This is an automatically translated article.
Tuberculosis of the skin is a chronic infection caused by the bacterium Mycrobacterium Tuberculosis, M. ovis and also by the bacillus Calmette-Guerin. The clinical manifestations of cutaneous TB can vary depending on the host's immunity and the site of infection.
1. Get an overview of skin tuberculosis
Tuberculosis of the skin (TB) is actually an invasion through the skin caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium Tuberculosis – the same strain of bacteria that causes pulmonary tuberculosis.
Tuberculosis was a major public health problem in the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. However, with the improvement of hygiene habits in the general population, the improvement of quality of life as well as the introduction of the BCG vaccine in the prevention of TB in general, the incidence of skin tuberculosis has decreased significantly. .
However, recently, with the increasing proportion of HIV-infected patients, multidrug-resistant strains of skin TB have emerged, causing skin TB to return and the number of patients on immunosuppressive therapy is increasing. increase.
Bệnh lao da gây ra bởi tác nhân là vi khuẩn Mycobacterium Tuberculosis – cùng chủng vi khuẩn gây ra bệnh lao phổi.
2. Classification of skin tuberculosis
Clinical manifestations of skin tuberculosis are quite diverse: nodules, inflammatory papules, chronic skin ulcers... and other lesions. Variants of skin tuberculosis can also be classified according to the number of bacteria on the patient's skin.
In general, the types of skin tuberculosis can be classified according to the following table:
Of the above types, Lupus vulgaris is the most common type of skin TB, usually occurs in adolescents and has the following forms:
Lupus tuberculoma : the islets will be raised above the surface of the skin and have small size (from 1mm - 3mm). When pressed, it will appear yellow. Psoriatic lupus : on the face the lesions appear thick scabs. Lupus tuberculous ulcer: on the skin appear many superficial ulcers, with seeds and pus inside. Tuberculous lupus : rough, grain-like lesions.
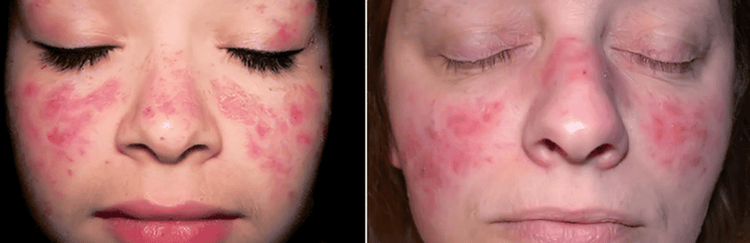
Lupus Vulgaris là loại lao da thường gặp nhất
3. Is skin tuberculosis contagious?
Normally, skin tuberculosis is usually a form of development from bacilli that are transported from internal organs to the skin, very rarely penetrate directly from the outside. In other words, skin tuberculosis is a variant from many other forms of tuberculosis such as pulmonary tuberculosis, lymph node tuberculosis... Primary cutaneous tuberculosis is very rare.
Some routes of transmission of TB bacteria to the skin are as follows:
Blood: some blood vessels from the TB reservoir can be destroyed and cause TB bacteria to directly infect the blood, from there moving to the whole body. other organs and to the skin. This route of infection often causes lupus tuberculosis, lymphadenopathy, necrotizing papilloma, ... Lymphatic route: bacilli will creep along the intercellular spaces and lymphatic vessels to the skin lesions, often causing lymph node tuberculosis.
Bệnh lao da có lây qua đường máu
4. How to prevent skin tuberculosis?
So far, vaccination with BCG is the best method to prevent tuberculosis in general and tuberculosis in particular.
BCG (Bacille Calmette-Guerin is a TB vaccine, often recommended for infants and young children, especially effective in preventing many forms of dangerous TB. If you have never been vaccinated against TB before, you should also be vaccinated
Currently, Vinmec International Hospital is providing BCG vaccination service that is appropriate for each age to be vaccinated and ensures safety from the outset. In addition, depending on different subjects, the hospital also provides a Package Immunization Program with diverse vaccines for infants, children, people Adults, pre-pregnancy women and pregnant women...
If you have a need for consultation and examination at Hospitals under the national health system, please book an appointment on the website to receive medical treatment. service.
Reference article source: NCBI
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.