This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
You may have heard people talk about stomach flu or stomach flu, viral gastritis at work or at your child's school. But what exactly is ma? This disease is viral gastroenteritis. It is an inflammation of the stomach and intestines caused by a viral infection.
Food poisoning is different. It is more common than viral gastroenteritis. It is estimated that about 48 million people get food poisoning each year.
Read on to learn more about the similarities and differences between viral gastroenteritis and food poisoning.
1. Viral gastroenteritis and food poisoning
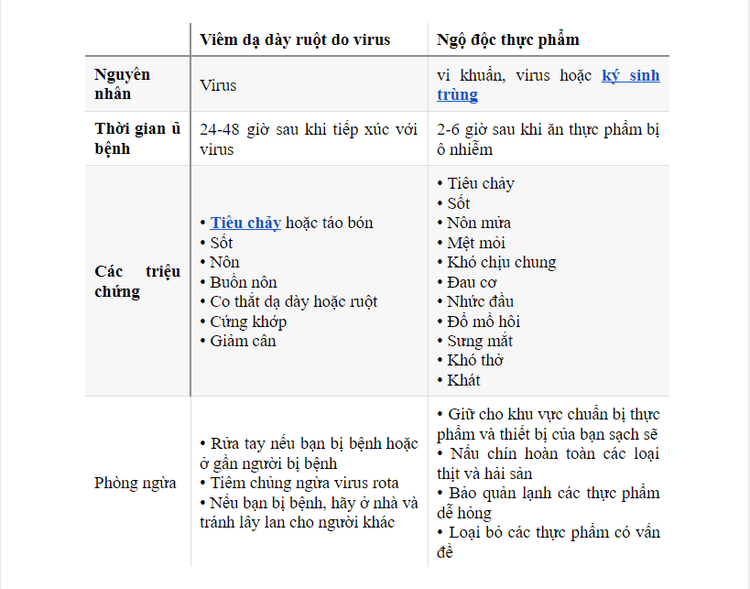
2. What is the difference in symptoms?
Symptoms of viral gastroenteritis
If you have stomach disease, also known as viral gastroenteritis, you may have one or more of the following symptoms:
Diarrhea Spasms of the stomach or intestines Nausea Vomiting Fever Weight loss Joint pain Muscle pain Thirst Headache General malaise Symptoms usually develop within 24 to 72 hours of exposure to the virus. In many cases, stomach ulcers go away on their own within a few days.
However, it's not uncommon to feel sick for 10 days. The longer the symptoms persist, the doctor should be consulted to rule out any other complications or diseases.

Triệu chứng của viêm dạ dày ruột do virus thường tiến triển trong vòng 24-72 giờ
How long are you contagious with viral gastritis?
Stomach flu can be very contagious. The length of time you are contagious is determined by the type of virus you have. Norovirus is the most common cause of stomach flu. People with stomach flu caused by norovirus are contagious as soon as they begin to have symptoms and remain contagious for several days afterward.
Norovirus can survive in stool for two weeks or longer. This can expose caregivers to diaper changes unless they take precautions such as washing their hands immediately.
Rotavirus is the leading cause of stomach flu in infants, toddlers and children. Stomach flu is caused by the rotavirus, which is contagious during its incubation period (one to three days) before symptoms appear.
People infected with this virus continue to be contagious for up to two weeks after they have recovered.
Food poisoning symptoms
Typical symptoms of food poisoning include:
Stomach or intestinal cramps Fatigue Diarrhea Fever Chills Muscle aches Headaches Sweating Thirst Unrest general In severe cases you may have:
Bloody stools or vomiting Severe abdominal cramps Shock Loss of consciousness Food poisoning symptoms can appear anytime within hours to days or several weeks after initial exposure. It depends on the pathogen causing the food poisoning. Symptoms usually improve within two days.
Food poisoning can happen to anyone, but is most common in infants, young children and the elderly.
Most forms of food poisoning are not fatal. A form called botulism can be fatal if people don't get the right treatment. Bacteria called Clostridium botulinum cause botulism. It produces toxins that act on the nervous system.
Botulism can cause blurred vision , drooping eyelids , slurred speech and other neuromuscular symptoms . Go to a medical facility for immediate examination if you suspect you have botulism.
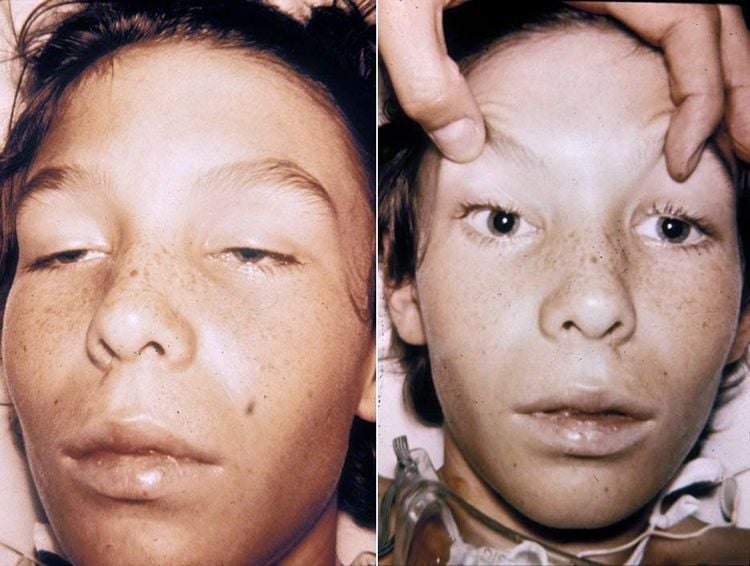
Chứng ngộ độc thịt gây ra mờ mắt, sụp mí mắt
3. What is the difference in cause?
What causes viral gastroenteritis?
Several different viruses can cause stomach bugs. Viruses that frequently cause this disease include norovirus, rotavirus, and adenovirus.
Norovirus alone causes 21 million cases of stomach bugs in the United States each year. Other viruses such as astrovirus can also cause this condition.
Stomach bug caused by rotavirus or norovirus infection is highly contagious. In the United States, infection most commonly occurs between October and April. The most common way to spread the virus is through direct contact with someone who is sick.
You can also get the virus from contact with something an infected person has touched that has their stool, saliva, or vomit with the virus in it.
What causes food poisoning?
Food poisoning develops when infectious organisms such as bacteria, viruses or parasites contaminate food. Bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella are among the top five germs that cause food poisoning in the United States. Norovirus is also on the top 5 list according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
You can get food poisoning from eating contaminated or undercooked meat. However, affected meat is not the only food causing food poisoning. The following foods can also lead to foodborne illness:
Raw and undercooked eggs Raw sprouts Soft or unpasteurized cheeses, such as Brie and feta Unwashed vegetables and fruit Raw fish or oysters Contaminated water Unpasteurized beverages, such as milk, cider, and juices Uncooked rice
Ngộ độc thực phẩm phét triển khi các sinh vật truyền nhiễm ký sinh làm ô nhiễm thực phẩm
4. Possible Complications
After a few days of stomach infection or food poisoning, you may become dehydrated. Watch for the following signs and symptoms of dehydration:
Decreased urine output Dark urine Dry your mouth or throat Dry diapers Lack of tears in babies and toddlers Tachycardia Low blood pressure Thirst Dizziness, especially when standing Children may have sunken eyes or fontanels when dehydrated. The fontanelle is also known as the soft fontanelle on an infant's head. You should seek medical attention if any of these symptoms occur.
5. Treatment
Treating stomach ailments
Dehydration can become a serious concern for people with stomach viruses. Watch for symptoms of dehydration. You should seek medical attention if any of these symptoms occur.
Make sure you drink plenty of water. Adults can drink fluids like Gatorade with electrolytes, and children can also drink rehydration solutions like Pedialyte. These drinks along with water will help restore the body's hydration balance. For best results, take several sips every half an hour to an hour.
Do not drink sugary drinks such as Kool-Aid or soft drinks, as these do not replace lost electrolytes. Drinking shaved ice or drinking plain water is another good option to stay hydrated.
Once you feel ready to eat again, give your stomach a rest by slowly introducing bland foods into your diet. These may include:
Cereals Grains Bread Potatoes Bananas Vegetables Fresh Apples Plain yogurt Avoid dairy, alcohol, caffeine and spicy foods that can upset your stomach.
Treating food poisoning
You should contact your doctor if you experience any of the following:
Blood or pus in your stool Diarrhea that lasts more than three days Fever over 100.4°F (38 °C) in adults or above 101°F (38.3°C) in children Symptoms of dehydration, including fatigue and extreme thirst Symptoms of botulism The following symptoms of food poisoning when visiting a developing country If you have mild food poisoning, it may respond well to rest and fever-reducing medication. In severe cases, you may need to be hospitalized for intravenous fluids. If you have severe bacterial food poisoning, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics.
Your doctor will review your symptoms and run tests to determine the best course of action.
Tùy thuộc vào tình trạng ngộ độc thực phẩm để có phương pháp điều trị phù hợp
6. Prevention tips
Prevent stomach bug
Although viral gastroenteritis is sometimes called stomach flu, your annual flu shot will not prevent it. Different viruses cause stomach bugs. Antibiotics will not help with stomach ailments because antibiotics work against infections caused by bacteria, not viruses
Take steps to prevent yourself from passing on stomach flu to others. You're usually most contagious when you feel your worst and a few days afterward. The bug can stay in your poop for up to two weeks. Wash your hands often and don't stay home from work or school for at least a few days after you feel better.
You should also consider getting your child vaccinated against rotavirus at 2 months of age.
Food Poisoning Prevention
Follow these steps to help prevent food poisoning:
Keep food preparation surfaces, utensils and your hands clean. Cook ground beef to 160°F (71°C). Cook steaks, steaks, and chops to 145°F (62°C). Cook chicken and turkey to 165°F (73°C). Make sure seafood is fully cooked. Make sure canned food is from trusted distributors. Refrigerate any perishable foods within one hour. Throw away food that looks or smells questionable Although many of the symptoms of stomach flu and food poisoning are similar, it's important to identify which illness you may have.
Symptoms of food poisoning can:
occur more quickly or later after exposure become more severe symptoms of stomach disease for a shorter time than symptoms of stomach upset Depending Depending on the cause, immune system function, and your overall health, food poisoning or viral gastroenteritis can become so severe that medical attention is needed. However, many people can usually manage the condition with rest, rehydration, and medical treatment at home.
If you're not sure what's causing your symptoms, see your doctor just to be safe. Other health problems can cause similar symptoms of gastroenteritis. In any case, call your doctor for help if your symptoms worsen.
Department of Endoscopy - Gastroenterology is one of the key specialties at Vinmec International General Hospital. For timely examination, advice and treatment of digestive diseases, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide or book an appointment on the website for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References
Bosch A, et al. (2014). Human astroviruses. DOI: 10.1128/CMR.00013-14 Food poisoning symptoms. (2019). cdc.gov/foodsafety/symptoms.html Mayo Clinic Staff. (2017). Food poisoning. mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/food-poisoning/symptoms-causes/syc-20356230 Norovirus. (n.d.). bphc.org/whatwedo/infectious-diseases/Infectious-Diseases-A-to-Z/Pages/Norovirus.aspx Norovirus: Transmission. (2018). cdc.gov/norovirus/about/transmission.html The symptoms of norovirus. (2018). cdc.gov/norovirus/about/symptoms.html Trichinosis (food poisoning). (2010). my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/7142-trichinosis-food-poisoning Viral gastroenteritis (stomach flu). (2018). mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/viral-gastroenteritis/symptoms-causes/syc-20378847