe and complete source of nutrition, and no other milk can replace it. Formula-fed babies may lack some nutrients and may cause high liver enzymes in some children.
- Pregnant women should maintain an ideal weight and minimize overweight and obesity.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.