This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by a doctor of Obstetrics and Gynecology Department.Uterine polyps are one of the leading gynecological diseases causing infertility in women if not handled properly. So what is uterine polyp and how dangerous is it?
1. What are uterine polyps?
Uterine polyps are overgrowths that occur in the endometrium, the inner lining of the uterus (the uterus is the organ through which a fetus develops). For that reason, uterine polyps are sometimes called endometrial polyps. Polyps can be pedunculated or sessile. The polyps can be round or oval, and range in size from a few millimeters (the size of a sesame seed) to several centimeters (the size of a golf ball) or larger. There may be one or several polyps present.Uterine polyp is a tumor that develops in the uterine cavity. Uterine polyps most commonly occur in perimenopausal or postmenopausal women, although younger women can also develop the condition.
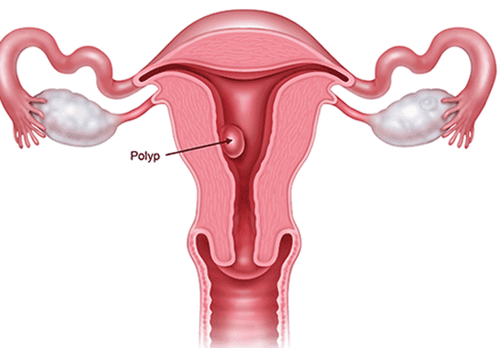
Polyp buồng tử cung là sự phát triển quá mức xảy ra ở nội mạc tử cung
2. Signs of uterine polyps
Uterine polyps often progress silently and show no obvious symptoms. However, if you have the following symptoms, you may have uterine polyps
Irregular menstrual cycles. Irregular bleeding during menstruation. Bleeding after menopause. The most common symptom of uterine polyps is irregular or unpredictable periods. About half of women with uterine polyps experience irregular periods.

Triệu chứng phổ biến nhất của polyp buồng tử cung là kinh nguyệt không đều hoặc không dự đoán được
3. Are uterine polyps dangerous?
Uterine polyps, if not detected and treated promptly, can lead to dangerous complications such as:
Infertility: When polyps or polyps grow large, the endometrium is changed form, detrimental to the implantation of the fetus. Increased risk of polycystic ovaries. Uterine polyps are easy to cause gynecological diseases because vaginal secretions are abundant, the vaginal environment is unbalanced, beneficial bacteria are destroyed and cannot protect the vagina, harmful bacteria grow and cause infections such as Vaginitis, vulvovaginitis, cervicitis, ... Polyps of the uterus during pregnancy are growing, causing the fetus to lose attachment points, easily leading to miscarriage, premature birth or birth defects. abnormal development. Pregnant women have an increased risk of placenta previa. Increases the risk of cervical cancer and uterine cancer: Large polyps are easy to necrosis and cause bleeding. These polyps themselves are usually benign, but if not promptly treated, they will become infected and necrotic, and the infection will spread to the endometrium and uterine muscle, leading to uterine cancer for a long time. This is the most serious consequence of uterine polyps and cervical polyps.
4. Treatment of uterine polyps
Treatment depends on the progression of the disease. If polyps are small and have no symptoms, they can heal on their own, conduct regular monitoring. There are also a number of other treatments:
Medications: Medications that help regulate hormonal balance, shrink the uterus, and help relieve symptoms. However, symptoms will usually return once the medication is stopped. Laparoscopic polypectomy with surgery: The doctor will insert devices through the laparoscope (an instrument that doctors use to see inside the uterine cavity) to remove uterine polyps.
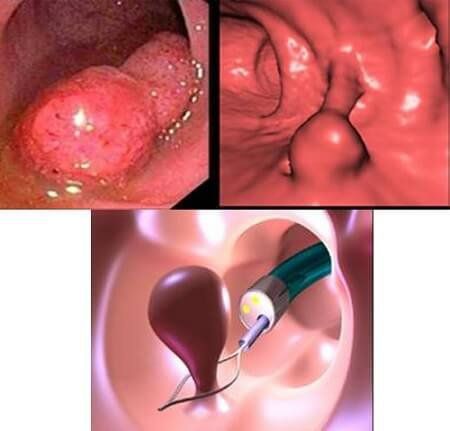
Mổ nội soi cắt polyp buồng tử cung bằng phẫu thuật
Hysterectomy: If during the examination it is found that uterine polyps contain cancerous cells, surgery is required to remove the uterus. There is no way to prevent uterine polyps. It is important to have regular gynecological exams. If you notice any abnormal signs, you should immediately see a doctor for timely examination and treatment, to avoid dangerous complications for health. Risk factors such as obesity, high blood pressure, or taking Tamoxifen to treat breast cancer can increase the risk of developing polyps.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.