This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Doctor Vo Thi Thuy Trang - Gastrointestinal Endoscopy - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Da Nang International Hospital.Acute pancreatitis is an increasingly common disease. There are many causes of acute pancreatitis such as acute pancreatitis caused by alcohol, hyperlipidemia, after trauma... However, in which, 16-40% of patients with acute pancreatitis are caused by gallstones. .
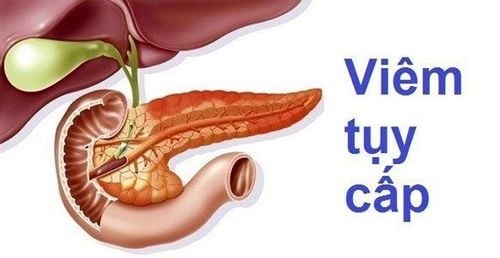
1. What is acute pancreatitis?
AThe main pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis is due to the activation of pro-enzymes into active enzymes in the lumen of the pancreas, which in turn leads to a series of other chain reactions.
Almost all patients with acute pancreatitis have severe abdominal pain in the epigastrium, below the sternum. The pain usually radiates to the back in about 50% of cases. Pain rarely begins in the lower abdomen.
In addition, all patients experience nausea and vomiting, sometimes to the point of dry vomiting. In some patients, especially those with acute pancreatitis caused by alcohol abuse, there are usually no symptoms other than moderate pain. But for other patients, the pain is intense.
Patients often collapse, sweating, tachycardia (100 - 140 beats/min), rapid and shallow breathing. Blood pressure can be high or low, but usually tends to drop when the person stands up suddenly, causing lightheadedness.
As acute pancreatitis progresses, the patient may become lethargic or even lose consciousness completely. The conjunctiva will sometimes be yellow.
2. Why do gallstones often cause acute pancreatitis?
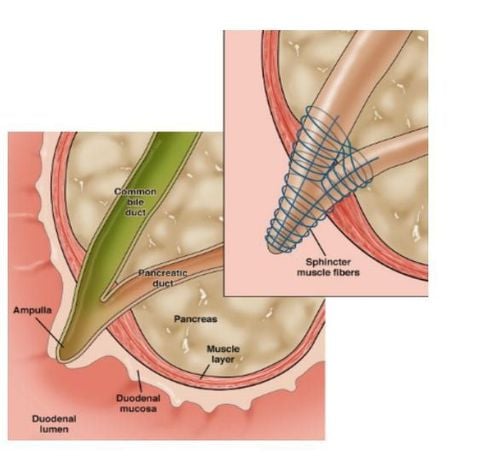
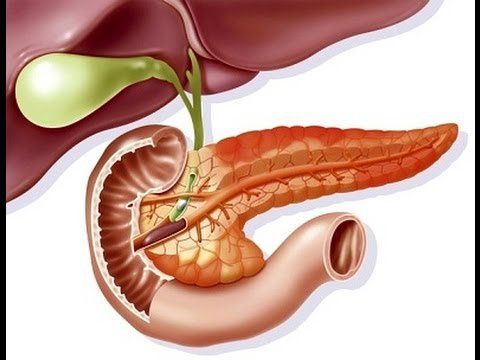
Pancreas has two functions:Endocrine: The pancreas secretes two main hormones to regulate blood sugar, which are insulin (lower blood sugar) and glucagon (raise blood sugar). Exocrine: The pancreas produces enzymes that digest food. The common cause of gallstones causing acute pancreatitis is that the pancreas belongs to the digestive system, located behind the peritoneum, going from the 2nd part of the duodenum to the nipple, across the lumbar spine, up and left.
In patients with gallstones, especially in cases of common bile duct stones causing obstruction of the bile duct, bile will back up into the pancreatic duct, changing the pH of the pancreatic juice, the pH of the pancreatic juice becomes alkaline, similar to the pH in duodenum, pancreatic enzymes are activated to become active in the lumen of the pancreatic duct and as a result, pancreatic cells are destroyed leading to a series of inflammatory reactions occurring.
Injuries to the pancreas and nearby organs are caused by improperly activated pancreatic enzymes and the systemic symptoms are caused by a systemic inflammatory response, so gallstones often cause acute pancreatitis.
3. Manifestations of acute pancreatitis due to gallstones

Abdominal pain is Symptoms appear in almost 100% of cases. Typical abdominal pain usually appears suddenly in the area above the navel, intense pain, spreading to the chest, to the sides of the ribs, obliquely behind the back, gradually increasing, reaching the most intense after a few hours and lasted many hours. Sometimes the cramping pain, like gallstone pain, or coincides with gallstone pain, makes the pain symptom worse. This is often the first symptom that brings a person to the hospital. Symptoms of nausea and vomiting occur in about 70-80% of patients. Vomiting occurs with pain. Vomit is bile, food, and sometimes blood (in severe cases). Along with abdominal pain and vomiting are symptoms such as abdominal distension, bowel obstruction, there may be loose stools or shortness of breath due to abdominal distension or accompanying pleural effusion. Patients panic fear or struggle with excitement, lethargy (brain-pancreatic syndrome), low blood pressure, pale skin, rapid pulse, small, difficult to catch. Abdominal examination may show abdominal distension, local reaction above the navel, pain in the right and left flanks. Hard plaque can be palpable above the umbilicus, which is not mobile due to the phenomenon of fat necrosis, low percussion due to peritoneal effusion. Examination may show jaundice with enlarged liver, enlarged gallbladder due to gallstones causing cholestasis or hepatitis. Bruises may also be seen on either side of the ribs (Cullen's sign) or around the navel (Grey's sign), especially in severe acute pancreatitis.
4. Diagnosis and treatment of acute pancreatitis due to gallstones
4.1. Diagnosis of acute gallstone pancreatitis Diagnosis of acute gallstone pancreatitis is based on abdominal pain and vomiting. Laboratory tests showed elevated amylase and lipase enzymes in the blood and urine. Ultrasound and especially abdominal computed tomography allow to determine the degree of inflammation such as enlarged pancreas, peripancreatic fluid or necrosis of the pancreas and clearly see the image of stones causing obstruction of the common bile duct, gallstones. , stones in the bile ducts in the liver. 4.2. Treatment of acute pancreatitis caused by stones Adequate fluid and electrolytes infusion, prevention of acute gastrointestinal ulceration, reduction of pancreatic secretion, analgesia, blood glucose control, antibiotics, continuous dialysis if acute pancreatitis is severe or pancreatic shock. In the initial phase, the patient should be completely fasted and will be given parenteral nutrition. Removal of gallstones to release biliary obstruction by endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is highly effective without causing further injury to the patient. Some cases of acute pancreatitis due to gallstones also have surgical indications such as surgery to release biliary obstruction (when ERCP cannot be performed) or acute pancreatitis with bacterial necrosis.5. Prevention of acute pancreatitis

Gallstones: The most effective way to prevent gallstones is to eat a lot of vegetables every day. Maintain a healthy weight by eating less fat to lower your cholesterol. At the same time, each day you should set aside 15 to 30 minutes for exercise, to reduce the risk of developing gallstones. Alcohol: Reducing alcohol intake, or completely giving up alcohol, helps prevent your pancreas from being damaged. It is recommended not to drink more than 14 units a week. With nearly 20 years of working at Da Nang General Hospital in the field of gastroenterology - hepatobiliary disease, every year, Doctor Vo Thi Thuy Trang participates in endoscopy more than 1500 cases including: endoscopic diagnosis of stomach diseases stomach, colon such as: detecting inflammation, ulcers, polyps, cancer, finding HP bacteria, detecting cancer early in the digestive tract...; Endoscopic treatment such as: Hemostasis in gastrointestinal bleeding, esophageal varices ligation in cirrhosis, endoscopic gastrointestinal polypectomy...
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.