This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Doctor Phan Diem Doan Ngoc - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Uterine polyps, if not detected and treated promptly, can lead to dangerous complications such as infertility, infertility, increased risk of polycystic ovaries, cervical cancer and uterine cancer. , if you are pregnant, you may have a miscarriage, premature birth or birth defects,...
1. What is uterine polyp?
Uterine polyps are an overgrowth of cells in the lining of the uterus (also called the endometrium). Uterine polyps are round or oval and range in size from a few millimeters to a few centimeters. Most uterine polyps are benign, but some are cancerous or will turn cancerous. This type of cell proliferation greatly affects a woman's fertility and menstrual cycle.The exact cause of uterine polyps is still unknown. However, increased levels of hormonal factors such as estrogen may play a role.
Uterine polyps occur in women of all ages, but are more common in their 40s and rare in women under the age of 20. This type of polyp usually develops during perimenopause or postmenopause. Women can control the disease by reducing risk factors.
Factors that increase the risk of uterine polyps include:
Pre-menopause or post-menopause High blood pressure Obesity Treatment of breast cancer with tamoxifen Symptoms of uterine polyps include:
Bleeding Abnormal uterine bleeding: 64 - 88% of cases of uterine polyps have abnormal bleeding, which can be often intermenstrual, oozing, or menorrhagia May be accompanied by abdominal pain, anemia, vaginal bleeding after menopause, and dryness vagina Some cases are asymptomatic, detected during infertility investigation, or cervical cytology, uterine biopsy.
Polyp tử cung là sự phát triển quá mức của tế bào lớp niêm mạc tử cung
2. How do uterine polyps affect women?
Uterine polyps, if not detected and treated promptly, can lead to dangerous complications such as:Infertility, infertility: When polyps or polyps grow large, the endometrium is deformed. , which is detrimental to the implantation of the fetus Easy to cause gynecological diseases: Uterine polyps are easy to cause gynecological diseases because vaginal secretions are abundant, harmful bacteria grow, causing infections such as vaginitis, vulvovaginitis , cervicitis ... Pregnant women: Polyps in the uterus during pregnancy grow more and more, causing the fetus to lose its attachment point, easily leading to miscarriage, premature birth or fetal malformation, placenta previa,. .. Large polyps are very easy to necrosis, if not promptly treated, they will become infected and bleed.
3. Diagnosis of uterine polyps
To diagnose uterine polyps, your doctor will ask you some questions about your menstrual history to find out the length of your period and its regularity. If you suspect you have uterine polyps, your doctor may perform some of the following tests:Transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) is the first choice to evaluate gynecological pathology in these settings. uterine polyps. This method can be up to 90% accurate. Uterine infusion ultrasound: In this procedure, a doctor injects a sterile fluid into the uterus through a catheter to enlarge the uterus and provide a clearer picture of any growths in the uterus. uterine cavity by ultrasound. Hysteroscopy: To diagnose or treat uterine polyps. In this procedure, the doctor inserts a long, thin, lighted camera into the vagina and cervix to examine the inside of the uterus. Endometrial biopsy: The doctor will use a straw to collect samples from the wall of the uterus and send them to a lab to see if there are any abnormalities;
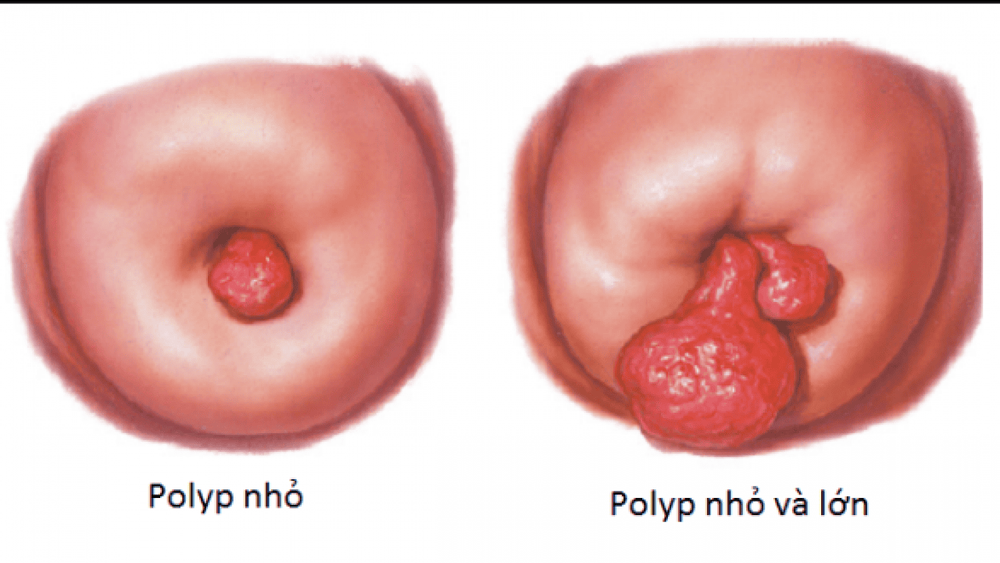
Khối polyp phát triển to làm nội mạc tử cung bị biến dạng
4. Polypectomy surgery through hysteroscopy
4.1. Indications and contraindications Indications for uterine polyp removal when the patient has uterine polyps with symptoms of bleeding; infertility; cancer risk. Contraindications to uterine polyp removal in the following cases: cervical stenosis, uterine muscle thickness remaining less than 1cm, pregnant women; Contraindication to general anesthesia. 4.2. Steps to perform surgery Step 1: The patient lies in the gynecological position, disinfects the patient's genital area and sterilizes the diagnostic and surgical hysteroscope. Step 2: General examination and specialist assessment of comorbidities; Ultrasound, uterine pump ultrasound, hysteroscopy to identify polyps in the uterus. Step 3: Relieve the patient's whole body pain. Catheterization and catheterization; vaginal valve or speculum; Cervical clamp with Pozzi forceps, then probe the uterine cavity with a protractor. Step 4: Place the hysteroscope to see the hysteroscope, the scope is slowly inserted through the cervix into the uterine cavity, observing the cervical canal and uterine cavity to determine the location and number of polyps.. Step 5 : Stretch the uterus with one of the high molecular weight solutions: Hyskon or a solution without electrolytes such as mannitol, sorbitol, dextran. Then, conduct observation of the entire uterine cavity to evaluate the lesion of uterine polyps. Step 6: Carry out polyp removal with a monopolar electrocution loop. Ensure the principle of cutting only when the scissors retract the electric knife. In turn, cut from the surface to the depth until the polyp is gone or to the point of contact with the surface of the lining of the uterus. Step 7: Take the cut pieces out. 4.3. Post-operative monitoring After hysteroscopy polypectomy for several hours, it is necessary to monitor the whole body, pulse, blood pressure, and blood flow from the vagina. Ultrasonography, rescan of the uterus after several months to assess the integrity of the uterine cavity. 4.4. Some complications when surgery to remove uterine polyps Bleeding Cervical tear Endometritis Uterine perforation To help customers detect and treat other gynecological diseases early, Vinmec International General Hospital There is a package of basic gynecological examination and screening, helping to detect early gynecological diseases to improve efficiency and reduce treatment costs. At the same time, screening for early detection of gynecological cancer (cervical cancer) even when there are no symptoms.Basic gynecological examination and screening package for female customers, with no age limit, who have the following symptoms:
Abnormal vaginal bleeding Menstrual problems: period abnormally long, irregular menstrual period Abnormal vaginal discharge (smell, different color) Pain, itching in the intimate area Female client has several risk factors such as poor personal hygiene, sexual relations unsafe sex, abortion,... Have other symptoms such as: itching, pain in the intimate area, abnormal vaginal discharge, abnormal vaginal bleeding. If you have unusual symptoms, you should be examined and consulted with a specialist.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.