This is an automatically translated article.
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) test is a non-specific test for the diagnosis of the disease but is simple and easy to perform to help detect a preliminary abnormality of the body. may be involved in the body's inflammatory response to screen and diagnose many diseases.1. What is a erythrocyte sedimentation test?
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate test is a erythrocyte sedimentation test, which is performed by placing anticoagulated blood in a vertical column and assessing the height of the remaining plasma column after 1 hour. The remaining plasma column height expressed in mm will represent the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, as it depends on the number of red blood cells and the concentration of high molecular weight proteins in the blood. Changes in these proteins in the blood lead to different aggregation of red blood cells. The faster the red blood cells settle, that is, the faster the rate of aggregation indicates inflammation and necrosis. Therefore, the clinical erythrocyte sedimentation test is not specific in any disease because it only indicates the presence of inflammatory cells, but does not determine the location and cause of inflammation. In order to make an accurate diagnosis, more specific blood tests are indicated.
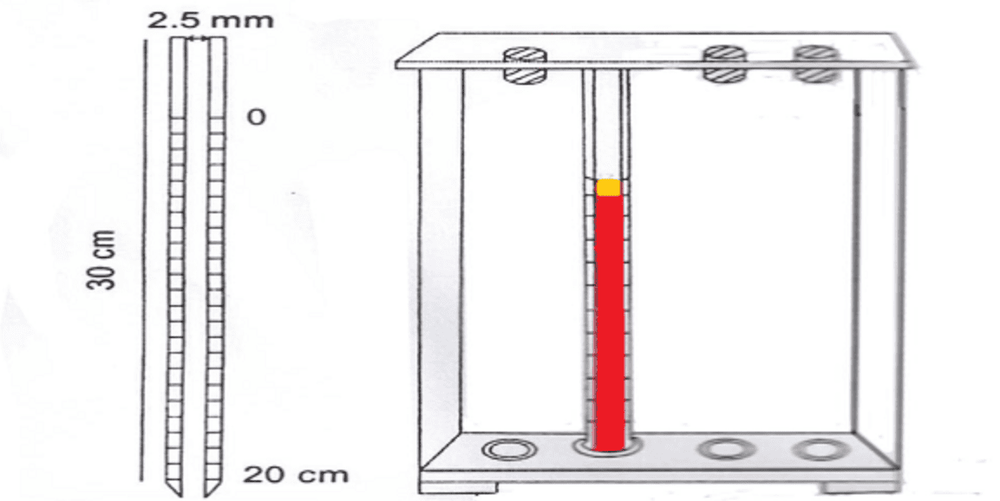
Phương pháp xét nghiệm tốc độ máu lắng
2. What is the erythrocyte sedimentation test for?
Very high erythrocyte sedimentation rate can be seen in lung and urinary tract infections, non-infectious inflammatory syndromes, cancer and necrotizing tissue lesions, temporal arteritis, erythrocyte sedimentation is usually very high. Erythrocyte sedimentation testing also allows monitoring of progression of an established etiology (eg, to monitor an infection treated with antibiotics or an autoimmune disease treated with corticosteroids). The value of erythrocyte sedimentation rate decreases gradually reflecting the patient's etiological condition is improving and vice versa.
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate test is also indicated to monitor inflammatory status, malignancy such as: acute myocardial infarction, low-grade fever...
In some cases, erythrocyte sedimentation rate test is used to test the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. monitor specific diseases (eg infections treated with antibiotics, autoimmune diseases treated with corticosteroids...). When the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is normal, the disease is improving.
In addition, in rheumatic fibromyalgia, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate should be monitored periodically with an erythrocyte sedimentation rate test to determine the dose of prednisolone to use.
3. What causes increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate?
Bacterial infections: Acute (such as pneumonia, appendicitis) or chronic (infective endocarditis, osteomyelitis, abscess, tuberculosis,..) Tumor and cancer pathologies ( such as lymphoma, multiple myeloma) Chronic inflammatory reactions (Crohn's disease, chronic progressive polyarthritis, rheumatic fibromyalgia, Horton's disease) Autoimmune diseases (such as systemic lupus erythematosus). Acute myocardial infarction Fungal or parasitic infection Severe anemia
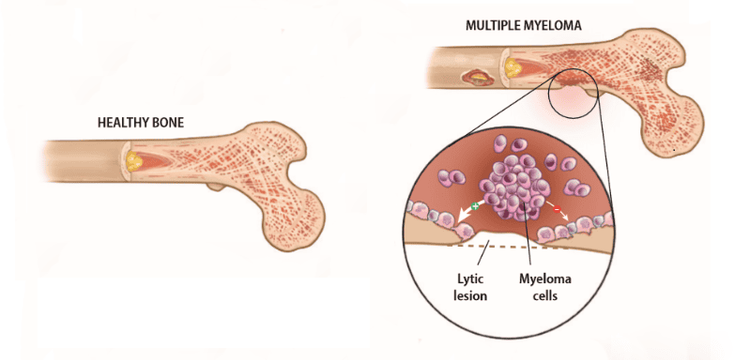
Đa u tủy là một trong nhiều nguyên nhân gây tăng tốc độ lắng hồng cầu
Congestive heart failure Hemophilia Hypoalbuminemia Primary polycythemia vera Sickle cell anemia However, erythrocyte sedimentation rate can be influenced by many factors. Thus, information about the inflammatory response may be obscured. These complicating factors include:
Age Anemia Pregnancy Kidney problems Thyroid problems Certain cancers, such as multiple myeloma Infections To register for a Hospital examination and treatment Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
MORE:
Meaning of blood test numbers What diseases can blood tests indicate? What you need to know about the blood count test