This is an automatically translated article.
Testicular biopsy is a method of finding the presence of sperm in the testicles/epididymis, indicated when the ejaculate sample is absent, for the diagnosis of malignancy as well as for use in fertility support.
1. What is a testicular biopsy?
Testicular biopsy is a technique in which the doctor will take a sample of testicular tissue for the purpose of carrying out a pathological examination for the presence of malignancy, to diagnose the cause of infertility, or to use in assisted reproduction.
2. Why is a testicular biopsy necessary?
Testicular biopsies are performed for a variety of purposes, based on the individual patient, including:
Determine the nature of the abnormal mass in the testicle or determine the existence of testicular cancer complete. Diagnosis of male infertility. Collecting sperm for assisted reproduction (intra-cytoplasmic sperm injection – ICSI).
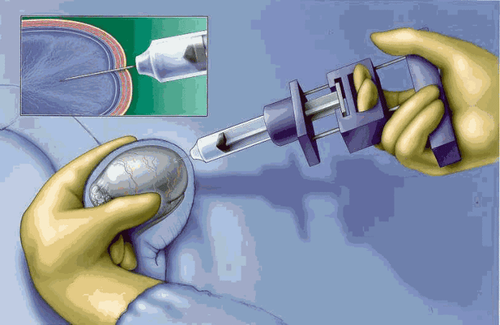
Sinh thiết tinh hoàn được thực hiện nhằm phục vụ nhiều mục đích khác nhau
3. Testicular biopsy techniques
Testicular biopsy may use the following techniques:
Open biopsy: This technique can be performed under sedation or sedation. The doctor will open the scrotum to take a sample of testicular tissue for biopsy purposes. This is the technique that ensures the highest accuracy if it is necessary to determine the cause of cancer or the cause of infertility, and is also the most effective technique for obtaining sperm for assisted reproduction. Percutaneous biopsy: This technique uses a true-cut needle or fine needle aspiration (FNA). The advantage of percutaneous biopsy technique is that there is no need for surgical equipment, just anesthesia without anesthesia, patient preparation as well as post-operative care is simple. However, fine needle biopsy also has limitations, such as the accuracy of detecting testicular cancer in situ (CIS) has not been fully evaluated by studies, or the number of sperm obtained. will be lower than with an open biopsy.
4. Possible risks of testicular biopsy
Like any other technique, a testicular biopsy has certain risks during the procedure, including:
Bleeding Infection Severe damage to the testicle or surrounding structures (rare) Birth Testicular implantation does not cause erectile dysfunction or fertility problems after the technique.
5. Prepare before performing a testicular biopsy
Patients can consult their doctor about all their questions. The patient also needs to sign a written consent to perform the testicular biopsy technique. Patients should inform their doctor about their medical history, as well as all medications and supplements they are taking, especially anticoagulants. Patients should inform their doctor if they are sensitive or allergic to anything. Depending on the technique of testicular biopsy that will be performed, and depending on the patient's case, the doctor will give specific preparation instructions and specific requirements (if any).
6. Care after a testicular biopsy
Depending on the testicular biopsy technique performed and the specific patient's condition, the doctor will guide how to care.
Patients are usually instructed to avoid sex for one to two weeks after the biopsy. Pain after a biopsy is common, take pain medication as prescribed by your doctor. Patients can also use ice to reduce pain during the first 24 hours.
Đau sau sinh thiết là điều thường gặp
Inconvenience, swelling and pain will disappear after a few days. If any of the following signs appear, contact your doctor as soon as possible:
Increased bleeding. A hematoma appears. Swelling, pain getting worse. Fever and/or chills.
7. Get testicular biopsy results and next steps
Testicular tissue samples taken from the biopsy will be taken for pathological examination or sperm collection for assisted reproduction, depending on the purpose of the initial biopsy.
Other abnormal biopsy results may be:
Testicular cancer. Semen cyst: A fluid-filled cyst located on the duct of the testicle. Orchitis: Painful swelling of the testicles, with or without bacterial infection. Depending on the specific results of each case, the doctor will explain, advise the patient and make further decisions. The doctor may assign the patient to do some more tests if necessary, or discuss with the patient in detail about possible treatments, to agree on the optimal plan for the patient's case. sick. Patients should follow the doctor's instructions, and complete and timely follow-up visits to achieve the best treatment results.
It is best to choose a testicular biopsy at a large, reputable medical facility not only in the general hospital system but also to stand out and take the lead in the field of cancer diagnosis and treatment.
For detailed advice on testicular biopsy techniques at Vinmec, you can go directly to Vinmec medical system nationwide or contact to book an online examination HERE.
Reference article: NCBI
MORE:
Don't ignore the early signs of testicular cancer Testicular cancer screening and diagnosis