This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thanh Hung - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Meningococcal disease is not uncommon, but not many people know about it. So what is meningococcal meningitis? What are the symptoms of the disease, is there any way to prevent the disease?
1. What is meningococcal disease?
Meningococcal disease is an acute respiratory infection caused by the bacteria Neisseria meningitidis. The disease recurs during the year, but can become epidemic in the fall, winter and spring. According to the data of the Central Institute of Hygiene and Epidemiology, the incidence is: 2.3/100,000 population.Meningococcal group is divided into 4 main groups: A, B, C, and D. In which, meningococcal group A is the most common in our country. In addition, pathogenic serogroups of meningococcal bacteria such as W-135, X, Y and Z have been added. These serogroup bacteria may be less virulent but still cause disease. heavy.
Meningococcal disease is completely treatable. If detected in time, treated actively, with the right regimen, the cure rate will reach 85-95%.
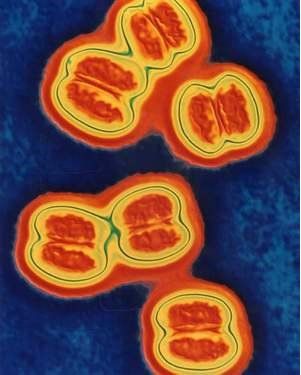
2. What are the symptoms of meningococcal disease?
Meningococcal disease is an acute infectious disease, so the symptoms of the disease appear suddenly, including:
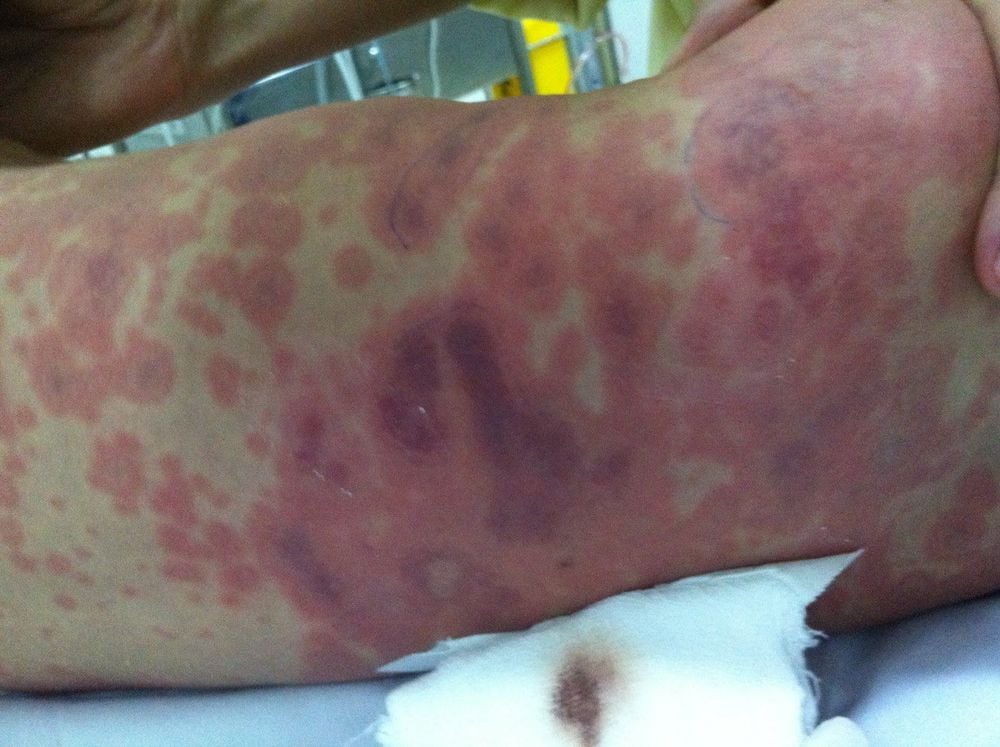
Sudden high fever. Severe headache. Nausea, vomiting. Stiff neck. May be drowsy or comatose. Typical appearance of a maculopapular rash: Occurs 1-2 days after fever, initially as a dot, then spreading rapidly as a map or as a blister, 1-2mm to a few centimeters in size. The rash is dark red or purple, irregular margins, flat surface sometimes with necrosis in the center, often occurs in the hip and lower extremities. In areas where the disease is endemic, the number of people infected with meningococcal disease without clinical symptoms accounts for 5-10%, which is a very important source of transmission in the community.
>>> Meningococcal disease: Infectious disease threatens healthy children's lives in just 24 hours
3. How to prevent meningococcal disease?
According to the guidance of the Department of Preventive Medicine - Ministry of Health, to prevent meningococcal disease in adults and children, it is necessary to:Propaganda and raise awareness, especially in localities where the disease is endemic, to people understand and detect disease early, isolate patients and cooperate with medical staff to prevent epidemics. Keeping the place of residence clean, keeping the environment clean; Kindergartens and classrooms must be ventilated, clean and well-lit. The old outbreak site must be monitored and immediately detected cases of fever and pharyngitis for monitoring. It is possible to test former patients and neighbors if possible, to find healthy people carrying meningococcal bacteria. The patient needs to be treated thoroughly in a medical facility. Persons in contact with the patient should receive preventive treatment. Meningococcal group A is common in Vietnam, but there is no vaccine, so strict epidemiological surveillance should be applied. If there are signs of meningococcal disease, it is necessary to immediately bring the patient to reputable medical facilities for timely examination and treatment.
Meningococcal disease is a dangerous disease that has the potential to become an epidemic because it is transmitted through the respiratory tract. Therefore, health experts often recommend vaccination, especially meningococcal type B and C vaccines for children 6 months and older and adults under 45 years old, or vaccines against meningococcal meningitis. meningococcal 4 types A, C, Y, W-135 onset 9 months or older and adults younger than 55 years of age.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference sources: Department of Preventive Medicine, Ministry of Health.