This is an automatically translated article.
Video content is professionally consulted by GS, TS, BS. Do Doan Loi, Cardiology Center - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital
Cardiovascular ultrasound techniques are now widely used and play an important role in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. In the types of echocardiography (transthoracic echocardiography, echocardiography, etc.), transesophageal echocardiography is the insertion of an ultrasound transducer through the mouth into the esophagus to perform ultrasound, get the most accurate results. Transesophageal echocardiography is a type of test that reconstructs a patient's heart.
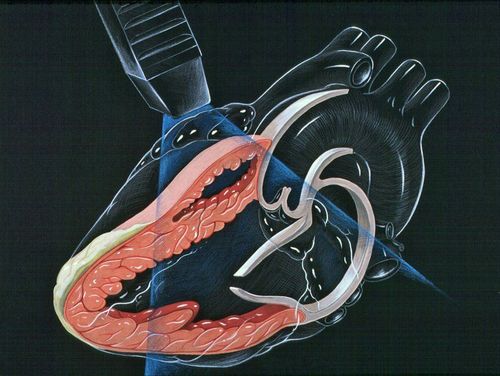
In transesophageal echocardiography, sound waves play an extremely important role, they are responsible for recreating the most detailed images of the patient's heart along with the blood vessels that originate or lead to the heart. Unlike conventional forms of echocardiography, the transesophageal echocardiogram transducer generates ultrasound waves and is attached by a very small catheter, which enters through the mouth, then down the throat and into the patient's esophagus.
The main purpose of transesophageal ultrasound tests is to use ultrasound waves to create the most detailed pictures of the heart chambers, heart muscle, and valves, along with the outer layer of the heart (also known as the heart). is the pericardium), and the blood vessels that are connected to the patient's heart.
Usually, transesophageal echocardiography is indicated when the doctor wants to know more details about the structure of the patient's heart, after performing other routine echocardiographic methods. In addition, the doctor will ask the patient to perform a transesophageal echocardiogram in the following cases:
The patient performed a transthoracic echocardiogram but the image is not clear Transesophageal echocardiography during the procedure surgery Transesophageal echocardiography during the recovery room In the catheterization rooms. To start a transesophageal echocardiogram, your doctor will insert an endoscope into your throat and ask you to swallow. The doctor will push the tube 12-14 inches down the esophagus. The transducer will take pictures of the person's upper right chamber of the heart, called the right atrium, and then move the tube 4 to 6 inches deeper. The transducer takes pictures of the lower left chamber of the heart, called the left ventricle. The probe will be placed at each position for 5 to 10 minutes. A small plastic straw will help the patient drain the saliva from the mouth.
Transesophageal ultrasound technology contributes to improving the treatment efficiency of complex cardiovascular diseases. Moreover, transesophageal echocardiography does not cause pain and discomfort to the patient, so you can rest assured to perform this echocardiographic therapy at prestigious hospitals across the country. .
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.