This is an automatically translated article.
Blood is a liquid tissue and circulates in the circulatory system of the whole body. Blood has a function Blood participates in mechanisms to protect the body such as regulating the activities of cells and organs, ensuring the synchronization in the activities of the organs. Blood consists of two components, blood cells and plasma. So where do blood cells come from? The article will help readers find the answer to the question.
1. Composition of blood
Blood is made up of two parts: cells and plasma. Cells include red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Plasma is related to other factors such as blood clotting, hormones, proteins, and minerals.Function of blood:
Blood carries hormones, electrolytes such as Ca++, K+, Na+... to help regulate circulation and maintain blood pressure. Transport O2 and CO2 exchange between the alveoli and the cellular organizations, thereby helping to provide oxygen to produce energy for the whole body. Transporting sugars, amino acids, fatty acids, vitamins... to provide cellular organization Helps regulate human body temperature quickly so that the body always has the same temperature. Provide materials for body building. Protect and fight against infected inflammatory areas by immune mechanisms.
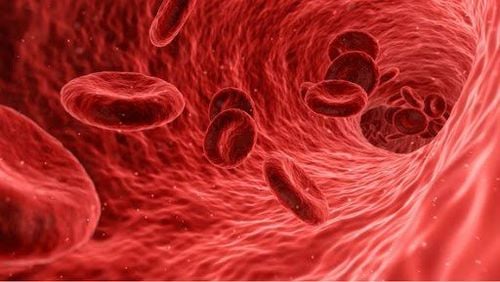
Máu là một mô lỏng và lưu thông trong hệ thống tuần hoàn của cả cơ thể
2. The role of bone marrow with blood cells in the body
Bone marrow is a spongy or viscous tissue located inside the bones. There are 2 types of bone marrow: bone marrow and yellow marrow. Red marrow has an important role in blood formation. The hematopoietic stem cells found in the red marrow develop into different types of blood cells that help in the production of red blood cells, platelets, and white blood cells.
Yellow marrow is responsible for storing fat. Over time, yellow marrow will gradually replace red marrow. Therefore, most adult bones will contain yellow marrow.
3. Where are blood cells born?
As mentioned above, human blood cells consist of 3 components: red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets.
Red blood cells
Red blood cells in the blood make up the most number. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, which gives blood its red color. Red blood cells are responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and receiving carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs for elimination. Red blood cells have a life span of 120 days from adulthood, after which they are destroyed usually in the armpits and liver. Red marrow participates in the process of hematopoiesis, creating new red blood cells to replace and maintain a stable amount of red blood cells in the body. White blood cells
White blood cells are produced in the bone marrow. White blood cells are mainly located in the blood, but there are still a large number of them residing in the body's tissues and have a protective job by detecting and destroying disease-causing factors. Helps heal wounds by preventing infection, consuming dead cells, thin tissue and old red blood cells. White blood cells help protect the body from foreign bacteria such as allergy-causing bacteria, and protect the body from mutant cells such as cancer-causing cells.
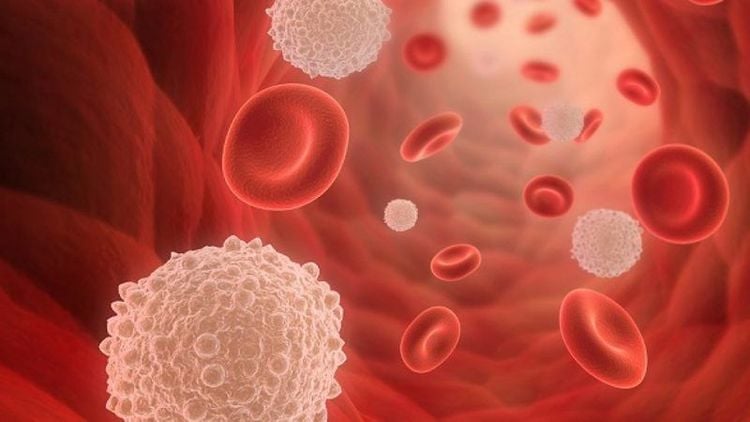
Bạch cầu được sinh ra từ tủy xương
Platelets are very small pieces of cells, much smaller than red blood cells or white blood cells. They have the function of stopping bleeding by platelets aggregating together to form platelet plugs, creating a blood clot that leads to bleeding cessation. Helps blood vessel walls soft and supple because platelets can also "rejuvenate" endothelial cells. The life cycle of platelets is from 7 to 10 days from maturity. The bone marrow is also the site of the production of platelets.
4. The effect of human blood cells on bone marrow
Blood cells in the body are born from the bone marrow, so they have a very close relationship to produce blood cells. There are many conditions that can affect the bone marrow, which in turn affects blood cell counts. Common symptoms of these conditions include:
Fever is caused by not having enough healthy white blood cells in the body. Fatigue, weakness: This is the result when the body lacks hemoglobin - this is the protein that carries oxygen in red blood cells Increased risk of infection because of fewer white blood cells Shortness of breath: decreased red blood cells cause for less oxygen transport to the body's tissues Bleeding and easy bruising: Because the blood cells in the body have few platelets, the cells involved in the process of helping blood clot.
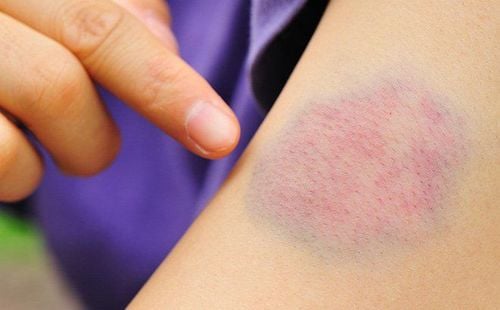
Tế bào máu trong cơ thể có ít tiểu cầu gây ra các vết bầm tím dưới da
When the body loses blood, dehydration or lack of blood-forming materials all affect the function of the body. Blood loss can be from acute bleeding or other causes of gradual blood loss. Dehydration can be caused by vomiting, diarrhea, fever, or a lack of body fluids. The diet does not provide enough, unbalanced nutrients, blood-forming materials all cause deficiency of blood components. In addition, foreign factors such as bacterial infections, viruses, parasites, acquired diseases all affect the function of blood components.
Health check-ups and especially periodic blood tests to detect early risks of abnormal blood components for timely intervention.
If you have a need for consultation and examination at Vinmec Hospitals under the nationwide health system, please book an appointment on the website for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.