This is an automatically translated article.
Ovarian mucinous cyst tumors represent a wide range of neoplastic disorders, including benign mucinous cysts, pseudotumor peritoneal neoplasms, mucinous tumors of low malignant potential, and ovarian carcinomas. invade. These tumors are closely related, differing only histologically. The early detection and active intervention from the beginning of any case of ovarian mucinous cyst will have significant prognostic implications for a woman's life.
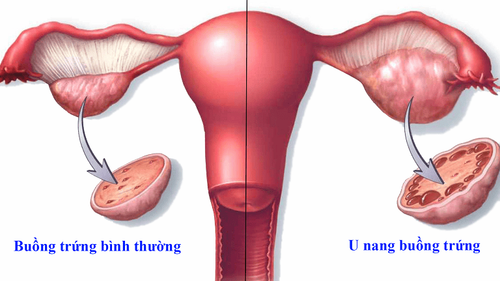
1. What is an ovarian mucinous cyst?
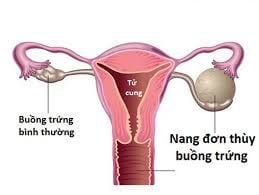
Ovarian mucinous cyst is a large, multi-nodular tumor with mucus-filled fluid inside the cyst that occurs on one or both sides of a woman's ovaries. This is the primary manifestation of most cases of epithelial ovarian cancer. In the remainder, among benign ovarian tumours, mucinous ovarian cysts account for only about 10-15% of the total cases.Accordingly, when a woman is found to have a tumor at the ovary site of mucinous nature, usually identified by imaging means, further clinical decision-making needs to be made. much caution. Because mucinous tumors have a high incidence representing a wide range of histological malignancies and the risk of invasion is high if there is no aggressive treatment plan in the first place. In this context, the pathological criteria are still considered the main criteria in making the correct diagnosis.
2. What are the symptoms of ovarian mucinous cyst?
Ovarian mucinous cysts occur most commonly in women between the ages of 20 and 40. However, there are many cases acquired during puberty as well as in post-menopausal patients.
Patients may be completely asymptomatic, not realizing the presence of ovarian mucinous cyst until they go to the doctor because of the uncomfortable signs it causes. At this time, the average size of cases when detecting ovarian mucinous cyst is 18cm; Therefore, this is classified as a large organic ovarian cyst. Occasionally, ovarian mucinous cysts can become extremely large and fill the entire lower abdominal cavity causing patients to seek medical attention because of the following symptoms:
Lower abdominal pain, described as a bout of pain. dull, persistent pain. Abdominal bloating or pelvic fullness Nausea, vomiting, Poor appetite, Poor bowel habits, Painful intercourse, Vaginal bleeding after intercourse, Abnormal vaginal bleeding, Menstrual disorders Dysmenorrhea, Infertility

U nang nhầy buồng trứng có thể không gây ra triệu chứng gì cho người bệnh
At the same time, the size of mucinous ovarian cysts can sometimes be of value for histology, determining their primary or metastatic nature. In particular, primary ovarian mucinous cysts are usually larger in size and located in a single ovary compared with metastatic lesions that are smaller and bilateral. Accordingly, the mean size of primary ovarian mucinous cysts has been reported to be about 16–20 cm (range 5–48 cm) compared with an average of 11–12 cm (range 5–48 cm). micro 2–24cm) for metastatic ovarian cancer. However, size is not recognized as a determining factor in the prognosis of the disease because more than 40% of metastatic tumors are still larger than 10 cm in size.
3. How to diagnose ovarian mucinous cyst?
As with all types of ovarian cysts in general, the clinical symptoms of mucinous ovarian cysts are not definitively suggestive of this lesion. However, when the above signs appear, when going to a gynecology specialist, a woman will be examined and evaluated comprehensively, both to detect ovarian mucinous cysts or other types of ovarian cysts in general. as well as exclude other similar gynecological diseases.
Accordingly, the doctor needs to have examinations and appoint specialized tests to diagnose ovarian mucinous cysts as follows:
Abdominal examination: One side of the pelvic fossa is palpable, painful or tight. Because most cases of ovarian mucinous cysts are large in size. In contrast, if ovarian mucinous cyst necrosis, hemorrhage or rupture event, this is an acute surgical abdomen, the patient has signs of resistance to the abdominal wall.
Vaginal or anorectal examination of the appendix for non-sexual women: Because of the large size of the cyst, the lesion may be palpable by hand on examination. Ovarian mucinous cyst is a form of organic ovarian cyst, palpable density is relatively dense, firm, distinguishing from functional ovarian cyst, the inside usually contains fluid, so the density is softer.
Test blood or urine HCG levels to rule out pregnancy.
Measurement of Tumor Markers: Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) is the most useful serum tumor marker to identify malignant ovarian mucinous cysts preoperatively and to monitor patient progress postoperatively. .
Transvaginal or abdominal adnexal ultrasound for women who have not had sex: This method uses ultrasound waves to reconstruct the image, assess the location, size and density of the tumor ovarian cysts. The characteristics that help towards ovarian mucinous cysts are usually dense, homogeneous; There may be invasion, adhesions, and metastasis of adjacent anatomical structures. At the same time, ultrasound also helps to confirm signs of abdominal cavity syndrome such as ureteral obstruction, hydronephrosis.
Computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): These are more advanced imaging tools than ultrasound, with higher sensitivity and specificity in the ability to confirm the nature of mucinous cysts The ovaries are benign or malignant when combined with contrast agents, contrast agents. In addition to the role of diagnosing lesions in the ovaries, this tool also allows finding the source of primary ovarian cancer, if any.
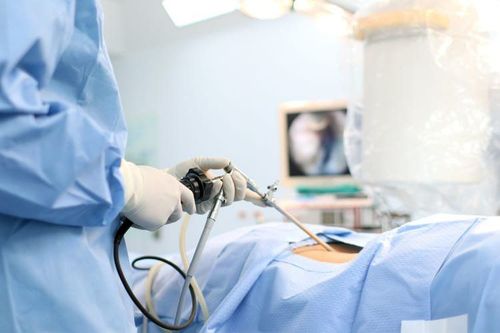
Exploratory laparoscopy combined with therapeutic endoscopy: This is an interventional method. By inserting a small laparoscope through the abdominal wall or through the vagina, surgeons can access the tumor and take a local biopsy. Histological evidence is the definitive criterion for the diagnosis of mucinous ovarian cyst as well as the assessment of possible malignancy. At this time, the surgeon can also actively dissect the tumor via laparoscopic route or convert to open surgery if the size of the ovarian mucinous cyst is too large.

Chụp CT/MRI là một trong những phương pháp chẩn đoán u nang nhầy buồng trứng hiện đại và chính xác
4. Treatment options for mucinous ovarian cysts
The recommendation for surgery is always made in most cases of malignant mucinous ovarian cysts. At this time, the gold standard for treatment including intact adnexal resection has been associated with intraoperative pathological assessment. Accordingly, when the ovarian mucinous cyst is large, laparotomy will be performed to remove the entire uterus, remove the bilateral fallopian tubes and remove regional lymph nodes.
In case the patient still wishes to become pregnant at the same time with the result that the ovarian mucinous cyst is benign, the reproductive system will still be preserved. At the same time, the dissection of the tumor should be performed with utmost caution, in order to maintain the integrity of the ovaries and fallopian tubes, and limit the healing of the adhesions later.
In contrast, if the disease occurs in a postmenopausal patient, total hysterectomy and bilateral oophorectomy may be considered regardless of the histological findings of mucinous ovarian cysts.
In any case, when the surgeon enters the abdomen, care should be taken to remove the involved ovary intact without spilling the mucus. The reason is that when the mucus is broken during surgery of the ovarian mucinous cyst into the abdomen, it can increase the likelihood of recurrence as well as the risk of malignant transformation later.
Besides, before the end of surgery, the entire abdomen and pelvis should also be carefully explored and noted abnormal areas. If the tumor is a secondary metastasis, surgery at the primary site can also be combined with a single-stage surgery.
In summary, mucinous ovarian cysts may have distinct histological features but the rate of malignancy is relatively high compared with other ovarian cysts. These differences guide the treatment of specific women, but radical surgery and total adnexa are always strongly recommended from the start to provide a better prognosis.
Vinmec International General Hospital applies laparoscopic surgery technology using robots capable of overcoming some difficulties in conventional surgery, such as giving clear 3D camera images instead of 2D images, arms Quick and flexible surgery helps to cut and burn quickly and accurately, wide viewing angle overcomes vision difficulties in some areas of the body that are difficult for doctors to see.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.