This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Dr. Bui Xuan Truong - General Internal Medicine Department - Vinmec Times City International HospitalSince the bacteria Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) was discovered by two Australian medical scientists, R Warren and B Marshall in 1982 and officially published evidence that H. pylori bacteria have the ability to cause gastritis on Medical journal The Lancet in 1983, so far there have been tens of thousands of medical studies related to H. pylori bacteria in human disease have been published.
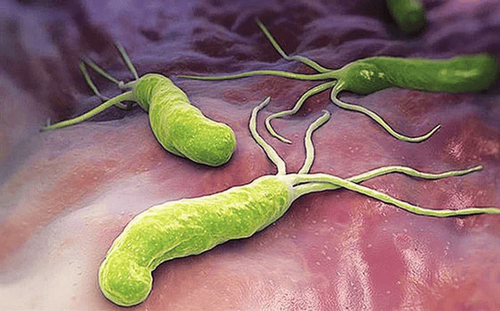
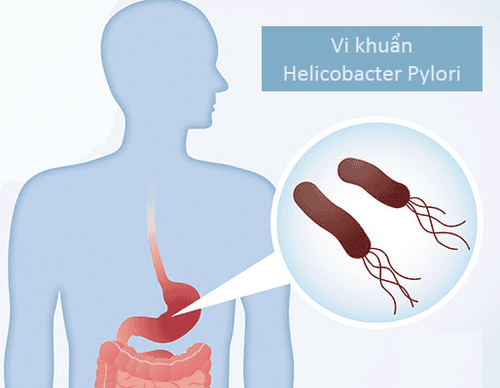
1. What is Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) bacteria?
In 1994, the World Health Organization (WHO) classified H. pylori bacteria as a group 1 risk factor capable of causing cancer in humans, and then in 2014 the World Health Organization recommended treatment to eradicate H. pylori is considered a strategy to reduce the risk of stomach cancer. H. pylori infection is quite common, according to epidemiological research data recently published in 2017-2018, about 47-50% of the world's population is currently infected with H. pylori bacteria, in which Developed countries in Western Europe - North America, Australia and New Zealand have relatively low infection rates. In contrast, many developing countries in Africa, Central America and South America, Southeast Asia - South Asia are areas with high prevalence of H. pylori infection, ranging from 50% to over 70% of the population. .However, when we are infected with H. pylori bacteria, we should not lose heart and worry too much, why is that?
Although the number of people infected with H. pylori bacteria is very large and very common, only about 15-20% of people infected with H. pylori bacteria have the ability to develop diseases and those diseases are also very common. very diverse, such as:
Functional digestive disorders Gastritis, duodenitis Gastric ulcer, duodenal ulcer Stomach cancer Gastric lymphoma Hemorrhagic thrombocytopenia Therefore, among many infected people H. pylori bacteria, only a small percentage have the ability to develop stomach cancer, not as many people today mistakenly believe that every infection with H. pylori bacteria will definitely lead to stomach cancer.
Cancer in general and stomach cancer in particular is a complex disease with the participation of many factors with many different pathological mechanisms, of which H. pylori is only one factor. With the development of current medicine, we have many methods of diagnosing H. pylori infection with high accuracy, and at the same time we can completely eradicate H. pylori bacteria out. out of the body.
One of the non-invasive testing methods applied quite commonly in many countries, including Vietnam, is the breath test (Urea Breath Test).
Xét nghiệm hơi thở làMột trong những phương pháp xét nghiệm không xâm nhập được áp dụng khá phổ biến ở nhiều nước
2. Why does a breath test diagnose Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection?
Normally, the stomach is a fairly acidic environment with a pH ≈ 2, stomach acid plays an important role in the digestion of food, and plays a role in the body's natural protective barrier. before pathogens (bacteria, viruses...) enter the body through the mouth. Almost all bacteria and viruses, when entering the stomach, will not last long and will be destroyed by the acidic environment of the stomach.H. pylori bacteria is a type of bacteria that has different characteristics from many other bacteria, one of the basic factors that help H. pylori can survive for a long time in the acidic environment of the stomach is bacteria. H. pylori bacteria can secrete urease, and urease has the ability to neutralize acid, helping to create the right environment for H. pylori bacteria not to be destroyed by stomach acid.
The process of urease hydrolysis of H. pylori bacteria in the stomach will produce the end products are ammonia (NH3) and carbon dioxide (CO2) in which CO2 is absorbed into the blood, following the circulatory system to the lungs. and is excreted to the outside through the airways. Based on this principle, we can develop testing techniques to measure the CO2 concentration in the breath and draw conclusions to diagnose whether a person is infected or not infected with H. pylori bacteria.
The most common breath test technique today is to use carbon isotope 13C or 14C, first we measure the concentration of CO2 in the breath without taking medicine containing 13C or 14C carbon isotope, then we Take a pill containing a carbon isotope 13C or 14C and then measure the CO2 concentration a second time. Based on the difference in CO2 concentration between two times of not taking the drug and taking the drug, the carbon isotope 13C or 14C, we can make a diagnosis of whether a person is infected or not infected with H. pylori bacteria.
Breath test technique - breath test has a very high diagnostic accuracy, about 90-98%, and is a non-invasive test (no need to conduct gastroscopy to biopsy samples) The specimen is one or two pieces of gastric mucosa), so breath testing is currently receiving the attention and consensus of many patients.
However, it should be noted that carbon 14C is a radioactive isotope, so it should not be used by pregnant women, breastfeeding women or children. In contrast, carbon 13C is not a radioactive isotope, so it can be assigned to all objects.
Currently, hospitals under the Vinmec International General Hospital system, use 13C carbon isotope in the breath test to diagnose H. pylori bacteria with the leading advanced machine with 02 airbags, both affordable and affordable. diagnostic treatment is very high (> 95%) and ensures patient safety.
>> See more: Photodynamic therapy and vaccines in the treatment of helicobacter pylori - Posted by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Gastroenterologist - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - General Hospital Vinmec Central Park International Faculty
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.