This is an automatically translated article.
Man-eating bacteria is a scary name. In fact, there are many types of bacteria that can cause "cannibalism", and more recently the name Vibrio vulnificus has emerged.1. What is flesh-eating bacteria?
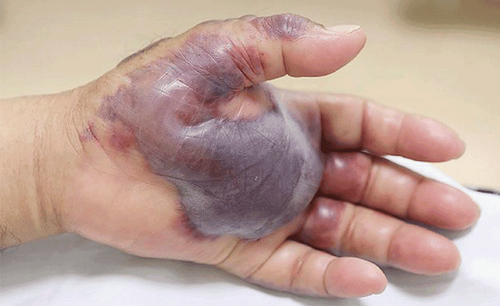
In fact, there is no type of bacteria that can literally eat humans, but the phrase "cannibal bacteria" often mentioned in the media is essentially bacteria that cause disease. necrotizing fasciitis (NF). Necrotizing fasciitis is an uncommon, rapidly progressive, deep subcutaneous infection caused by bacterial toxins that cause inflammation leading to destruction of connective tissue, adipose tissue, and muscle tissue.
The most common bacteria causing necrotizing fasciitis is group A beta hemolytic streptococcal (GABHS). In addition to group A beta-hemolytic streptococci, there are many other bacteria that cause necrotizing fasciitis, such as Vibrio vulnificus, Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus aureus), Klebsiella, Clostridium (Clostridium perfringens, Clostridium septicum, ...) , E. coli, Aeromonas hydrophila,...
Necrotizing fasciitis is usually classified into two types. Type I necrotizing fasciitis is caused by a mixed infection (infection with many bacteria), usually with a combination of an anaerobic organism, and one or more facultative anaerobes. Necrotizing fasciitis type II is caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal infection, and between the two types of necrotizing fasciitis, type II necrotizing fasciitis accounts for the majority of cases. However, due to climate change, sea water warming is suitable for the growth of Vibrio vulnificus, so an increase in cases of necrotizing fasciitis caused by Vibrio vulnificus has been observed, making Vibrio vulnificus a factor that has received much attention in recent times.
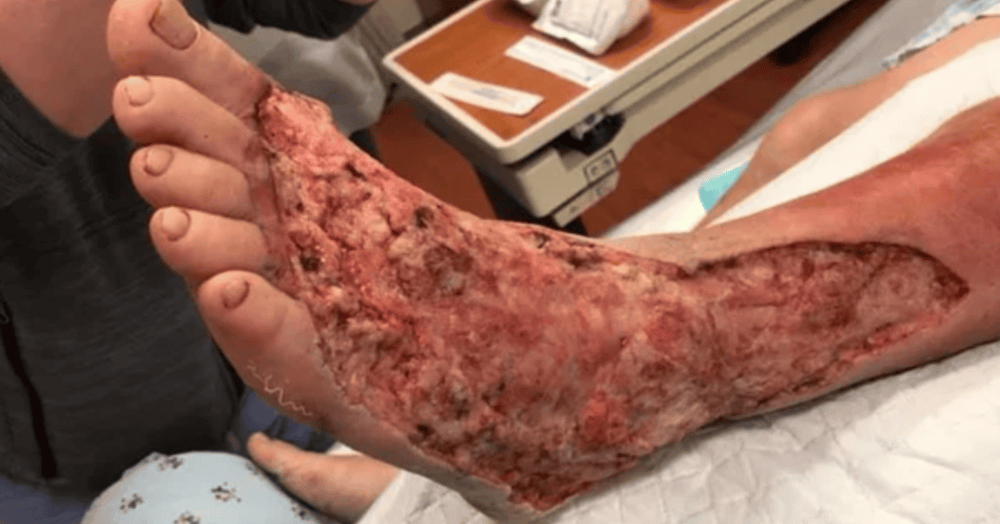
Hình ảnh viêm cân mạc hoại tử
2. What kind of bacteria is Vibrio vulnificus?
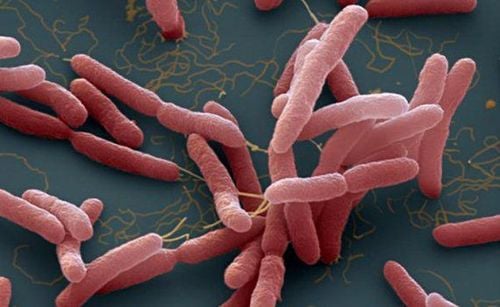
Vibrio vulnificus is a motile gram-negative bacterium. Vibrio vulnificus is one of the species of Vibrio (there are quite a few species of Vibrio that cause disease in humans, of which the best known are Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio parahaemolyticus, which cause acute gastrointestinal infections with severe diarrhea), belonging to the genus Vibrio. family Vibrionaceae. Vibrio vulnificus is commonly found in warm waters and grows well when the water temperature is above 200C. Vibrio vulnificus was not associated with contamination. In addition to necrotizing fasciitis, Vibrio vulnificus can also cause very serious fulminant systemic infections when contaminated seafood is not properly prepared (including shrimp, fish, clams, etc.) especially raw oysters), with an average mortality rate of up to 50%.
3. Vibrio vulnificus infection route
Necrotizing fasciitis is a bacterial infection deep under the skin, so it is easy to see that to cause necrotizing fasciitis Vibrio vulnificus will enter the body through open wounds. Besides, as mentioned above, eating seafood contaminated with Vibrio vulnificus without proper preparation is also a route of infection.
According to the recommendations of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) of the United States, people with chronic liver disease or medical conditions that cause immunodeficiency are also Use of drugs that affect the immune system should be very careful before Vibrio vulnificus , because serious infections can occur and lead to death.

Vi khuẩn Vibrio vulnificus đi vào cơ thể qua các vết thương hở
4. Is Vibrio vulnificus a common bacterium?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, there are about 95 infections in the United States every year, of which about 85 require hospitalization, with about 35 patients dying.
According to Sheri Hutchinson, a spokesperson for the Florida Department of Health Care, in 2014 there were 11 reported cases with 2 deaths on July 25, while in 2013 there were 41 cases of illness. reported and 11 deaths.
5. Who is most at risk, and how can the risk be minimized?
People with the habit of eating raw seafood and people with open wounds exposed to warm sea water in which Vibrio vulnificus is present are most at risk of infection, and people with underlying medical conditions, especially those with chronic liver disease and immunocompromised individuals face an even higher risk.
Therefore, if you have an open wound or skin damage, you should not enter the water, and at the same time should not eat raw seafood, especially raw oysters.

Những người có nguy cơ không nên ăn hàu sống
6. What are the symptoms of Vibrio vulnificus?
People who eat raw seafood infected with Vibrio vulnificus may experience sudden onset of signs and symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
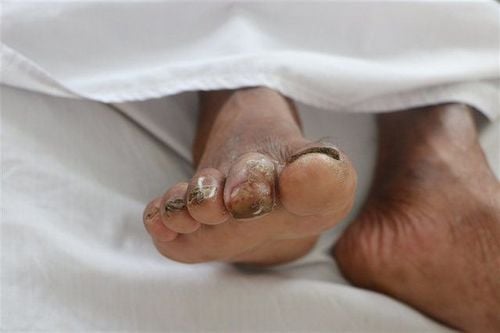
An open wound infested with Vibrio vulnificus may progress to a red, purulent ulcer, accompanied by red streaks, increasing in size, followed by necrosis.
People with weakened immune systems may present with symptoms such as fever, chills, severe hypotension with shock, and pus-filled blistering lesions on the skin.
If you experience the symptoms just described, go to the emergency room immediately.
7. How is Vibrio vulnificus infection diagnosed and treated?
In addition to taking the history and physical examination, the doctor will conduct blood tests, wounds or stool tests to confirm the diagnosis. However, infection with Vibrio vulnificus causes very acute illness, so treatment will usually be initiated immediately, before laboratory results confirm the infection.
The course of treatment will take place with many different treatment methods being coordinated:
Using antibiotics intravenously: the dose used to treat and the duration of antibiotic use will depend on each antibiotic. Clean the wound, remove the necrotic tissue, in severe cases amputation may be necessary to prevent the infection from spreading. Other treatment methods depend on the specific case.
If you have unusual symptoms, you should be examined and consulted with a specialist.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Articles refer to the source: webmd.com