This is an automatically translated article.
Not only for patients with foreign bodies in the airway, but also for patients with fainting, apnea, circulatory arrest, it is necessary to release the airway. That proves that opening the patient's airway is very important.
1. Why is it important to clear the airway in an emergency?
Clearing the airway or opening the airway is a very important emergency procedure for the person performing the emergency to ensure adequate oxygen and ventilation for the patient.
The main tasks of patient airway care are:
Protect the airway; Release congestion; Sputum suction technique. Emergency airway clearance measures can be as simple as changing the patient's head position (e.g., tilting the chin, holding the jaw) or removing a foreign body obstructing the airway, if present.
Opening the airway is a first priority in the emergency room. Then you need to conduct mouth ventilation - mouth or mouth - nose, mouth - mask, ambu ball. Finally, airway protective measures taken by medical professionals such as oropharyngeal catheterization, intubation, or tracheostomy .
2. What causes airway obstruction?
Airway obstruction is the leading cause of patients needing airway clearance. There are many different causes of airway obstruction.
Endogenous causes include: Due to collapse of soft tissues in the oropharynx due to decreased muscle tone, jaw fracture; Laryngeal edema or laryngospasm; Acute epiglottitis; Acute laryngitis; Diphtheria larynx; Bilateral vocal cord paralysis; Allergies causing swelling of the mucous membranes of the throat and trachea, usually due to an allergic reaction to a bee sting, the use of antibiotics or drugs that lower blood pressure (ACE inhibitors); Laryngeal trauma; Laryngeal tumor. Exogenous causes include: laryngeal edema; Purulent fossa in the oropharynx; The hematoma can be caused by a clotting disorder, trauma, surgery; Thyroid tumor ; Lymphoma; Tumor or foreign body in the esophagus. Foreign object causing airway obstruction: Food Toys with children or any object with people with dementia or people with mental illness.
Ngườ bệnh mắc U tuyến giáp cần được giải phóng đường thở trong cấp cứu
3. Airway clearance techniques
3.1. Change the patient's position When the patient is unresponsive (coma, circulatory arrest) you need to do the following:
Need to quickly check for neck or face trauma, if the patient has trauma cervical spine in an intermediate supine position; If the patient is lying on his side or on his stomach, it is necessary to use the "turn over the log" technique (turning over the head, body and limbs at the same time) to return the patient to the supine position; Open the patient's airway in one of two ways: Tilt the patient's head or lift the chin if a cervical spine injury is not suspected. Or hold down the patient's jaw if a cervical spine injury is suspected, this method needs to be trained properly; Tongue regurgitation is the most common cause of airway obstruction. In this case, just applying one of the two methods above may be enough to pull the tongue forward and open the airway for the patient. The position to open the airway for other cases is as follows:
Patients with respiratory failure, cerebral edema, cerebrovascular accident apply the fowler position; Patients with acute pulmonary edema should apply a sitting position for the patient. 3.2. Clearing the airways in the event of airway obstruction Early detection of airway obstruction is critical. Foreign bodies may partially or completely obstruct the airway.
In the case of a partial foreign body obstruction, you should do the following:
It is possible that the gas exchange rate is still near normal, the patient is awake and able to cough, you need to encourage the patient cough to expel the foreign body; If the patient remains airway obstruction, gas exchange worsens, dyspnea increases, cyanosis requires urgent intervention. When the patient has a foreign body completely blocking the airway, the patient will not be able to speak, cough, breathe, may even go into a coma and need immediate emergency care. If measures to adjust the patient's position to open the airway have failed or you see a foreign body in the mouth or pharynx, the following measures should be applied:
3.2.1. Abdominal compressions (Heimlich maneuver) Using your hand to press on the patient's epigastrium quickly, pushing the diaphragm upward, causing increased pressure in the thorax to create a strong airflow to expel the foreign body from the airways, similar to the cough reflex.
If the patient is sitting or standing, stand behind the patient and wrap your arm around the patient's waist. A clenched fist, thumb above the line between the other fingers, rests on the abdomen below the breastbone. Hold the other hand on top of the other and perform a quick and decisive jerking up and back. You can repeat the movement until the airway is cleared or the patient's consciousness worsens.
When the patient is comatose, you need to lay the patient on his or her back, face up, if the patient vomits, tilt the head to one side and wipe the mouth. Then you kneel to the sides of the patient, place one hand on the abdomen between the navel and the sternum, the other hand facing up. Next, you bring your body forward and quickly press up to expel the foreign object, do it again if necessary.
When you are alone and have to give chest compressions and give artificial respiration to the patient, you should kneel on one side of the patient for easy movement and use your hands to press as above. If there are more people, one person gives CPR and CPR, the other does the test.
If you are a person with airway obstruction due to a foreign body, you can perform abdominal compressions yourself by making a fist and pressing on your abdomen or pressing your abdomen against solid surfaces such as the back of a chair, table top, sink, etc.
After each abdominal compression, use 2 to 3 fingers to hook the patient's oral cavity to check. Once the patient's airway has been removed, you should assess the patient's breathing and circulation and institute appropriate interventions.
3.2.2. Back pats and chest compressions The use of the Heimlich maneuver on young children can cause abdominal trauma, so combine back patting and chest compressions to rule out foreign bodies in young children. Only by patting the back can remove the foreign body, if it is not effective, then follow with chest compressions, then check the airway. Place the baby in your arms in a prone position along the axis of the arm and with the baby's head low. Using the palm of your hand, give the child five quick and five pats between the shoulder blades. If back-slapping doesn't push the object out, turn the baby over and give five chest compressions. The position and method of chest compressions are similar to chest compressions but done at a slower pace. You need to clear the baby's airways between back blows - chest compressions, observe the baby's oral cavity and use your hands to take it. any foreign body if visible, however do not use your finger deep into the throat area to remove the foreign body.
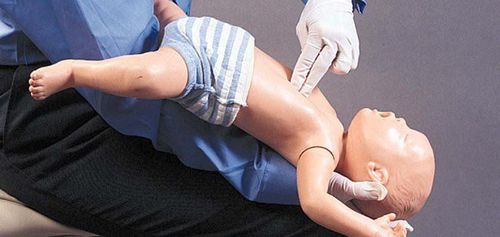
Vỗ lưng và ép ngực giúp khai thông đường thở
3.3. Assess the effectiveness of the clearance of the obstructed foreign body After each airway clearance, you need to determine if the foreign body has been completely cleared and the patient's airway is open, if not is required to repeat the appropriate sequence of movements until successful.
Determine successful foreign body removal when you see:
You are sure that the foreign body has been expelled; Patient can breathe clearly and speak; The patient is more awake ; The patient's skin color returned to normal. If upper airway opening maneuvers have not been effective, take other, more vigorous measures if possible:
Use a laryngoscope and remove the foreign body with Magill forceps; Tracheostomy through the cricothyroid membrane; Percutaneous tracheostomy. These techniques are advanced techniques that require special training to perform.
In summary, airway clearance is a very important emergency procedure for emergency personnel to ensure adequate oxygen and ventilation for the patient. Emergency airway clearance measures can be as simple as changing the patient's head position or removing a foreign object obstructing the airway if present.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.