This is an automatically translated article.
The pulsatile window is a rare congenital heart disease that causes severe complications and increases the risk of death for children, so early diagnosis and treatment are very important. Fortunately, this is a disease that can be detected through prenatal screening.
1. What is the disease of the master window?
A valvular or aortic fistula is a condition in which there is communication between the ascending aorta and the pulmonary trunk just above the sigmoid valve. This is a rare congenital heart disease caused by an abnormality in the joint walling of the aorta and pulmonary arteries.
The bronchopulmonary window is usually quite wide, round or oval in shape, this window is the direct connection without the medial catheter between the left border of the aorta and the right border of the pulmonary artery. Normally, about 50% of children with aortic window disease have other accompanying lesions such as congenital aortic stenosis, existing ductus arteriosus, ventricular septal defect, tetralogy of Fallot... Concomitant treatment will increase the risk of heart failure, increase pulmonary artery pressure.
Classification of the bronchopulmonary window according to Richardson includes 3 types:
Type I: The bronchial window is located between the ascending aorta and the pulmonary artery just above the sinus of Valsalva. Type II: The window is located more distal, between the ascending aorta and the origin of the pulmonary artery P from the pulmonary trunk. Type III: Right pulmonary artery arises from the aorta.
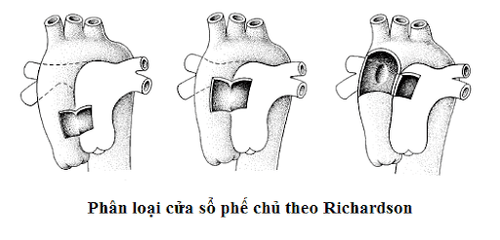
Phân loại cửa sổ phế chủ theo Richardson
When there is a communication flow between the aorta and the pulmonary artery through the pulmonary aorta, it will cause damage depending on the size of the orifice. Possible consequences of having this flow include:
Will cause urinary overload and severe pulmonary hypertension, rapidly progressing to obstructive pulmonary vascular disease. Causes aortic regurgitation syndrome with strong peripheral vascular hyperactivity and left ventricular diastolic load, gradually causing left ventricular failure, This is a severe congenital heart disease, the course of which can be fatal. for children. However, if detected and treated early with surgery, children can recover completely.
2. What are the clinical signs of bronchopulmonary disease?
2.1 Signs in young children
Most of the symptoms of the disease will manifest in this stage, accounting for more than 80%. Symptoms that can be noticed in this condition include:
Symptoms appear loudly, manifest as rapid breathing, repeated bronchitis. Children sweat a lot, growth retardation due to circulatory failure, heart failure. Children may have multiple episodes of pneumonia, making the condition worse. On examination, the peripheral pulse was strongly pushed, the heart area was enlarged, and a systolic murmur was heard at the base spreading along the left border of the sternum. Subclinical: X-ray showed an enlarged heart, an enlarged and hyperactive pulmonary artery. Electrocardiogram showed ventricular thickening and mainly left ventricle, left atrium. Echocardiography helps to confirm the blood flow between the aorta and the pulmonary artery.
2.2 For older children
Only about 15-20% of symptoms appear at this stage. Possible manifestations such as:
Difficulty breathing, moderate fatigue. Symptoms can be progressively worse. Examination reveals a continuous systolic murmur or a bilateral murmur. The clinical examination is similar to that of an infant, requiring ultrasonography to confirm the diagnosis.

Thở nhanh là một trong các dấu hiệu lâm sàng của bệnh cửa sổ chủ phế
2.2 Amnesia in adults
This is very rare, if at all it is usually the case of small stomas and spontaneous disease causing generalized heart failure, right heart failure, pulmonary hypertension and advanced disease difficult surgery. Manifestations such as:
In the history, there is a period with a left-right shunt. Cyanosis reappeared gradually. Visible in both upper and lower extremities. Auscultating the heart is a systolic murmur at the base of the heart, a strong T2 sound in the pulmonary valve. Subclinical: Electrocardiogram shows signs of biventricular hypertrophy replaced by signs of increased right ventricular systolic load. Chest x-ray shows a reduced heart shadow with reduced peripheral pulmonary circulation. Echocardiography through the cross-section on echocardiography can show signs of disease.
3. Complications of broken master windows
Previously, before surgery, the disease progressed very seriously and children often died before the age of 15 and without surgery 40% of children died within the first year. Some complications of bronchopulmonary regurgitation include:
Cardiopulmonary failure: This is a condition caused by increased pressure on the arteries and increased pressure on the lungs Obstructive pulmonary disease: Due to pulmonary vascular hypertension After a period of time, it will lead to pulmonary embolism. Infective endocarditis: Children with developmental delays are susceptible to infections such as respiratory tract infections and endocarditis which is a serious condition leading to death.
4. How to treat the aortopulmonary window?
When diagnosed with bronchiectasis, surgery is indicated in most cases. Except for cases where the disease has progressed severely or has contraindications to surgery. In addition, combined with temporary medical treatment in the period of heart failure with superinfection.
Surgery can offer a good chance of survival for many children with a success rate of over 95%. If detected early, surgery can save the child completely from having a similar life to other children.
Windows of the aorta is a dangerous congenital heart disease that develops rapidly, seriously affecting health and can be fatal if not treated. The aortopulmonary window can be detected through fetal malformation screening when the mother is pregnant. Therefore, mothers need to have a full examination during pregnancy for the earliest detection and early treatment.
With many years of experience in examining and treating diseases in children, now the Pediatrics Department at Vinmec International General Hospital has become one of the major health care centers, capable of examining , screening and treatment of many specialized diseases in children. Therefore, if a child shows signs of schizophrenia, parents can take the child to Vinmec International General Hospital for examination and receive support and advice from doctors and other health professionals. .
Especially to prevent this disease, right from the pregnancy stage, mothers also need to perform regular antenatal check-ups to detect fetal abnormalities early - This is the great strength of Vinmec, which has been implemented here. Screening to detect fetal malformations very early and implementing Fetal Medicine interventions provide the opportunity for many couples to have a healthy baby. Therefore, mothers can be completely assured of the Obstetrics - Pediatrics expertise at Vinmec International General Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.