This is an automatically translated article.
Tenoxicam is an active ingredient commonly indicated in the treatment of osteoarthritis, extra-articular rheumatoid disorders and post-traumatic swelling. This is also the main active ingredient in Tenotil.
1. What is Tenotil 20?
Tenotil is a drug manufactured by Korea United Pharm Joint Stock Company of Korea with the main ingredient being Tenoxicam - an active ingredient in the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory pain relievers with analgesic effect in rheumatoid arthritis. osteoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, gout and extra-articular rheumatic disorders, post-traumatic swelling... and is available in the form of film-coated tablets.
Tenoxicam is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent with significant anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects, mild hypothermia effect. Currently, the exact mechanism of action of tenoxicam is not known, but many theories suggest that the drug inhibits prostaglandin biosynthesis, reducing the concentration of leukocytes at the site of inflammation.
2. What are the effects of Tenotil?
Tenotil is indicated for use in the following cases:
Relieves symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis; Short-term treatment in acute musculoskeletal disorders such as: excessive muscle strain, sprains, other soft wounds...
Thuốc Tenotil có tác dụng trong điều trị bệnh viêm khớp dạng thấp, thoái hóa xương khớp
3. Dosage and how to take Tenotil
Tenotil is taken orally, high doses of Tenotil should not be used because it usually does not achieve a higher therapeutic effect but increases the risk of undesirable effects of the drug. In the symptomatic treatment of acute musculoskeletal diseases, the drug usually requires more than 7 days, in severe cases, Tenotil can be used up to 14 days. Tenotil should be taken on a full stomach with a full glass of water about 150ml and avoid alcoholic beverages during treatment with Tenotil.
Dosage of Tenotil for adults over 18 years old (including the elderly):
Use Tenotil single dose 20mg, take the drug at the same time every day; For some patients, just 10mg of Tenoxicam, once a day is enough; The lowest effective dose of Tenotil must be used, which is usually limited to 20 mg/day. Tenotil dose for patients with renal impairment:
If the patient's creatinine clearance is > 25ml/min: the usual dose of Tenotil can be used but must be carefully monitored; If the patient's creatinine clearance is < 25 ml/min: There are insufficient data to recommend a dose of Tenotil. The specific dose of Tenotil depends on the condition and the progress of the disease, patients should consult their doctor or medical professional before taking Tenotil.
4. Tenotil overdose and treatment
Symptoms of NSAID overdose generally include: nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, diarrhea, gastrointestinal bleeding, tinnitus, headache, blurred vision, dizziness. Toxicities that are more severe after ingestion of significant doses of Tenotil include convulsions, irritability, somnolence, hypotension, apnea, electrolyte-depleted coma, renal failure, and possible exacerbations of asthma.
When there is an overdose of Tenotil, it is necessary to stop taking the drug and use activated charcoal, gastric lavage, use of antacids, proton pump inhibitors ... Within 1 hour after taking a toxic dose of Tenotil, it is possible to use activated carbon. There is no specific antidote for tenoxicam overdose. Hemodialysis does not significantly remove NSAIDs from the blood.
Need to ensure the amount of urine to maintain enough water in the body, need to closely monitor the liver and kidney function of Tenotil overdose users. Patients should be monitored for at least 4 hours after an overdose of Tenotil. If seizures are frequent and prolonged, the patient should be treated with intravenous diazepam.
5. Tenotil side effects
When using Tenotil, patients may experience undesirable effects (ADRs) with the following rates:
Digestive system: 11.4%; Nervous system: 2.8%; Skin: 2.5% (urticaria, itching). Common symptoms:
Vomiting, nausea: 14.7%, Indigestion: 2.3%; Bleeding at the surgical site: 4.3%; Wound infection: 92.7%; Dizziness: 5.7%; Headache: 10.7%. Some other side effects of Tenotil:
Fatigue, edema, loss of appetite, dry mouth; Circulatory: Palpitations. Diarrhea, stomatitis, gastrointestinal bleeding, duodenal - gastric ulcer, gastritis, black blood in the stool; Psychiatric: Sleep disturbance; Hypersensitivity reactions (asthma, anaphylaxis...); Blood: Anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, bleeding due to inhibition of platelet aggregation; Hypertension; Blurred vision, sensitivity to light, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Lyell syndrome; Urogenital - Genitourinary: Difficulty urinating; If gastrointestinal ulceration or gastrointestinal bleeding occurs while taking Tenotil, the drug must be discontinued immediately. Use antacids or H2 receptor antagonists to improve.
If liver function tests are abnormal or worsen while taking Tenotil, it is also necessary to stop the drug immediately, treat symptomatically and provide supportive treatment as needed.
Some ADRs of NSAIDs may occur such as nephrotic syndrome, nephritis, thrombocytopenia, anemia, severe skin reactions or hypersensitivity reactions... may respond to glucocorticoids.
Khi sử dụng thuốc Tenotil có thể gặp các tác dụng phụ về hệ tiêu hóa như chảy máu đường tiêu hóa cần ngừng thuốc và tham khảo ý kiến bác sĩ
6. Contraindications of Tenotil
Tenotil is contraindicated in the following cases:
Progressive peptic ulcer, history of peptic ulcer, gastrointestinal bleeding (bloody stools, vomiting blood); Asthma, cases of easy bleeding such as cirrhosis, heart failure, renal failure (creatinine clearance < 30ml/min); Hypersensitivity to tenoxicam; People prone to hypersensitivity reactions (rhinitis, angioedema, urticaria) to other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
7. Precautions while using Tenotil
It is necessary to carefully monitor patients taking Tenotil when there is a gastrointestinal disease; Monitor cardiac, hepatic, and renal function in patients with pre-existing renal disease, nephrotic syndrome, dehydration, liver disease, congestive heart failure, especially in patients receiving concomitant diuretic or toxic drug therapy. with kidneys; For elderly patients, it is necessary to monitor interactions when taking concomitant therapy with other drugs, and to monitor renal, hepatic and cardiovascular function because the risk of hyperkalemia may be increased in the elderly; Caution should be exercised in patients undergoing major surgery because tenoxicam reduces platelet aggregation which may prolong bleeding time; The safety of tenoxicam in pregnancy has not been established, however, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may cause arterial closure in the neonate, so Tenotil should not be administered to pregnant women, especially against indicated for pregnant women in the last 3 months of pregnancy; It is not known whether Tenotil is excreted in breast milk, so Tenotil should not be used by women who are breast-feeding.
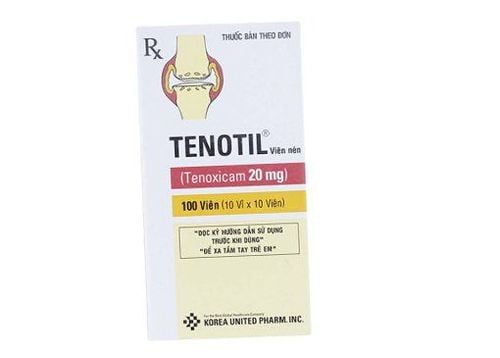
Dùng thuốc tenotil theo chỉ định của bác sĩ
8. Tenotil drug interactions
Antacids may decrease the rate of absorption but do not affect the extent of absorption of tenoxicam;
Other NSAIDs/glucocorticosteroids: Salicylates can displace tenoxicam from protein binding, increasing the clearance and volume of distribution of tenoxicam; therefore, concomitant treatment of Tenotil with salicylates, aspirin, and other anti-inflammatory drugs should be avoided. other non-steroidal or glucocorticosteroids due to increased side effects, especially in the gastrointestinal tract;
Lithium: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs cause lithium retention, if using tenoxicam, it is necessary to strengthen monitoring of lithium levels and inform patients about maintaining water intake and symptoms of lithium toxicity for timely detection. time;
Diuretics / Antihypertensives: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can cause water retention, sodium, potassium, affect the sodium excretion effect of diuretics, increase the risk of nephrotoxicity of NSAIDs. Dose adjustment is required, which is especially important when treating patients with impaired cardiac function or hypertension.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.