This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Le Duc Hoang - Emergency Medicine Doctor - Emergency Department - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital. The doctor has a lot of experience in the treatment of Resuscitation - Emergency care for adults.Hypothermia in emergency and cardiovascular resuscitation is a modern technique with the main purpose of minimizing cell damage in the body, especially brain cell damage. So how does hypothermia in cardiovascular emergency take place?
1. What is hypothermia?
The technique of patient hypothermia in cardiovascular resuscitation is a method of using a number of cooling techniques to reduce and control the patient's body temperature to 32 - 36 degrees Celsius. Then, depending on the requirements. the need for a course of treatment where the patient's temperature will be controlled to achieve the target body temperature proactively. Besides, it is necessary to combine with other treatments to prevent complications and side effects of hypothermia.When the body's circulatory system stops working, the heart loses its contractile function, resulting in a lack of blood supply to the organs in the body, causing cells to stop working, causing necrosis and death. by program. Among them, the most important organs are the cells of the central nervous system.
Damage to brain cells after circulatory arrest will be irreversible and leave many serious complications, even respiratory failure and death. Therefore, hypothermia in cardiovascular resuscitation helps to significantly prevent this damage process, thereby helping the patient to have a better chance of survival and less complications.
2. How many methods of hypothermia?
Currently, there are 2 methods of hypothermia being applied in cardiovascular emergency, including:Hypothermia outside the body (surface cooling): Using water, cold blankets, heat exchangers or hypothermia. Localized heat by cap... Hypothermia (intravascular cooling): Insert a catheter into the central venous system and introduce cold solutions or fluids into the general circulation to control body temperature.
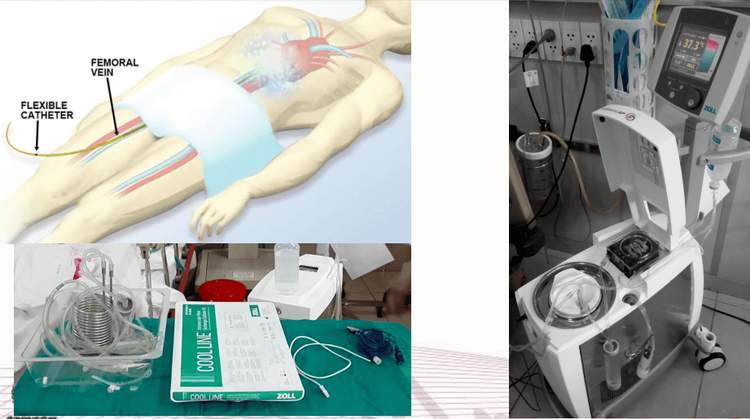
3. Indication method of hypothermia in cardiovascular resuscitation
The method of hypothermia is applied in patients after circulatory arrest and meets the following 3 criteria:The patient has been intubated, is started receiving hypothermia treatment within 6 hours after circulation stops. Current heart rate without ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. Systolic blood pressure maintained above 90 mmHg (with or without vasopressors). The patient remained in a coma after circulatory arrest and remained comatose during hypothermia.
4. Contraindications to hypothermia in cardiovascular emergency
At present, this method has no absolute contraindications, only cases that require caution include:Patient is bleeding and is life-threatening. Have a serious blood clotting disorder. Severe cardiogenic shock. Untreated infection. However, hypothermia can still be initiated after the patient is hemodynamically stable, coagulopathy corrected, or localized infection treated.
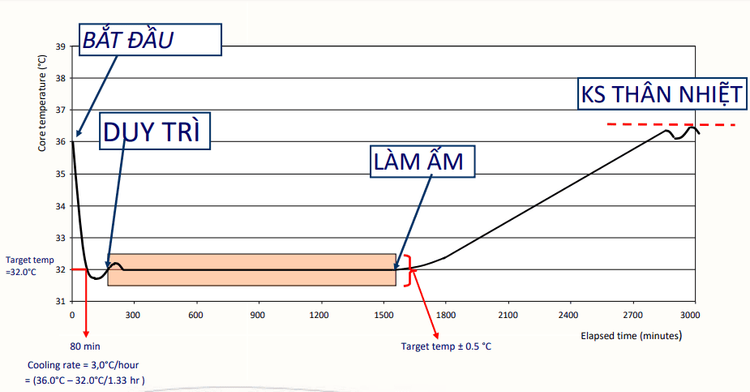
5. Technical process of hypothermia method
Stage 1 In the first stage, what is needed is rapid hypothermia. With the methods of hypothermia being applied today, the doctor will choose the method depending on the patient's condition to quickly bring the core body temperature to the target level (about 32°C to 36°C). ) for an average of 1-3 hours.Stage 2 After hypothermia to the therapeutic target, the patient should be maintained at this temperature. Depending on the patient's condition and the requirements of cardiovascular resuscitation, the patient's target core temperature can be maintained for 24-48 hours.
Stage 3 After the end of hypothermia, the patient should be rewarmed. The requirement of the temperature increase is to increase from 0.25°C to 0.5°C per hour, the body temperature should not be raised too quickly to avoid complications of acute pulmonary edema or hemodynamic disturbances caused by sudden hyperthermia.
Stage 4 After the patient's body temperature returns to normal, the treating physician needs to maintain this normal body temperature. The goal of this phase is that the patient's core body temperature should be maintained between 36.5°C -37.5°C over a 24-hour period.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.