Nội dung bạn đang tìm kiếm không có phiên bản tiếng Việt.
Vui lòng chọn tiếp tục để xem nội dung tiếng Anh hoặc đi đến trang chủ Tiếng Việt.
Rất xin lỗi về sự bất tiện này.

Home
Tag Whitmores disease
Articles in Whitmores disease

Uses of Flamitra
Flameitra is manufactured and registered by Flamingo Pharmaceuticals Limited, which belongs to the group of drugs for the treatment of parasites, anti-infectives, antivirals and antifungals. To ensure safety for your health and maximize the effectiveness of your treatment, you need to take Flamitra exactly as directed by your doctor.
Xem thêm

What is Whitmore's disease and how does it manifest?
Melioidosis, also known as Whitmore's disease, is an infectious disease that can infect humans or animals. The cause of the disease is the bacterium Burkholderia pseudomallei that exists in contaminated water and soil. This disease mainly occurs in tropical countries, especially in Southeast Asia and northern Australia, and is transmitted to humans and animals through direct contact with contaminated sources.
Xem thêm

Is Whitmore's disease dangerous? How to treat?
Melioidosis, also known as Whitmore's disease, is an infectious disease caused by the Gram-negative bacillus Burkholderia pseudomallei. The bacillus is found in soil and water. It is a major health problem in endemic areas, especially Vietnam and Northern Australia. The disease exists in acute and chronic forms with symptoms of back pain, pain in bones and joints, severe cough, skin infections, lung lymph nodes and pneumonia.
Xem thêm
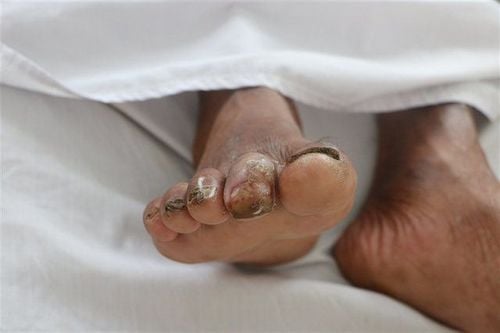
The risk of spread of Whitmore's disease
Whitmore's disease is a dangerous infectious disease. However, the disease is not transmitted from person to person, nor does it cause an epidemic, but it can cause people infected with Whitmore's disease to die quickly.
Xem thêm
Is Whitmore's disease contagious?
Whitmore's disease, also known as Melioidosis, is a dangerous acute infectious disease caused by the bacteria Burkholderia pseudomallei. Whitmore's disease has a very diverse clinical picture, the disease progresses rapidly and can lead to death. In particular, the disease has a high mortality rate if the patient is not properly diagnosed and treated with appropriate antibiotics.
Xem thêm
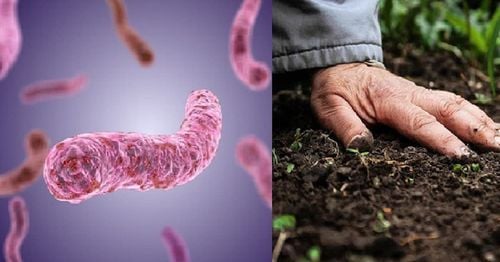
Preventing Whitmore's disease as recommended by the Ministry of Health
Prevention of Whitmore disease can be done by keeping the environment clean, disinfecting skin wounds promptly, and seeing a doctor immediately if you notice any suspicious signs. There is currently no vaccine to prevent Whitmore disease.
Xem thêm
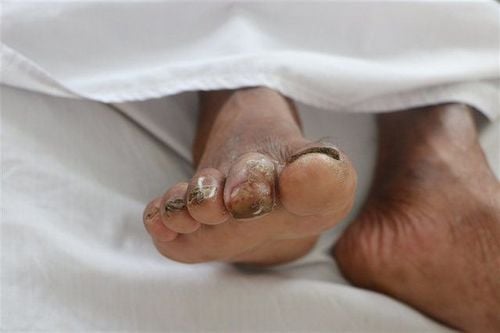
More people with Whitmore's disease - precautions to avoid
Whitmore is one of the acute infectious diseases with high danger level, causing rapid death and increasing rate. Because Whitmore is a disease that has no vaccine for vaccination, everyone needs to proactively take measures to prevent Whitmore disease to protect the health of themselves and their families.
Xem thêm

Distinguishing "flesh-eating bacteria" from the bacteria that cause Whitmore's disease
Recently, public opinion has been abuzz about the flesh-eating bacteria that causes Whitmore's disease - a dangerous disease that can be fatal. This has caused panic and anxiety among the people. However, in reality, the bacteria that causes Whitmore's disease is not a flesh-eating bacteria as people have speculated.
Xem thêm

Q&A about "flesh-eating bacteria"
Flesh-eating bacteria is a scary name. There are actually many types of bacteria that can cause “flesh-eating” effects, and the most recent one to emerge is Vibrio vulnificus.
Xem thêm
Understanding Burkholderia Cepacia
The burkholderia cepacia bacteria is one of the agents that cause many dangerous diseases. In particular, they can weaken the patient's immune system and cause lung necrosis.
Xem thêm
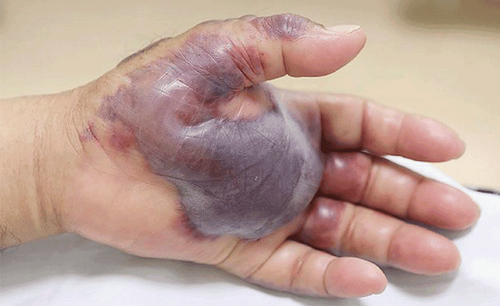
Whitmore's disease: Who is at risk?
Whitmore disease can occur at all ages, both men and women, however, this disease may be more risky for people whose occupations involve direct and frequent contact with mud, water and people with chronic diseases such as diabetes, kidney disease, lung disease or weakened immune systems....
Xem thêm