This is an automatically translated article.
Each of these chronic lymphocytic leukemia groups is further subdivided into several subtypes, which differ at the genetic level. This means that the disease manifests itself differently depending on the different genotypes. Two people with chronic B-cell lymphoma may still have different clinical presentations.1. Things to know about lymphocytes in the body
Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell that plays a major role in the body's immune system. Lymphocytes are classified into 3 main groups:
T lymphocytes: have the ability to call on other cells of the immune system to fight infections and break down damaged cells. B lymphocytes: responsible for the production of antibodies. Natural killer (NK) cells: responsible for destroying microorganisms and malignant cells. Lymphocytes in the blood circulate throughout the body and are produced in many different organs in the body such as:
Lymph nodes: are small, bean-shaped organs that exist everywhere in the body. against inflammatory conditions. Spleen: plays a role in filtering the blood, is the place to store old red blood cells and store blood in the body. Thymus: located behind the breastbone, in the ribcage, and gradually recedes with age. The thymus is the site of transformation of immature T-lymphocytes into their mature and immune-functioning form. Bone marrow: mainly the red marrow of large bones and flat bones where lymphocytes are produced.
Tế bào lympho được sản xuất ở tủy xương
2. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Overview
Leukemia is the name given to a group of malignancies of the hematopoietic system. Leukemia occurs when healthy blood cells change and multiply rapidly out of control. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia or chronic lymphocytic leukemia is a malignancy involving lymphocytes.
In people with chronic lymphocytic leukemia, the disease progression is slow, taking many years before clinical symptoms appear to require treatment. In fact, there are patients who do not need any treatment for their disease. However, the disease can still progress severely at a faster rate and requires early treatment in some cases.
In people with chronic lymphocytic leukemia, the proliferation of abnormal cells interferes with the regeneration of other cells in the bone marrow. An abnormally high density of lymphocytes interferes with the production of other healthy cells, including:
Red blood cells that carry oxygen around the body Other types of white blood cells such as neutrophils or granulocytes It is part of the body's immune system. Platelets, an important component in hemostasis.
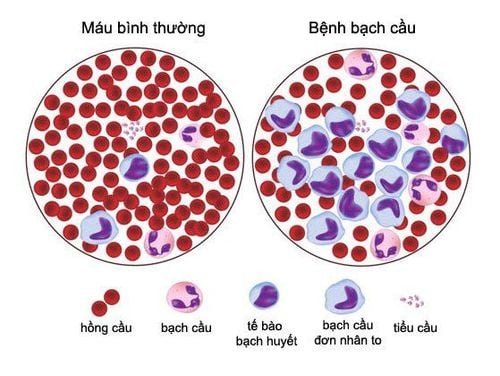
Tế bào máu khi mắc bệnh bạch cầu mãn tính dòng lympho
Usually, chronic lymphocytic leukemia is diagnosed when there are too many abnormal lymphocytes in the blood, called lymphocytosis.
3. Classification
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is divided into two main types, depending on whether the affected cells are B lymphocytes or T lymphocytes. a case of illness.Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B: accounts for more than 95% of cases of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. 1% of this group belongs to the group of B-cell proliferative leukemia. Chronic T-lymphocyte leukemia: also known as T-cell pre-proliferative leukemia. This group makes up a small percentage of the total cases. cases, not common in clinical practice.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Articles refer to the source: cancer.netSEE MORE:
Mechanisms of the body's defenses of white blood cells Risk factors for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) Common types of leukemia