Upper abdominal pain is a common symptom in different age groups. Many people often assume that this is a symptom related to stomach pain. However, in reality, the causes of this pain are truly diverse. This article will provide a better understanding of this condition and effective treatment methods.
1. Causes of upper abdominal pain depending on location
Depending on the intensity of the pain, the time of onset, the location of the upper abdominal pain and some other characteristics, we can identify a wide range of diseases, including:
1.1 Upper abdominal pain on the right or left side
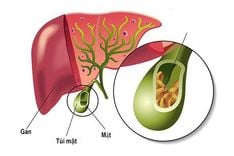
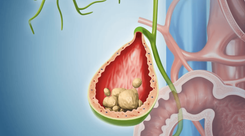
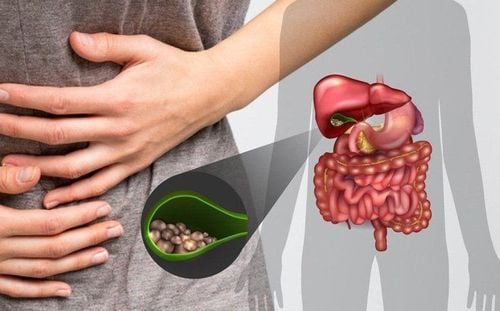
1.1.1 Gallbladder stones
Severe pain in the upper abdomen, especially on the right side, is a warning sign of gallbladder obstruction resulting from gallbladder stones. In addition, patients also experience systemic symptoms such as fatigue, vomiting, and exhaustion. If not treated promptly, prolonged gallbladder stones can damage the pancreas and liver.
1.1.2 Pancreatitis
Problems with the pancreas can cause pain in the upper abdomen, either on the right or left side, accompanied by symptoms such as fever, nausea, and vomiting. In some cases, this is a warning sign of pancreatic tumors.
1.1.3 Gastric and duodenal inflammation and ulcers
Upper abdominal pain on both sides is often a typical sign of gastric and duodenal inflammation and ulcers. Dull pain, accompanied by heartburn, belching and nausea are typical symptoms of the disease. If left untreated, the condition may lead to dangerous complications such as pyloric stenosis, gastric perforation, and even gastric cancer.
1.1.4 Gastritis
Gastritis is one of the causes of upper abdominal pain. When inflamed, the stomach lining becomes swollen and painful. In particular, acute gastritis can appear quickly due to HP bacteria infection.
For cases of chronic gastritis, patients should seek immediate medical evaluation and treatment. In order to prevent the symptoms from getting worse, it is also crucial to modify your diet and take painkillers and medications that protect the stomach lining.
1.1.5 Gallbladder pain
The gallbladder, an organ located under the liver, on the right side of the abdomen, has the function of storing bile from liver cells. This bile is subsequently released into the small intestine and duodenum to aid in food digestion. Patients with gallbladder problems often experience pain in the left upper abdomen. In severe cases, the patient's gallbladder may need to be removed.
1.2 Abdominal pain accompanied by nausea and diarrhea
There are several causes leading to upper abdominal pain accompanied by diarrhea and nausea, such as:
1.2.1 Colitis
Patients with colitis not only endure cramping upper abdominal pain but also experience prolonged constipation or diarrhea. The patient's stool often contains mucus and blood, along with a sensation of incomplete evacuation.
1.2.2 Gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis, caused by a virus in the stomach, often presents with symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and abdominal pain in the epigastric region or near the xiphoid process. To reduce the unpleasant symptoms caused by gastroenteritis, patients should avoid overeating and drink plenty of water.
1.2.3 Bowel obstruction
Due to the obstruction of digestive fluids and gas in the intestinal lumen, patients may experience gastrointestinal issues such as abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting, constipation, or diarrhea. If not treated promptly, this condition can lead to intestinal perforation and infection.
1.2.4 Gastrointestinal disorders
Patients with gastrointestinal disorders often experience dull, persistent pain in the upper abdomen or abdominal cramps accompanied by a feeling of nausea, heartburn and frequent bowel movements.
1.2.5 Diarrhea
Patients experiencing diarrhea often endure severe abdominal pain in the upper abdomen, accompanied by frequent episodes of loose, watery stools. Supplementing water and electrolytes is extremely necessary to prevent dangerous complications that may arise.
1.2.6 Food poisoning
A person is most likely suffering from food poisoning if they experience upper abdominal pain, nausea, and frequent bowel movements after eating.
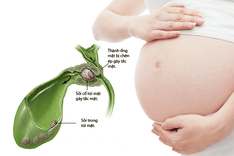
1.3 Upper abdominal pain in pregnant women
The causes of upper abdominal pain in pregnant women may include:
The developing fetus exerts pressure on the uterine wall, leading to frequent upper abdominal pain, particularly in the late stages of pregnancy.
The growth of the fetus requires considerable space, causing the skin and muscles surrounding the mother's abdomen to stretch to the maximum, which can lead to pain in the upper abdominal area.
Digestive system disorders, including pancreatitis, gastric discomfort, and colitis, may lead to upper abdominal pain.
1.4 Upper abdominal pain at night
At night, upper abdominal pain may arise from various factors such as:
Gastroesophageal reflux, characterized by symptoms such as nausea, upper abdominal pain, and chest pain. The condition of gastric acid reflux can be affected by sleeping position.
Patients suffering from gastric ulcers frequently endure upper abdominal pain at night, accompanied by symptoms such as heartburn and a burning sensation.
People with irritable bowel syndrome frequently experience abdominal pain in the upper abdomen during nighttime, particularly after overeating.
2. Is upper abdominal pain dangerous?
Upper abdominal pain due to indigestion is not a dangerous condition and can be improved by home care or medication. However, these pains can be a sign of some serious diseases such as myocardial infarction, acute cholecystitis, acute pancreatitis, gastric ulcers, acute hepatitis... Therefore, patients should seek timely medical evaluation and treatment to prevent future complications.
3. Treatment
3.1 Home remedies
In cases where upper abdominal pain is transient, does not lead to significant fatigue, and has a minimal impact on work and daily activities, we can take some supportive measures to relieve the pain.
Applying a warm compress to the painful area for 10-15 minutes can help relax smooth muscle and effectively reduce pain.
Drinking warm ginger tea may assist in relaxing the muscles and soothing pain associated with gastric diseases and gastrointestinal disorders.
Consuming pure honey can effectively inhibit bacteria, fungi, and viruses, which can contribute to pain alleviation.
Gently massaging the painful abdominal area in a circular motion can significantly reduce pain. The incorporation of eucalyptus essential oil into this practice will enhance blood circulation, bring a feeling of comfort, and provide immediate pain relief.
3.2 Medical intervention
The first thing to pay attention to when experiencing upper abdominal pain is to calmly monitor the pain. If the pain starts periodically, disappears after a few hours, particularly following episodes of overeating or the consumption of difficult-to-digest foods, it is usually not dangerous. Patients only need to modify their eating habits to prevent future occurrences.
However, if upper abdominal pain persists for several hours, remains dull over multiple days, or intensifies sharply, accompanied by vomiting, patients should see a doctor immediately for a thorough examination. It is crucial for everyone to pay special attention to the warning signs of serious conditions:
An abnormally distended abdomen can be a sign of gas accumulation in intestinal fluid, causing partial or complete obstruction.
A high fever above 38 degrees Celsius along with abdominal pain can be a warning sign of an intestinal infection.
Frequent vomiting can be a symptom of various unidentified diseases. Therefore, it is essential to administer fluid and electrolyte replacement to prevent fluid imbalance.
Abdominal pain begins from the area above the navel and gradually radiates to the area below the navel.
The article above has provided valuable information regarding the management of intermittent upper abdominal pain. Should any similar symptoms arise, patients are advised to pay close attention to the characteristics of the pain and to provide their physician with comprehensive details regarding their symptoms, medical history, and overall health to ensure the most accurate diagnosis.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.