This is an automatically translated article.
Salmon are prized for their health benefits. This fatty fish is rich in omega-3 fatty acids that are beneficial for the body. However, not all salmon has the same nutritional content. Today, the majority of salmon on the market is not caught in the wild, but is bred on fish farms. This article explores the difference between wild and farmed salmon.
1. Fish resources and environmental impacts
Wild salmon are caught in natural environments such as oceans, rivers and lakes. But half of the salmon sold worldwide today comes from fish farms, using an aquaculture process. Global annual farmed salmon production has increased from 27,000 to more than 1 million tonnes in the past two decades. While wild salmon eat other organisms found in their natural environment, farmed salmon are provided with a high-fat, highly-processed food to breed large fish.
2.Difference in nutritional value
Farmed salmon is raised on processed fish food, while wild salmon eat many other animals in the wild. For this reason, the nutritional composition of wild and farmed salmon varies widely.
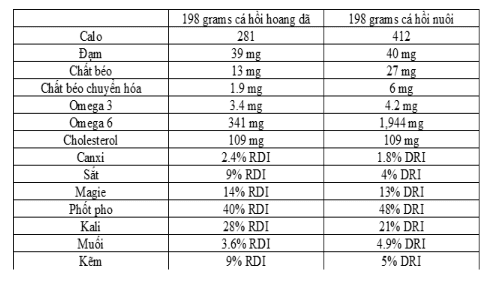
The nutritional difference between wild and farmed salmon is obvious. Farmed salmon is much higher in fat than wild salmon, containing more omega-3s, more omega-6s, and three times the amount of saturated fat. It also contains 46% more calories - mostly from fat. In contrast, wild salmon is high in minerals, including potassium, zinc and iron.
3.Unsaturated Fat Content
The two main polyunsaturated fats are omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. These fatty acids play important roles in the human body. These two types of fats are also known as essential fatty acids, or EFAs, because the body needs them to function properly. However, the balance between Omega 3 and Omega 6 is very important. Most consumers today are consuming too much omega-6, which distorts the balance between these two fatty acids.
Many scientists speculate that this may increase inflammation and may play a role in causing chronic conditions, such as heart disease. While farmed salmon has three times as much total fat as wild salmon, a large portion of these fats are omega-6 fatty acids. For this reason, the ratio of Omega 3 to Omega 6 is 3 times higher in farmed salmon than in wild salmon.
However, this 1:3 ratio of salmon is still very well balanced and safe to consume, only inferior to wild salmon with a ratio of 1:10. Both farmed and wild salmon showed large improvements in omega-3 intake for consumers. In a four-week study in 19 people, eating farmed Atlantic salmon twice weekly increased blood levels of omega-3 DHA by 50%.
4. Farmed salmon has higher levels of pollutants

Cá hồi nuôi có xu hướng ăn các chất gây ô nhiễm
Fishes tend to eat contaminants present in water sources, which can potentially harm the user's body when using fish-based foods. Studies published in 2004 and 2005 found that farmed salmon had much higher concentrations of contaminants than wild salmon.
European farms have more contaminants than American farms, but species from Chile generally have the least amount of harmful substances. Some of these contaminants include polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), dioxins, and some chlorinated pesticides.
A study published in 2004 determined that the concentration of PCBs in farmed salmon was eight times higher than in wild salmon. These levels of contamination are considered safe by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) but are not recognized by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). The researchers suggest that if EPA guidelines for permissible PCB concentrations were in place, users would be encouraged to limit salmon consumption to no more than once per month. However, one study found that levels of common contaminants, such as PCBs, in Norwegian farmed salmon fell significantly between 1999 and 2011. These changes indicate levels lower levels of PCBs and other contaminants in fish feed. In addition, many argue that the benefits of consuming omega-3s from salmon outweigh the health risks that these compounds present..
5.Concentration of mercury and heavy metals
Two large studies observed little difference in mercury levels between wild and farmed salmon. However, one study determined that wild salmon had levels three times higher. While arsenic levels were higher in farmed salmon, levels of cobalt, copper and cadmium were higher in wild salmon. In fact, the levels of these trace metals are usually very small and do not affect health.
6. Antibiotic content in farmed salmon
Cá hồi nuôi có sử dụng kháng sinh
Due to the high density of fish in the aquaculture environment, farmed fish are often more susceptible to infections and diseases than wild fish. To overcome this problem, antibiotics are often added to fish feed.
Unregulated and irresponsible use of antibiotics is a problem in the aquaculture industry, especially in developing countries.
Antibiotic use is not only an environmental problem, it is also a concern for the health of consumers. These antibiotics may cause allergic reactions in susceptible individuals. The overuse of antibiotics in aquaculture increases the risk of drug resistance in human gut bacteria through genetic modification. The use of antibiotics is still loosely regulated in many developing countries, such as China and Vietnam. However, salmon is not usually farmed in these countries. Many of the world's largest salmon producers, such as Norway and Canada, are considered to have an effective regulatory framework. The use of antibiotics is strictly regulated, and antibiotic levels in fish meat need to be below safe limits when the fish is harvested.
7.Is wild salmon worth more?
Although there is a difference between nutrient density. The use of farmed salmon still has very positive effects on health. Additionally, farmed fish tend to be larger and provide more omega-3s.
Wild salmon is much more expensive than farmed fish and may not be suitable for regular consumption by many people. However, due to environmental and dietary differences, farmed salmon contains much more potentially harmful contaminants than wild salmon.
Although these contaminants are thought to be safe for the average person to consume, some experts recommend that children and pregnant women only eat wild salmon to be on the safe side. maximum risk of harm.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference article: healthline.com