This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thi Thanh Thuy - Endocrinologist - Dialysis - Kidney Transplant - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Acute renal failure causes a sudden and prolonged decrease in kidney function, due to a variety of causes. The mortality rate of acute renal failure is high, so it is necessary to take timely measures.
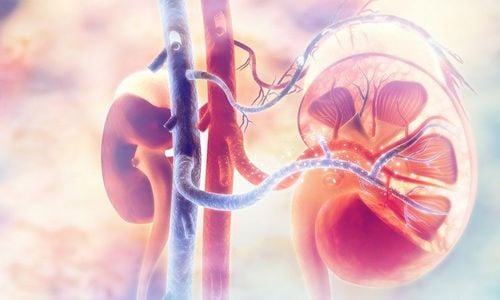
1. Kidney function
The kidney is considered one of the five important organs of the human body, helping the body to maintain life, is an organ located behind the two sides of the spine in a symmetrical position. Each person has 2 kidneys. The kidneys are responsible for filtering the blood by removing unnecessary waste and excess water from the body, helping to maintain the need for salt and electrolytes in the blood to help the body carry out efficient metabolism. As a result, the kidneys also help the body regulate blood pressure.When the kidneys are damaged for any reason, waste products and water can accumulate in the body causing symptoms such as swollen ankles, vomiting, weakness, poor sleep and difficulty breathing. .
2. What is acute kidney failure?
Acute renal failure is a condition in which kidney function is suddenly reduced and lasts for several hours or days, leading to a decrease in glomerular filtration rate, accumulation of nitrogen metabolism products (urea, creatinine) and by-products of renal metabolism. non-nitrogen metabolism (electrolytes, acid-base).These disorders depend on the extent and duration of kidney failure, which manifests as metabolic acidosis, hyperkalemia, and excess fluid in the body. Severe acute renal failure with its etiology can lead to multi-organ failure such as coagulopathy, brain damage, lung injury, and hemodynamic effects.
Acute renal failure often occurs in severe patients in the intensive care unit. The cause leading to acute renal failure is usually infection, especially in the group with severe infection with shock, multi-organ failure in the group with severe surgical events such as multiple trauma, after surgery. According to some studies, up to 55-57% of patients with acute renal failure are initially caused by infection with or without shock syndrome.
In the past two decades, although there have been many advances in the application of new techniques to help diagnose diseases early, many modern treatment measures are aimed at replacing kidney function, promoting quick recovery of kidney function. However, the incidence and mortality of acute renal failure have not decreased significantly.
Suy thận cấp thường xảy ra ở nhóm bệnh nhân nặng nằm trong các khoa hồi sức
3. Clinical manifestations
Most patients with acute renal failure have oliguria as the first sign. In addition, depending on the cause leading to acute renal failure, the clinical manifestations may vary.3.1 Acute renal failure due to pre-renal causes Often see symptoms of dehydration such as:
Tachycardia, orthostatic hypotension, hypotension. Skin, reduced skin elasticity, dry mucous membranes, collapsed neck veins. The amount of urine gradually decreases. 3.2 Acute renal failure due to renal etiology Risk factors such as prolonged shock, use of nephrotoxic drugs, contrast agents, rhabdomyolysis, hemolysis. One or more of the following signs may be seen:
Blood in the urine results in red or dark urine in acute glomerulonephritis. Low back pain due to ureteral stones, kidney stones. Oliguria, edema, hypertension. Fever, muscle pain and itching, rash after taking the drug. 3.3 Acute renal failure of post-renal causes Acute renal failure of post-renal etiology has signs of urinary tract obstruction, including:
Renal colic, pain in the dorsal fossa or pain in the ureter points. Large kidneys due to fluid retention, pus. Symptoms of the bladder, pain in the bladder area, painful urination, urinary incontinence. Oliguria or anuria.
4. Causes of acute kidney failure
Acute renal failure actually has many different causes, so there are many ways to classify it. Scientists believe that the cause of acute kidney failure may affect the pre-renal, renal, post-renal and in some cases the cause is unknown.4.1 Prerenal acute renal failure Prerenal acute renal failure also known as functional acute renal failure includes:
Hypovolemic shock, cardiogenic shock, septic shock, hypersensitivity shock. Hypovolemic shock due to hemorrhage due to trauma, surgery, abortion, burns, diarrhea, vomiting, diuretic use... Cardiac shock due to myocardial infarction, arrhythmia... Septic shock due to infection septicemia, biliary tract infection, uterine infection... Hypersensitivity shock due to anaphylaxis. 4.2 Acute renal failure in the kidney Acute renal failure in the kidney is also known as acute renal failure with physical damage including:
Acute tubular necrosis, acute glomerulonephritis, acute pyelonephritis, acute interstitial nephritis, vascular disease hematuria, hepatorenal syndrome, kidney disease in pregnancy, other kidney diseases... Acute tubular necrosis with ischemic kidney caused by prerenal acute renal failure or functional renal failure; kidney poisoning due to mercury, arsenic, uranyl, cisplatin, carbon tetrachloride, anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, carp bile... Acute hemolysis due to blood transfusion of different groups, malignant malaria, toxic poisoning , allergic... Muscle wasting due to severe muscle trauma, muscle disease... Acute glomerulonephritis due to streptococcal infection, systemic lupus erythematosus ... Acute pyelonephritis caused by Gram-negative bacteria infection, necrosis of the kidney nipple. Acute interstitial nephritis due to drugs, chemicals, hypercalcemia. Renal vascular disease due to renal vascular occlusion, malignant hypertension. Hepato-renal syndrome due to cirrhosis ascites, leptospirosis. Renal disease in pregnancy due to post-eclampsia, acute renal failure after birth. Other diseases such as chronic kidney disease with exacerbation or end-stage. 4.3 Post-renal acute renal failure Post-renal acute renal failure due to obstruction due to urinary stones, bladder tumor, prostate tumor, intra-abdominal tumor, wrong ureteral ligation during surgery...
5. Complications of acute renal failure
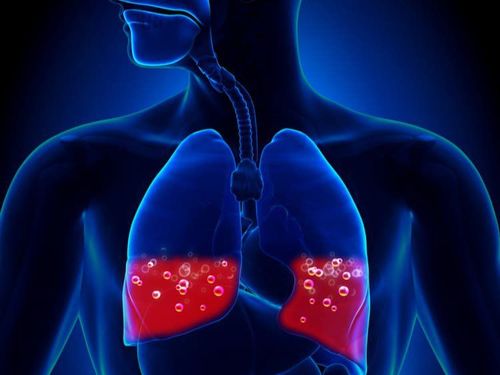
Tình trạng thừa dịch nặng cùng với tăng huyết áp có thể gây phù phổi cấp
5.2 Nervous System uremia is not only seen in the oliguria stage but can still be seen in the stage where the patient returns to urinate or urinates a lot, causing neuromuscular disorders, possibly convulsions, coma.
5.3 Gastrointestinal Gastroenteritis, acute pancreatitis, gastrointestinal bleeding - this is a very serious complication and increases the risk of death
5.4 Metabolic disorders The patient is prone to dehydration and electrical disturbances solutions such as hypercalcemia, hyperphosphataemia, hyperuricemia, hypermagnesemia. Decrease in potassium, blood sodium in the period of polyuria and possibly death if not properly treated and closely monitored. Decreased insulin metabolism, increased parathyroid hormone and decreased T3-T4 thyroid hormone. Malnutrition . 5.5 Infections Superinfections of the lungs, urinary tract, skin wounds, sepsis.
5. Prevention of agents causing acute kidney failure
To prevent agents leading to acute renal failure, it is necessary to carefully monitor the use of drugs that can cause acute renal failure such as sulfamide, gentamycine; gentamycine should not be combined with cefalotine; prevent poisoning due to taking the wrong medicine or using the wrong substances such as mercury, silver, copper... in technical operations. At the same time, it is necessary to take measures to protect labor, reduce traffic accidents, prevent fire and explosion, prevent malignant malaria, reduce obstetric complications...In the preventive treatment, pay attention to the prevention of disease. dehydration, hypovolaemia in cases of dehydration and acute blood loss; do not let the blood pressure drop for a long time; correct and timely infection control.
When encountering cases of acute renal failure, it is necessary to urgently focus on treatment means appropriate to each stage of disease progression; prepare psychologically and pay attention to nursing work from the beginning because the disease may require long-term treatment for many months.
In summary, acute renal failure is a disease that reduces kidney function, due to many different causes and has a high mortality rate, especially in the group of patients in the intensive care unit. Therefore, patients with acute renal failure need timely and appropriate treatment measures.
Master. Doctor. Nguyen Thi Thanh Thuy is a nephrologist with more than 15 years of experience in diagnosing and treating medical kidney disease, hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, pre-transplant screening and post-transplant monitoring. Currently, Dr. Thuy is working at the Department of General Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.