This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Internal Medicine Oncologist - Internal Oncology Department - Vinmec Times City International Hospital.It is a phenomenon in which cancer cells break away from the primary tumor (where they formed), travel through the blood and lymphatic system to other parts of the body, forming new tumors. similar in nature to the primary tumor.
1. Is metastatic cancer serious?
The main reason cancer is a serious disease is because of its ability to spread in the body. Cancer cells can invade surrounding areas by moving into nearby normal tissues. Cancer can also travel regionally, to nearby lymph nodes, tissues, or organs. This phenomenon occurs, it is called metastatic cancer. At that time the cancer was in stage VI. The process by which cancer cells from one part of the body spread to other parts of the body is called metastasis.When viewed under a microscope and tested in other ways, metastatic cancer cells have the same characteristics as the primary cancer and are unlike the cells where the lesion was found. This is the basis for doctors to think it is cancer that has spread to another part of the body.
Metastatic cancer has the same name as the primary cancer. For example, breast cancer that has spread to the lungs is called metastatic breast cancer, not lung cancer. It is treated like stage IV breast cancer, not lung cancer.
Sometimes doctors can't tell where metastatic cancer begins. This type of cancer is called cancer of unknown origin, or CUP.
When a new primary cancer occurs in a person with a history of cancer, it is called a second primary cancer. Second primary cancers are rare. In most cases, when a person with cancer develops new lesions, it means that the first primary cancer has metastasized.
2. How does cancer metastasize?
During metastasis, cancer cells spread from where they first formed to other parts of the body.Cancer cells spread through the body in steps. These steps include:
Grow, or invade, nearby normal tissue. Move through the barriers of nearby lymph nodes or blood vessels. Moves through the lymphatic system and blood to other parts of the body. Stops in small blood vessels in a different location, invades blood vessel walls and migrates into surrounding tissues. Grows in this tissue and forms another tumor. Growing new blood vessels, creating a blood supply, allows the tumor to continue to grow. Most of the time, cancer cells that have spread die at some point during metastasis. But, the decline is favorable for cancer cells to form new tumors in other parts of the body. Metastatic cancer cells can also become dormant at some point, and when conditions are favorable they will become active again.
Trắc nghiệm: Thử hiểu biết của bạn về bệnh ung thư
Ung thư là nguyên nhân gây tử vong hàng thứ 2 trên thế giới. Thử sức cùng bài trắc nghiệm sau đây sẽ giúp bạn có thêm kiến thức về yếu tố nguy cơ cũng như cách phòng ngừa bệnh ung thư.
Bài dịch từ: webmd.com
3. Where does the cancer metastasize?
Cancer can spread to almost any part of the body, although different types of cancer are more likely to spread to certain organs. The most common organs where cancer spreads are the bones, liver, and lungs. Some common cancers metastasize to common sites:Bladder cancer: Metastatic parts include bones, liver, lungs. Breast cancer: The metastases are usually bones, brain, liver, lungs. Colon cancer: The metastases are usually liver, lung, peritoneum. Kidney cancer: The metastases are usually the adrenal glands, bones, brain, liver, and lungs. Lung cancer: The metastases are usually the adrenal glands, bones, brain, liver, and lungs. Pancreatic cancer: Metastases are usually liver, lung, and peritoneum. Prostate cancer: The metastases are usually the adrenal glands, bones, liver, and lungs. Rectal cancer: Metastases are usually liver, lung, and peritoneum. Thyroid cancer: Metastases are usually bones, liver, lungs. Uterine cancer: The metastases are usually bone, liver, lung, peritoneum, vagina.
4. Symptoms of metastatic cancer
Metastatic cancer does not always cause symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they will depend on the size and location of the metastatic tumors. Some common signs of metastatic cancer include:Pain and fractures, when the cancer has spread to the bones. Headache, convulsions or dizziness, when the cancer has spread to the brain. Shortness of breath, when the cancer has spread to the lungs. Jaundice or swelling in the abdomen, when cancer has spread to the liver.
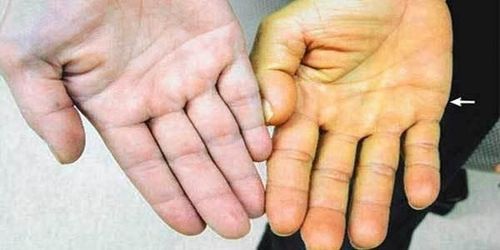
5. Treatment of metastatic cancer
When cancer metastasizes, it can be difficult to control. Although some types of metastatic cancer can be cured with modern treatments, most are difficult to cure.The goal of treatments for metastatic cancer is to stop or slow the growth of the cancer or relieve the symptoms it causes. In some cases, treatment for metastatic cancer can help prolong life.
Treatments for metastatic cancer depend on the type of primary cancer, the site of metastasis, previous treatments, and general health.
If you are told you have metastatic cancer, you and your loved one can discuss palliative care. Even if you choose to continue treatment to try to limit your cancer or control its growth, you can always get care to manage your symptoms and treatment side effects.
Researchers are studying new ways to kill or stop the growth of primary and metastatic cancer cells. This research includes finding ways to help your immune system fight cancer. Researchers are also trying to find a way to disrupt the steps in the process that allow cancer cells to spread.
Early cancer screening is considered a perfect measure in the timely detection and treatment of all types of cancer. Vinmec International General Hospital currently has a high-tech cancer screening and examination package, including genetic testing, imaging, and biomarkers for early tumor detection. A single gene test can assess the risk of 16 common cancers in both men and women (lung cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, cervical cancer) Bowel cancer , stomach cancer , prostate cancer ,....)
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: cancer.gov