This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Ms. Ly Thi Thanh Ha - Medical Genetics Block - Vinmec High-Tech Center
Genetic disease is the result of genetic or chromosomal abnormalities, these abnormalities are passed from the previous generation (grandparents, parents) to the next generation (children, grandchildren).
1. Situations where genetic testing is required
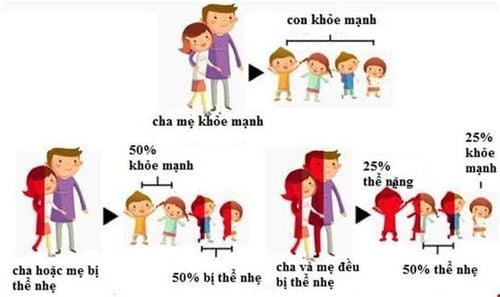
Families with a history of genetic diseases, especially families with people presenting the same clinical pathology across generations. In Vietnam, the common genetic diseases are hematologic diseases: Thalassemia hemolytic anemia, hemophilia,... Muscle diseases: Duchenne myasthenia gravis (DMD), muscular atrophy Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA), metabolic disease: Wilson, Citrin deficiency, ...
Pregnant women with multiple miscarriages may be related to genetic or chromosomal abnormalities. The primary cause of recurrent miscarriage is hormone abnormalities, followed by genetic or chromosomal abnormalities, and finally, uterine anatomy or unexplained abnormalities. .
Couples intending to get married who have a family history of potentially at-risk genetic diseases.
In addition, depending on the purpose of testing, genetic testing can be specified in many different application cases...
Bệnh thiếu máu huyết tán Thalassemia có tính chất di truyền
2. Meaning of Types of Genetic Testing
Types of genetic testing that are meaningful:
Contribute to finding the cause of the disease, combined with appropriate treatment to support the patient. The degree of disease expression of a person may be due to a combination of interactions between genetic factors (genes) and the environment, interactions between genes. Finding genetic abnormalities, combined with other factors, will contribute to improving the effectiveness of treatment for patients. Prenatal diagnosis: The birth of a baby with a genetic or chromosomal abnormality will be a psychological and economic burden for the family itself, and for society. Therefore, prenatal diagnosis is extremely important to identify abnormal risks in the fetus, provide treatment options (if any) and treatment plans. Perform preimplantation embryo screening when necessary: Preimplantation embryo screening has great significance, especially for infertile families. Embryo transfer failure is caused by the embryo carrying a large number of abnormalities in chromosome number or structure. Therefore, screening before embryo transfer will help find embryos that do not carry abnormalities, contributing to improving the pregnancy rate for mothers.
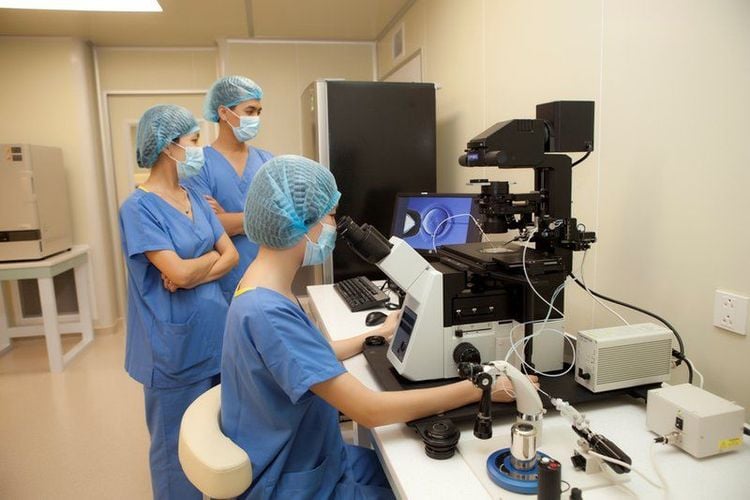
Sàng lọc phôi tiền làm tổ trước khi chuyển phôi
Determination of bloodline: DNA testing plays a decisive role in determining blood relations, especially in identifying martyrs' relatives. Determining the risk of certain cancers and some chronic diseases: Differences in biological (gene) information between individuals place individuals at varying degrees of risk for cancers and Chronic diseases. If each person knows their own risk, they will have a sense of proactive prevention to maintain health and reduce the possibility of disease. Personalize the use of drugs and appropriate dosages for each specific object: In the past, when it was not possible to explain why when using drugs, some people were "suitable" for using this drug, others were "suitable" for using this drug. other drugs to treat the same disease that people say is due to "location". Up to now, this is completely explainable based on the difference in each person's genome. It is this difference that does not cause disease, but makes a difference between the treatment of each individual in terms of drugs and doses used.
Recommended video:
Vietnamese Genome: Many big surprises
MORE:
Prenatal genetic testing chart Gene screening for pregnant women over the age of 35: What you need to know Genetic screening before embryo transfer? Why does it need to be done?