This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Vo Ha Bang Suong - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital.The thyroid is an important endocrine gland that controls metabolism. Any abnormality of the thyroid gland can be a cause, or a sign of, a medical condition. Understanding thyroid diseases for prevention or screening, early treatment is essential to ensure the health of yourself and your loved ones.
Thyroid disease is any benign or malignant condition that affects the structure and function of the thyroid gland.
Common thyroid diseases are hypothyroidism , hyperthyroidism and thyroid cancer . Women are 7 times more likely to have hyperthyroidism, and 8 times more likely to have hypothyroidism than men. The most common cause of thyroid dysfunction is iodine deficiency. Up to 1 billion people are at risk of iodine deficiency leading to thyroid disease. And of that, mostly found in women.
1. What are thyroid diseases?
To understand thyroid-related diseases, we must first understand what the thyroid gland is, and what role it plays in human life.
Shape and location: The thyroid is shaped like a butterfly located in front of the neck, level with the C5 - T1 vertebrae, composed of 2 lobes (left and right lobes) connected by an isthmus, lying on the anterior lateral aspect of the thyroid cartilage and the upper part of the trachea. Summary of thyroid function: This is the part that keeps the function of excreting, storing and releasing two hormones T3 (Triiodothyronine) and T4 (Thyroxine), which regulate metabolic processes in the body. When this part is working properly, the metabolism in the body always remains stable, not too fast, not too slow. On the contrary, an abnormality in the activity of the thyroid gland will greatly affect the patient's health, and is also a manifestation of a number of related diseases.
2. Thyroid-related diseases
2.1 Hypothyroidism/Hypothyroidism Hypothyroidism is an underactive thyroid disease that cannot secrete enough of the hormone Thyroxine.
Hypothyroidism has very vague signs and is similar to the manifestations of some other diseases such as drowsiness, fatigue, memory loss, hoarseness, constipation, women may have abnormal bleeding in the vagina. In case the disease develops at a late stage, the patient may have more serious manifestations such as loss of appetite, mental and physical exhaustion, and hair loss. In many cases, skin and mucosal syndrome manifests with edema of the mucous membranes, enlarged tongue on both sides, other manifestations such as bradycardia, low blood pressure, even sudden coma.
To treat hypothyroidism, patients need to be persistent in taking medication and following the doctor's instructions. In many cases, the patient will recover, but there are also patients who will require lifelong treatment.
2.2 Hyperthyroidism/Hyperthyroidism Hyperthyroidism is a condition that occurs due to increased secretion of thyroid hormones (triiodothyronine and thyroxine). In addition, we can have hyperthyroidism due to causes such as: Graves' disease, multinodular goiter, thyroiditis, toxic adenoma, eating too much iodine...
2.3 Thyroid cancer Thyroid cancer is a malignant disease of, accounting for about 1% of cancers with manifestations such as: thyroid gland enlargement in a short time and abnormally raised lymph nodes around; eat a lot but still lose weight; poor heat tolerance, sweating, always in a state of mental stress, insomnia; mood swings; weak trembling limbs; rapid activity fatigue, nervousness, shortness of breath; women see little menstrual period....
2.4 Benign thyroid nodules Thyroid nodules are the most common thyroid disease. The disease develops silently and without obvious symptoms, does not interfere with the patient's daily life, so it is difficult to detect. Patients only feel uncomfortable when they see a large bulge in the neck area, lumps, and pressure on the surrounding organs, causing a feeling of difficulty in swallowing, breathing, coughing a lot...
In endocrinology, the group's pathology group Thyroid gland is quite common in the population characteristics of our country.
Regarding epidemiological characteristics, women have thyroid diseases many times higher than men with the rate from 3 to 10 times. In particular, the highest incidence of the disease falls in the group of women in their 20s.
3. Why do women have more thyroid disease than men?
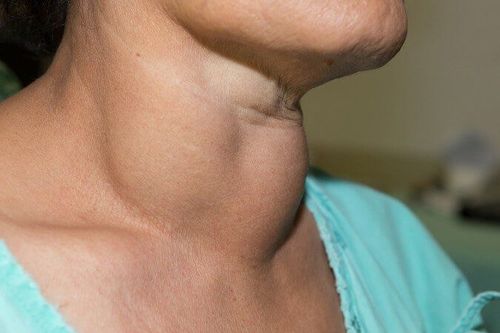
Nữ giới dễ bị các bệnh lý tuyến giáp hơn chủ yếu do phải trải qua nhiều cột mốc biến động về nội tiết tố
Stages of physiological - hormonal changes of the female body such as:
Puberty, in the menstrual cycle: Changes in sex hormones during puberty, in the menstrual cycle have an impact reciprocal and closely related to thyroid hormone.
Women in pregnancy, childbirth and lactation:
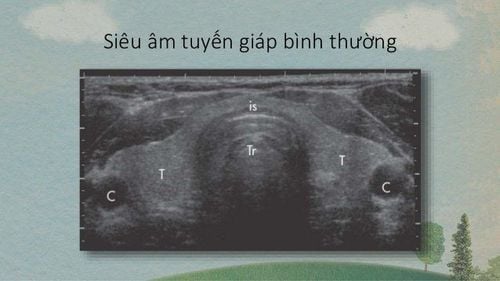
Hormonal changes in pregnancy. Normal changes of thyroid function in pregnant women. Hormonal changes: During pregnancy, your body produces two main hormones: βhCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) and estrogen. An increase in βhCG during the first trimester of pregnancy can cause a slight decrease in TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone), which is then referred to as subclinical hyperthyroidism. TSH will rise again later in pregnancy. Estrogen (female sex hormone) will increase serum protein-binding thyroid hormone, however, free thyroid hormone (FT3, FT4) will not increase, thus not affecting thyroid function. Thus, thyroid function remains normal if TSH, FT3 and FT4 are normal. Changes in size: The thyroid gland can change in size during pregnancy: About 10-15% larger in size, called a goiter. This rate is higher in women living in mountainous areas where there is an iodine deficiency. Ultrasound is the best way to detect an enlarged thyroid gland. When a pregnant woman has an enlarged thyroid gland, she should see her doctor for a thyroid function test. What is the impact of thyroid function on mother and baby?
During the first 10-12 weeks of pregnancy, the baby is completely dependent on the mother's thyroid function. At the end of the first 3 months, your baby's body will produce thyroid hormone on its own. However, the baby still has to depend mainly on the amount of iodine the mother eats. The World Health Organization recommends that pregnant women take 200 mcg of iodine per day to maintain thyroid function.
Women in menopause : Underlying thyroid disease during the past time can flare up thyroid disease in menopausal people. Other factors such as age, a decrease in female sex hormones, and an unreasonable diet can cause thyroid disease in this subject.
In addition, other risk factors such as using birth control pills, taking sedatives, antibiotics, using hormone-regulating therapy...
Women often experience insomnia, anxiety, stress Stress in life... also causes hormonal changes and is a risk factor for thyroid diseases. Immunodeficiency: A weakened immune system leads to changes in hormones in the body, thereby increasing the risk of thyroid diseases. Family history: A family history of thyroid diseases, especially thyroid cancer, will increase the risk of the disease in the next generation, especially women. Personal factors: a history of thyroid disease or surgery, radiation therapy affecting the thyroid gland also increases the risk of disease. Dietary excess or deficiency of iodine.
4. How to prevent thyroid disease
Symptoms of thyroid disease are often unclear, but we can also prevent thyroid diseases by:
Reasonable nutrition, increased intake of green vegetables and fruits to help balance thyroid hormones armor. Supplementing with a full diet of iodine helps the thyroid gland to have enough materials to produce hormones and prevent thyroid disease. In particular, pay attention to iodine supplementation for pregnant women to prevent the risk of complications during pregnancy, and at the same time to help the fetus develop intellectually. Regular exercise helps strengthen the body's immunity, prevent diseases and thyroid disease in particular. Build a healthy lifestyle, limit the use of fried foods and stimulant drinks. Do not use alcohol or tobacco.

Ăn nhiều rau xanh và trái cây giúp cân bằng hormone tuyến giáp
5. How to screen for thyroid disease?
Thyroid exams are part of the annual wellness check, recommended for all men and women, especially women 20 years of age and older.
In addition, when the subject has symptoms of hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism as described above, it is necessary to go to the doctor for early detection of thyroid disease. Some thyroid diseases may have no symptoms other than an accidental discovery of an enlarged neck, choking, hoarseness, a feeling of tightness, or tightness in the neck.
When you go to the doctor, you should choose reputable large hospitals and centers with endocrinology specialists to be screened accurately and perform all necessary paraclinical tests. One of the addresses that customers trust and choose to visit is the Vinmec International General Hospital system with the package of SCREENING, SCREENING FOR TREATMENT DISEASES.
When you choose the Package of Screening and Screening for Thyroid Diseases at Vinmec, you will be examined by experienced thyroid specialists to help screen and detect thyroid diseases early. common such as: simple goiter, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, thyroiditis, thyroid nodules, thyroid cancer,...
At the same time, you will have blood tests, evaluate the levels of functional hormones Thyroid function such as FT3, FT4, TSH, Anti - TPO, Anti TG and ultrasound, scan to evaluate the structure of the thyroid gland. After that, when the results are returned to the doctor, you will be consulted about thyroid pathology, and discuss the appropriate treatment options for yourself. From there, thyroid disease will be prevented in time, avoiding long-term health damage in the future.
In summary, thyroid disease is very common in women, affecting the metabolism of many organs in the body. The screening and screening package for thyroid diseases at Vinmec with a team of experienced endocrinologists will help you detect thyroid disease early, treat it thoroughly, and contribute to improving the prognosis for your health. the health of you and your loved ones.
For more information about thyroid screening packages at Vinmec International General Hospital, customers can contact hotline 0243 9743 566 or register online HERE.