This is an automatically translated article.
Uterine polyps of each patient vary in size, which can range from a few millimeters to several centimeters. Currently, laparoscopic surgery is the common method to treat uterine polyps. This method helps to minimize the complications and inconvenience that polyps cause for the patient.
1. What are uterine polyps?
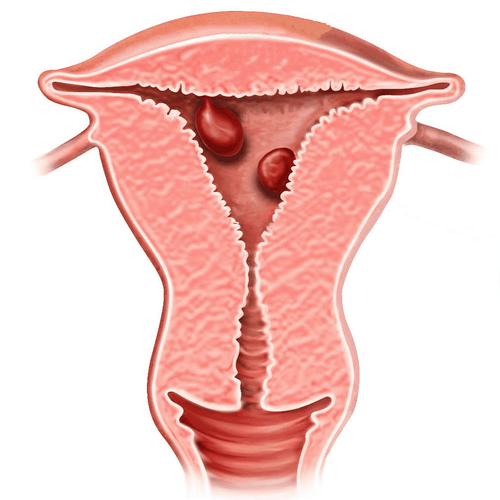
Uterine polyps are overgrowth of endometrial glands and stroma. The endometrium is located around the outside of a core of blood vessels and connective tissue. The number and size of polyps are variable, may be single or multiple, pedunculated or sessile, and may develop anywhere in the uterine cavity.
Uterine polyps are mostly benign, there are a few cases of complications on uterine cancer. However, it is easy to see that polyps affect the ability to become pregnant, give birth, fetus, daily life and reduce the patient's quality of life.
According to researchers, the leading cause of uterine polyps is due to increased levels and effects of endogenous or exogenous estrogen.
Tamoxifen: Uterine polyps occur in 2 to 36% of postmenopausal women treated with tamoxifen (a drug used to treat breast cancer) Obesity: Women with BMI ≥30 have The rate of uterine polyps (55%) was significantly higher than that of other women (15%). Some other risk factors are mentioned such as: Hormone replacement therapy in postmenopausal women containing estrogen, Lynch and Cowden syndrome... The most common symptom of uterine polyps is menstruation. irregular menstruation.
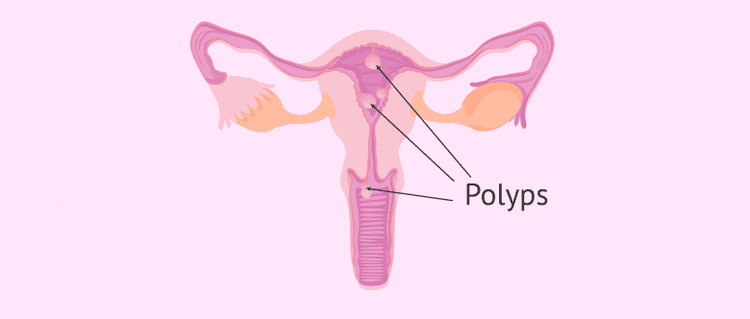
Polyp buồng tử cung
2. Laparoscopic surgery for uterine polyps
In addition to the transvaginal ultrasound method to diagnose uterine polyps, today hysteroscopy is also used to diagnose the disease. During hysteroscopy, it is possible to intervene in the treatment of uterine polyps. Laparoscopic polypectomy is usually performed through hysteroscopy, cutting the polyp stalk with scissors, a ring electrode, or cutting the polyp into pieces with a cutting ring.
Specifically, the steps to perform laparoscopic polypectomy are as follows:
Step 1. Dilation of the cervix. Use the Hégar candle to dilate the cervix to 9 so that the interventionoscope can be inserted with a diameter of 8 or 10. Step 2. Laparoscope placement: the bronchoscope is slowly inserted through the cervix into the uterine cavity, observing the cervical canal. uterus, uterine cavity to determine the location and number of polyps. Step 3. Polyp removal: loosen the cutting ring to the back of the polyp, turn on the electric current and pull the ring towards the cervix to cut the polyp. Clip the polyp and pull it out through the opening of the cervix. If the polyp is large, it can be cut into many pieces, starting at the top of the polyp and gradually going down the stalk. During the procedure, record the total amount of fluid in and out every 15 minutes. Step 4. Stop bleeding: use cutting electrode, switch to burning current to burn the bleeding points. Foley catheters can be used to stop bleeding at sites of heavy bleeding. Step 5. Withdraw instruments, send specimens for histopathology.
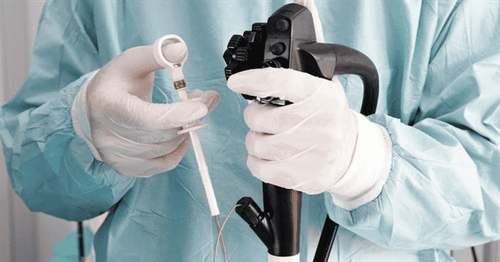
Mổ nội soi polyp buồng tử cung
After the laparoscopic surgery to remove uterine polyps, the postoperative process is also extremely important. Postoperative monitoring helps to limit the complications of the disease as well as prevent infection after endoscopy.
For the postoperative laparoscopic polypectomy, the biggest inconvenience is that the patient will have little vaginal bleeding or spotting bleeding for a few days, then it usually goes away on its own. In addition, the doctor will prescribe systemic antibiotics for the patient.
Although undesirable, there will be a few cases where complications will occur after surgery. If the patient, sees any of the following abnormal signs, immediately notify the doctor, to promptly handle:
Bleeding: If the patient still bleeds after burning the polyp, the doctor can A Foley catheter can be placed and the balloon inflated, and blood flow is monitored. If there is no bleeding, a hysterectomy is required. Cervical tear: The doctor will insert a gauze and carefully monitor Endometritis: If the patient has endometritis, the doctor will use an injectable Cephalosporin antibiotic for 7 days. Uterine perforation: If uterine perforation is detected during hysteroscopy, laparoscopy should be performed to evaluate nearby organs and treat according to the lesion. Absorption of large amounts of fluid into the blood: Electrolyte test, if the Na ion concentration falls below 125 mEq/L, need intensive care, diuretics and 3% NaCl solution infusion rate 1-1.5 mEq/l per hour. In order to help customers detect and treat other gynecological diseases early, Vinmec International General Hospital has a basic gynecological examination and screening package, which helps customers detect inflammatory diseases early and help treat diseases. Easy, inexpensive treatment. Screening detects gynecological cancer (cervical cancer) early even when there are no symptoms.
If you have unusual symptoms, you should be examined and consulted with a specialist.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.