This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Dinh Hung - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.And Specialist I Vo Cong Hien - Doctor of Radiology - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.
Pneumothorax is a common respiratory disorder that occurs in many different medical conditions and can occur at any age. X-ray of pneumothorax is a diagnostic method to confirm this condition.
1. Learn about pneumothorax
1.1 Anatomy and physiology of the pleura
Anatomically, the pleura is 2 layers of serosa surrounding the lung, including:Parietal leaflet: The part that covers the inside of the chest, the position of the face above the diaphragm, the mediastinal structures; Visceral: Adhesed to the outside of the lung parenchyma, splenic into the interlobular cleft of the lung. In the hilum, the visceral leaf is retracted to form a connection with the parietal leaf. Between the two pleura is the pleural space containing fluid.
Physiologically, normally the parietal and visceral leaves are close to each other, only separated by a thin layer of fluid to help reduce friction when they slide over each other at the time when the lungs and thorax expand. Normally no air would be present in the pleural space. When we breathe in, the volume of the thoracic cavity will increase, the parietal leaves follow the rib cage and separate from the visceral leaves, creating a negative pressure in the pleural cavity, which has the effect of stretching the lungs. The visceral leaves and lung parenchyma must expand to equalize the pressure in the pleural space.
1.2 What is pneumothorax?
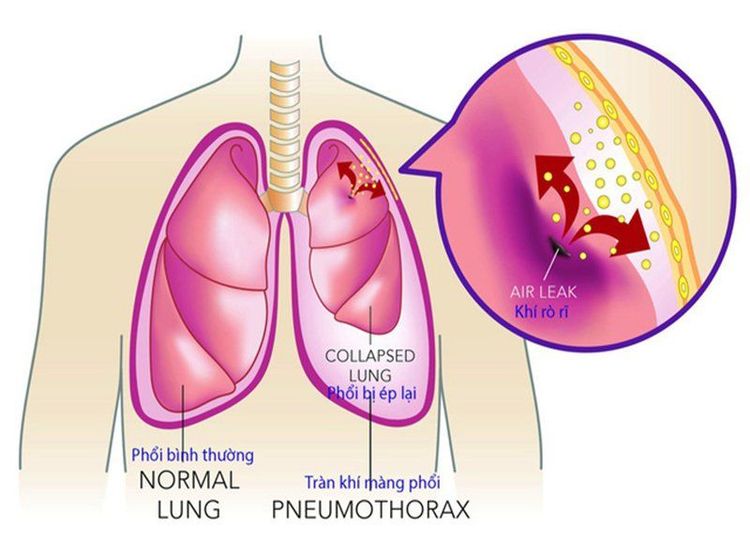
Pneumothorax is a condition in which air gets in between the 2 pleura, causing the lung to collapse. Air can enter the pleural cavity in 1 of 3 ways:
Through the airway, the alveoli into the pleura due to the cause of the visceral tear; Through the chest wall, diaphragm, mediastinum or esophagus in case of penetrating chest wall; Air is produced by microorganisms in the pleural cavity. Pneumothorax is classified into 2 types:
Spontaneous pneumothorax : Not caused by trauma or trauma to the chest; Traumatic pneumothorax: Due to trauma, trauma or procedures such as cardiopulmonary resuscitation, aspiration and biopsy of the lung - pleura, placement of a subclavian venous catheter. Common symptoms in patients with pneumothorax are sudden onset, severe chest pain, shortness of breath, stuffiness, possibly dry cough. The patient may have a fever. In the case of multiple pneumothorax, the patient has severe shortness of breath, signs of acute respiratory failure (cyanosis, rapid pulse, drop in blood pressure, struggle,...).
The diagnostic methods of pneumothorax include: Clinical examination, X-ray, computed tomography, pleural effusion,...
2. X-ray method to diagnose pneumothorax
2.1 What is an X-ray?
X-rays are a type of high-energy radiation. An X-ray machine is a device that emits high beams of X-rays. These X-rays will pass through soft tissues and fluids in the body, obtaining images of organs such as the heart, lungs, bones, blood vessels, etc. Through the captured images, doctors The doctor will rely on it to diagnose the patient's medical conditions.
About the X-ray procedure: The technician will ask the patient to sit, lie down or stand depending on the scanner. Behind the part to be photographed is placed X-ray film. The X-ray machine passes through the body, and when the X-rays meet the X-ray film, it creates an image. The more X-rays hit the film, the blacker the recorded image will be. Accordingly, solid body parts will form a white area, while empty or gas-filled body parts will give a black image. Images of soft tissues such as solid organs or muscles in the body are often gray in color. From the images obtained, the doctor will read the X-ray film and make a diagnosis.
Trắc nghiệm: Làm thế nào để có một lá phổi khỏe mạnh?
Để nhận biết phổi của bạn có thật sự khỏe mạnh hay không và làm cách nào để có một lá phổi khỏe mạnh, bạn có thể thực hiện bài trắc nghiệm sau đây.2.2 Picture of pneumothorax on X-ray
Chest X-ray is a technique used to confirm the diagnosis and evaluate the degree of pneumothorax. The picture of pneumothorax X-ray is: Brightened image without striation of the lung, the lung is compressed, the visceral border is clearly visible, sometimes shrinking into a lump similar to a tumor in the hilar area , the intercostal space is dilated, the diaphragm is lowered, pushing the heart and mediastinum.X-ray of pneumothorax may be limited if the patient is taken in the supine, semi-recumbent, or small-pneumothorax position. In case the picture of pneumothorax cannot be clearly seen on the X-ray but still suspect pneumothorax or small pneumothorax, it is recommended to take X-ray of the patient in the upright chest position and maximal exhalation will develop. clearly shows pneumothorax.
When taking X-ray, it is necessary to distinguish pneumothorax from large emphysema because if wrongly draining the emphysema, it can cause broncho-pleural fistula. On X-ray film, pneumothorax is characterized by protrusion of visceral margin toward the chest wall. In contrast, on X-ray film, the emphysema has features of concave visceral margin to the chest wall.
Note: Many cases of pneumothorax require a combination of X-ray and computed tomography (CT scan) to confirm the diagnosis.
X-ray is an accurate, simple and easy method to diagnose pneumothorax. When an X-ray is indicated, the patient should follow the detailed instructions of the medical staff to obtain an accurate diagnosis.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital with the motto: Always put the patient at the center, Vinmec is committed to bringing comprehensive and high-quality healthcare services to customers.
The general hospital uses new generation mobile and fixed digital X-ray techniques, 640-series CT scanners of the world's leading medical equipment manufacturers such as: GE, Toshiba.... as well as other modern techniques to diagnose and treat lung diseases.
With modern facilities of international standards, quality medical services, a team of medical professionals, experienced doctors will bring optimal treatment results to customers.
Friendly hospital environment, international standard pre-, post-operative care facilities will bring the most accurate diagnosis results, best treatment, fastest health recovery.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.