This is an automatically translated article.
Arterial hypoxia and tissue hypoxia are not two names for the same condition, but two different conditions and their relationship.
1. What is arterial hypoxia and organizational hypoxia?
Arterial hypoxemia (hypoxia) occurs when the amount of oxygen in the arterial blood is low and is confirmed by a blood gas test (result PaO2 < 60 mmHg or SaO2 < 90%).
If arterial hypoxemia progresses more severely, or is prolonged without intervention (or ineffective intervention), it will lead to tissue hypoxia, which means that the total amount of oxygen in the body is low and not effective. also meet the needs of the tissues.
Arterial hypoxia and tissue hypoxia are both dangerous, potentially life-threatening conditions. Whenever there are signs of arterial hypoxia and hypoxia, the patient should be treated immediately.
2. What are the manifestations of arterial hypoxemia and organizational hypoxia?

Nhịp tim nhanh là dấu hiệu của giảm oxy máu động mạch và thiếu oxy tổ chức
Symptoms of arterial hypoxia and tissue hypoxia are not exactly the same between cases, but the most common manifestations include:
Change in skin color, from pale blue to purple red. Loss of consciousness, confusion. Sweating. Tachycardia, or low heart rate. Increased respiratory rate, dyspnea, shortness of breath, wheezing. Cough.
3. What causes arterial hypoxia and organizational hypoxia?
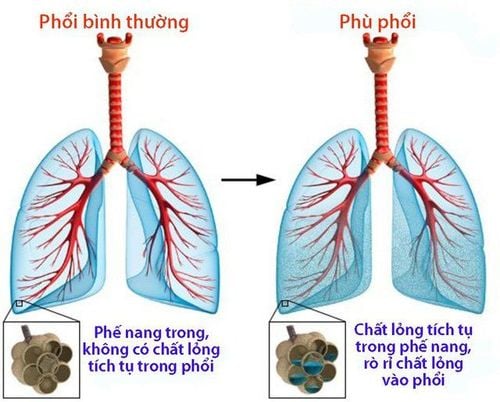
Phù phổi
Common causes of arterial hypoxia and tissue hypoxia include:
Acute bronchial asthma. Traumatic lung damage. Lung diseases such as: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pulmonary edema, pulmonary emphysema, bronchitis and pneumonia. Medications that cause respiratory depression. Cardiovascular disease. Anemia. Cyanide poisoning.
4. How to prevent arterial hypoxia and organizational hypoxia?
The most effective way to prevent arterial hypoxia and organizational hypoxia is to well control bronchial asthma every day, by following the treatment instructions of a specialist.
Use medicine exactly as ordered by your doctor to prevent acute asthma attacks. Eat a healthy, balanced diet and stay active. Identify and prevent asthma triggers. Please consult a specialist to understand how to handle an acute asthma attack, to avoid being passive when the situation occurs.
Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as customers wishing to be examined and treated at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide or register online HERE.
Reference article source: webmd.com
MORE
What is a normal blood oxygen level? What is the SPO2 index in a normal person? Signs of a lack of oxygen in the body