This is an automatically translated article.
The article is expertly consulted by Master, Doctor Truong Thanh Tam - Pediatrician - Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.1. What is Eczema?
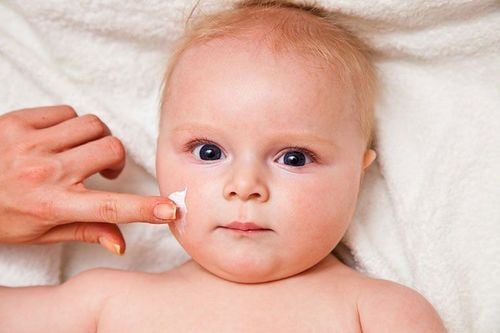
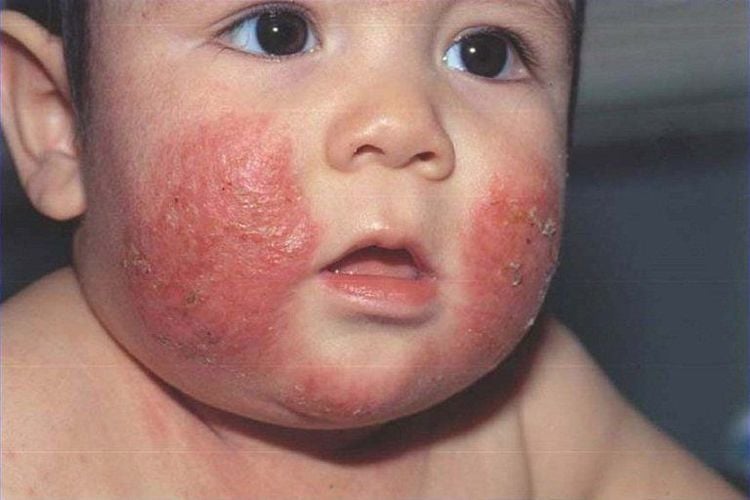
Eczema, also known as strabismus, is a form of atopic eczema that is common in babies as young as 2 months old. This is a chronic, non-contagious skin condition caused by allergies or genetics in children. The disease can persist until the child is 2 years old with typical lesions appearing on both cheeks.Eczema in babies is classified into 3 levels:
Acute: Skin lesions with pinkish red blisters, containing fluid, causing itching. Chronic: The skin is damaged in patches, dry, thick, scaly, skin pigmentation changes after inflammation. Subacute: Lesions in an intermediate stage between acute and chronic.
2. Why do babies often get eczema?
To date, the cause of infantile eczema is not well known, however the following factors are considered risk factors for the onset of the disease and can make it worse:Genetics, parents with the following conditions Allergic diseases such as asthma, skin allergies, weather, ... Allergies Living in a polluted environment or in direct contact with allergens such as pet dander, dust, cigarette smoke, Mold, pollen, soaps, detergents... Food allergies, such as eggs, milk, can also cause eczema. Allergic weather, cold, hot, dry climate changes. Dry skin, not guaranteed moisture, often bathing a lot, unbalance the moisture on the skin. Infections with viruses and bacteria that cause skin diseases.
3. Signs to recognize eczema in babies and complications
Eczema in babies can be recognized through the following signs:Location: on both cheeks, on the face, possibly on the legs, hands and spread all over the body. Lesions on the skin are initially red, small, and then develop into blisters. Blisters make children itchy, uncomfortable, when scratched and broken, they will secrete fluid, progress to scabs. Dry and scaly skin in an infant with eczema will be rough, dry, and tight to the touch. Other symptoms may be accompanied by allergies, rhinitis, asthma. During clinical examination, it is necessary to differentiate eczema from other inflammatory skin diseases such as urticaria, impetigo, white flakes... Specifically:
Urticaria: Lesions on the facial skin are rashes and edema, appearing scattered now. Impetigo: An area of skin damaged by blisters or blisters, which then evolves into pustules. The pustules are broken and dry, with thick yellow scabs. White scales: Unlike eczema, infantile ichthyosis is hypopigmented, white, finely scaly skin that appears on the cheeks, hands, and upper body. Eczema in infants will gradually subside and may resolve on its own when the child is older than 1. However, if the child is older (after the age of 4 years) but still does not heal, the disease often persists and often recurs, with It can develop into impetigo, pustular dermatitis (like chickenpox) and progress to eczema.
4. What to do when a baby has eczema?
Eczema in babies is easy to recur, especially when the child is exposed to and allergic to food or weather. Therefore, when diagnosed with eczema, children need to be cared for and treated according to the instructions of a dermatologist.The goal of eczema treatment is mainly to reduce itching, avoid bacterial infections, superinfections on the skin, normalize the skin and help limit recurrence, specifically parents should note the following information:
Limitation exposure to allergens that cause disease. Consult a dermatologist for advice on buying the right medication. Do not arbitrarily buy topical medications for eczema for children, especially those containing corticosteroids because they can cause skin atrophy, fungal infections, loss of skin pigmentation and aggravate the disease, even kidney failure. Do not arbitrarily use folk remedies such as applying leaves because it can make the disease worse. Babies with eczema need careful and thorough care from skin care to nutrition such as:
Try to breastfeed for the longest time, at least 6 months after birth . Avoid introducing solids too early, the average and suitable age for weaning is when the baby is 6 months old. Limit or avoid giving your child foods that are highly allergenic: seafood, eggs, peanuts, milk and dairy products, etc.

Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for examination, treatment and prevention of diseases, including the pediatric - neonatal specialty. When performing the examination process at Vinmec, customers will be welcomed and used modern facilities and equipment along with perfect medical services under the guidance and advice of experts. Good doctors, well-trained both at home and abroad.
Master. Truong Thanh Tam has 15 years of experience in pediatrics and especially has a lot of experience in hematology, resuscitation and pediatric oncology. The doctor has participated in many national and international scientific conferences on pediatrics and participated in many short-term training courses and was certified as "Pediatric Core Instructor", by Hue University of Medicine and Pharmacy. grant. Currently, she is a Pediatrician at the Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.