This is an automatically translated article.
Leukemia is cancer of the body's blood-forming tissues, including the bone marrow and the lymphatic system. But in people with leukemia, the bone marrow makes abnormal white blood cells, which don't work properly. Treatment for leukemia can be complicated - depending on the type of leukemia and other factors. But there are strategies and resources that can help make your treatment a success.
1. Blood cancer (Leukemia)
Leukemia is a cancer of the blood cells. There are several broad types of blood cells, including red blood cells (red blood cells), white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets. In general, leukemia refers to cancer of the WBC.
White blood cells (WBCs) are an important part of your immune system. They protect your body from bacteria, viruses and fungi, as well as from abnormal cells and other foreign substances. In leukemia, WBCs do not function as normal WBCs. They can also divide too quickly and eventually crowd out normal cells. White blood cells (WBCs) are mainly produced in the bone marrow, but some types of WBCs are also made in the lymph nodes, spleen, and thymus. Once formed, WBCs circulate throughout the body in your blood and lymph (the fluid that circulates through the lymphatic system), concentrating in the lymph nodes and spleen.
2. Causes of blood cancer
Scientists do not understand the exact cause of leukemia. It seems to develop from a combination of genetic and environmental factors.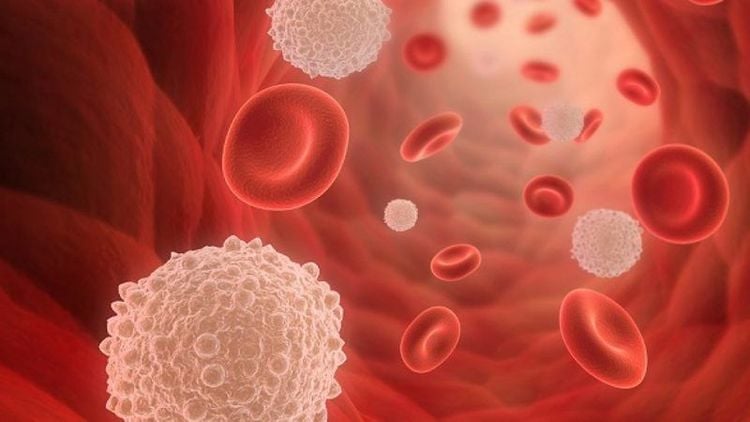
Chưa xác định được chính xác nguyên nhân gây ra bệnh bạch cầu
3. Risk factors for blood cancer
The causes of leukemia are known. However, some risk factors for blood cancer have been identified that may increase your risk. These include:
3.1 Family history of leukemia Previous cancer treatment, people who have had certain types of chemotherapy and radiation therapy for other cancers are at increased risk for certain types of leukemia.
Certain conditions are associated with an increased risk of blood cancer, including leukemia, due to an inherited gene mutation (a change in a gene).
These conditions are called familial cancer syndromes or hereditary (inherited) cancer syndromes. Most familial cancer syndromes are rare. Familial cancer syndromes that can lead to leukemia in both children and adults: Down syndrome, Fanconi anemia, Bloom syndrome.
3.2 Genetic disorders Genetic abnormalities appear to play a role in the development of leukemia. Some genetic disorders, such as Down syndrome, are associated with an increased risk of leukemia.

Rối loạn di truyền có ảnh hưởng đến sự phát triển của bệnh bạch cầu
3.3 Smoking Smoking increases the risk of acute myeloid leukemia.
3.4 Radiation and chemotherapy in the past Radiation therapy given in the past to treat cancer or other health conditions increases the risk of leukemia. Chemotherapy given in the past to treat cancer also increases the risk. Having both radiation and chemotherapy to treat cancer increases the risk more than either treatment alone.
3.5 Breathe in Benzene Benzene is found in unleaded gasoline and is used by the chemical industry. People can breathe in benzene at work or in a general environment or by using certain products. Benzene increases the risk of leukemia.
3.6 Breathing in formaldehyde Some studies have shown that inhaling formaldehyde increases the risk of leukemia. Factory workers, chemical workers, embalmers, and others may be exposed to formaldehyde in the workplace.
Embalmers have a higher risk of leukemia because they tend to be exposed to longer and use more formaldehyde on the job.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.