Chronic sinusitis or bleeding during minor surgery is often prescribed with lysozyme chloride. What is lysozyme chloride, and how should it be used to achieve the best effectiveness for patients?
1. What is Lysozyme Chloride?
Group of drugs: Pain relievers, antipyretics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, treatments for gout, and bone and joint diseases.
- Generic name: Lysozyme chloride
- Brand name: Lysozyme
- Dosage form: Tablets containing 90 mg of active ingredient.
- Packaging: Boxed with 10 blisters, each containing 10 tablets.
2. Uses of Lysozyme Chloride
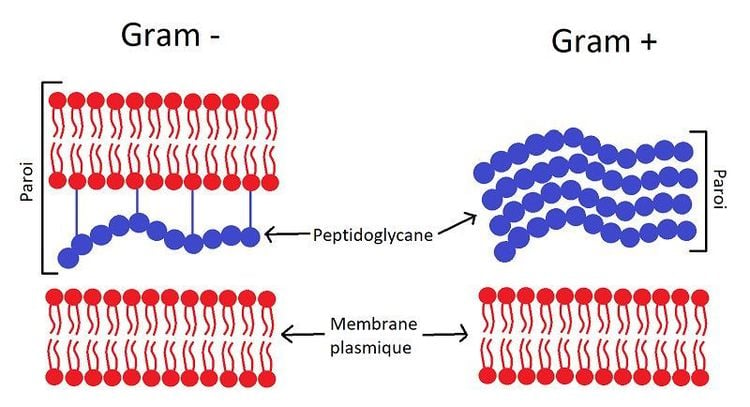
Lysozyme chloride contains lysozyme, which has antibacterial effects, specifically targeting Gram-positive bacteria. It supports the immune system and has an anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting histamine.
Lysozyme chloride is commonly prescribed to treat the following conditions:
- Chronic sinusitis
- Bleeding during minor surgery
- Phlegm production
- Shortness of breath
Lysozyme chloride is also prescribed in combination with HIV treatment medications to help reduce other help reduce HIV virus levels and boost the immune system.
3. Dosage and administration of lysozyme chloride
Patients should take lysozyme chloride with a full glass of water and swallow the tablet whole. Crushing, breaking, or chewing the tablet is discouraged, as it can increase absorption and cause harm to internal organs.
The usual adult dosage is 90 mg per dose, taken 2–3 times daily, depending on a doctor's recommendation. Dosage may vary based on symptoms, age, and overall health. Noteably, lysozyme chloride is not recommended for children unless prescribed by a doctor.
In case of overdose, consult a doctor to manage potential risks. If you forget a dose, take it as soon as possible. If it’s almost time for the next dose, skip the missed dose and continue with the regular schedule to avoid doubling up.
Long-term use of lysozyme chloride may lead to bacterial resistance. Therefore, follow the doctor’s treatment plan, and do not stop or prolong usage without consulting a doctor. If side effects worsen, discontinue use.

4. Interactions of lysozyme chloride with other drugs
Lysozyme chloride may alter the effectiveness of other drugs or increase side effects. Inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including prescriptions, over-the-counter drugs, traditional medicines, herbal products, or supplements. There is currently no research showing drug interactions with lysozyme chloride. However, in cases of interactions, your doctor will ask you some questions such as:
- Discontinue one of the interacting drugs.
- Substitute one drug with another of similar effects.
- Adjust the dosage or frequency of administration.
5. Precautions when using lysozyme chloride
Before using lysozyme chloride, you should inform your doctor about your health problems:
- Avoid use if allergic to any ingredient in the medication.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their doctor before use.
- Use with caution in elderly patients and children.
- Women planning to become pregnant should seek medical advice, as lysozyme chloride may cause birth defects.
In addition, individuals who use chloride lysozymes should note the following issues:
- Avoid alcohol and tobacco while taking the medication, as these may cause interactions.
- Inform your doctor about your health condition before using the drug because it will affect the effectiveness of the drug.
- Store the medicine in a cool place, away from direct sunlight, especially out of reach of children and pets.
- Dispose of unused medication and its container appropriately as directed.
- Do not store medication in the freezer or bathroom.
6. Side effects of lysozyme chloride
Common side effects of lysozyme chloride include skin rash, diarrhea, loss of appetite, stomach discomfort, nausea, belching,...
These are not all the side effects that lysozyme chloride can cause. Upon discontinuing the medication and over time, these side effects will subside.
If users notice symptoms persist, they should go to the nearest medical facility or hospital for examination to avoid further complications.










