This is an automatically translated article.
Buckwheat is increasingly known as a very healthy food due to its high mineral and antioxidant content. Incorporating buckwheat into your daily diet can help balance blood sugar levels, supporting weight loss.
1. What is buckwheat?
Buckwheat belongs to the food group known as Pseudocereals (pseudocereals), along with other popular pseudocereals such as quinoa, Amaranth seeds. Despite its name, buckwheat is unrelated to wheat and is gluten-free.
Buckwheat is usually processed into broken pieces, buckwheat flour, tea and buckwheat noodles. Buckwheat is used like rice, porridge and is the main ingredient in many traditional Eurasian dishes.
Currently there are 2 types of buckwheat: Common buckwheat and Tartary buckwheat, most commonly grown for food. Buckwheat is mainly harvested in the Northern Hemisphere, especially in Russia, Kazakhstan, China and Central and Eastern Europe.
2. Nutritional value of buckwheat
The nutritional value of buckwheat is far superior to that of many other grains. The main component of buckwheat is Carbs, followed by Protein, minerals and antioxidants. Estimated nutritional value for 100 grams of raw buckwheat is:
Calories: 343 grams. Water: 10% Protein: 13.3 grams. Carbs: 71.5 grams. Fiber: 10 grams. Fat: 3.4 grams.

Thành phần chính của kiều mạch là Carbs
2.1. Carbs
Carbs make up 20% of the weight of buckwheat flour. They are in the form of starch, which is the main storage form of carbs in plants. On the glycemic index (GI) scale (which measures how quickly certain foods raise blood sugar levels after meals), buckwheat scores low to moderate, demonstrating no sudden spike in blood sugar. . Certain soluble carbs in buckwheat, such as fagopyritol and D-chiro-inositol, have been shown to help balance blood sugar levels after meals.
2.2. Fiber
Buckwheat contains an abundant amount of fiber which is good for the digestive system. The fiber content accounts for about 2.7% of the boiled broken weight, mainly consisting of cellulose and lignin concentrated in the outer shell (husk) which is dark in color.
Rice husks also contain resistant starch that is resistant to digestion in the small intestine and is only fermented by bacteria in the colon. These beneficial bacteria produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like Butyrate, which play a nutritional role in the cells lining your colon, thereby improving gut health and reducing the risk of colon cancer. .
MORE: Types of fiber and their health benefits
2.3. The protein
Protein makes up about 3.4% by weight of boiled buckwheat groats. Due to the balanced amino acid composition, the protein in buckwheat is very good, especially the amino acids Lysine and Arginine. However, the digestibility of these proteins is relatively low because of antinutrients such as protease inhibitors and tannins. In animals, buckwheat protein has been shown to be effective in lowering blood cholesterol, preventing gallstone formation, and reducing the risk of colon cancer. Like other pseudocereals, buckwheat is gluten-free, making it suitable for people with gluten intolerance as well.
2.4. Vitamins and minerals
Compared to common grains like rice, wheat and corn, buckwheat is richer in minerals. However, buckwheat does not contain many vitamins.
Of the two main types, tartary buckwheat generally contains more nutrients than regular buckwheat. The most abundant minerals found in buckwheat are:
Manganese: Found in large amounts in whole grains, manganese is essential for healthy metabolism, growth, development and antioxidant capacity. of body. Copper is an essential trace element beneficial for heart health but often lacking in Western diets. Magnesium. When the diet provides adequate amounts of magnesium, this essential mineral can reduce the risk of various chronic diseases, such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Iron: Without getting enough of this mineral the body can develop iron deficiency anemia, which occurs due to a decreased ability to carry oxygen in the blood. Phosphorus plays an essential role in the growth and maintenance of body tissues. Compared with other grains, the minerals in cooked buckwheat flour are better absorbed. That's because buckwheat is relatively low in phytic acid, a mineral that is common in grains and seeds.
2.5. Other plant compounds
Compared to barley, oats, wheat and rye, buckwheat provides far more antioxidants, bringing certain health benefits. Here are some types of plant compounds found in buckwheat:
Rutin: The main polyphenol antioxidant found in buckwheat is Rutin, which reduces cancer risk and improves inflammation, blood pressure, and lipid levels. in blood. Quercetin: Commonly found in many plant foods, Quercetin is an antioxidant that has many beneficial health effects, including reducing the risk of cancer and heart disease. Vitexin : Animal studies have shown that vitexin offers certain health benefits. However, eating too much can contribute to an enlarged thyroid. D-chiro-inositol: This is a unique soluble carb that lowers blood sugar and is effective in managing diabetes. Buckwheat is the richest food source of this carb.
3. Health Benefits of Buckwheat
With its superior nutritional content, buckwheat offers a number of health benefits such as:
3.1. Control blood sugar
To maintain good health and reduce the risk of diabetes, it is extremely important to control post-meal sugar spikes.
As a good source of fiber, buckwheat has a low to moderate GI, which means it is a safe food for most people with type 2 diabetes. There are even some animal studies. It has also been shown that buckwheat helps reduce blood sugar levels by 12-19%.
This effect is thought to be due to the soluble carb D-chiro-inositol found in buckwheat which makes cells more sensitive to insulin (the hormone that causes cells to absorb sugar from the blood). In addition, certain components of buckwheat seem to prevent or delay the digestion of table sugar. Overall, these properties make buckwheat a very healthy choice for people with type 2 diabetes or those who are looking to balance blood sugar levels.
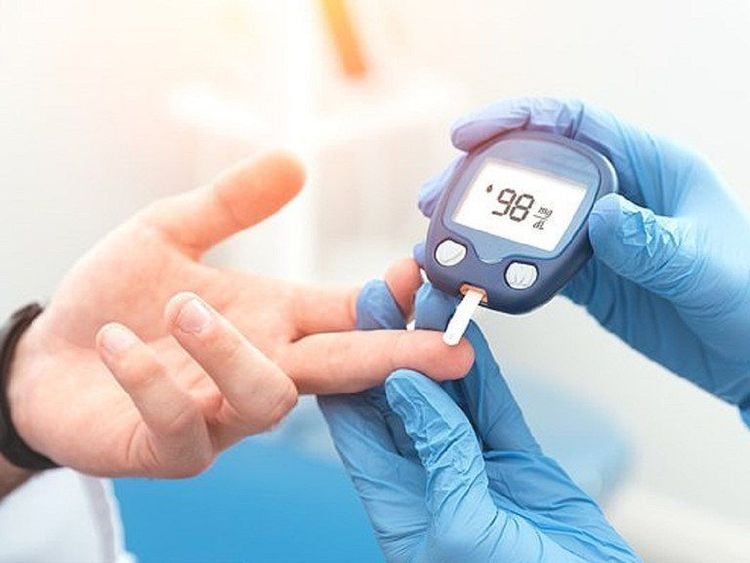
Kiều mạch giúp kiểm soát đường huyết
3.2. Good for heart health
Buckwheat contains many heart-healthy compounds such as rutin, magnesium, copper, fiber and certain types of protein, which in turn promote heart health.
Among cereals and pseudocereals, buckwheat is the richest source of rutin. Rutin may reduce the risk of heart disease by preventing the formation of blood clots, reducing inflammation and blood pressure.
A study of 850 adults in China linked eating buckwheat with lower blood pressure and improvements in blood lipids, including lowering LDL (bad) cholesterol and increasing HDL (good) cholesterol levels.
In general, buckwheat is a pseudocereal that does not grow on grass but is used in a similar way to other cereals. Buckwheat is gluten-free, is a rich source of fiber and minerals, and is rich in various plant compounds, especially rutin. As a result, consuming buckwheat products (buckwheat flour, buckwheat noodles, buckwheat tea...) will provide a number of health benefits, including aiding in glycemic index control and weight gain. increase heart health.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: healthline.com













