This is an automatically translated article.
Article by Doctor Nguyen Cong Hoa - Department of Intensive Care - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
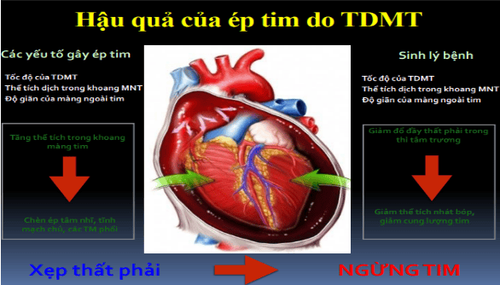
Cardiac tamponade is a clinical syndrome caused by a rapid increase in fluid volume in the pericardial cavity. This is a medical emergency.
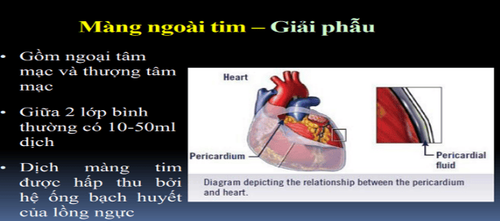
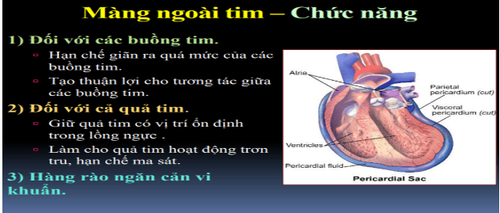
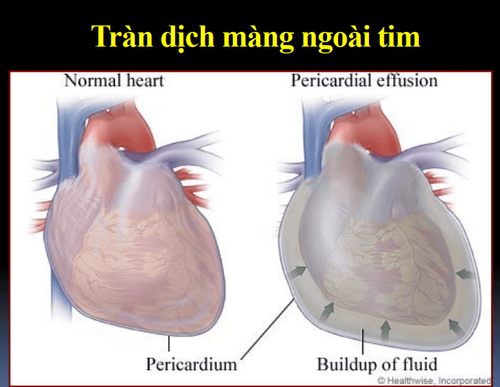
1. When is it called pericardial effusion?
Causes of pericardial effusion causing acute tamponade include:
Cancerous diseases, malignancies. HIV infection Infection - Bacterial virus (TB), fungus Drugs - Hydralazine, Procainamide, isoniazid, minoxidil Postoperative intervention (ie, coronary artery dissection and pericardial perforation.

Cardiovascular surgery (postoperative pericarditis) Post-myocardial infarction (free ventricular rupture, Dressler syndrome) Connective tissue disease - Systemic lupus erythematosus , rheumatoid arthritis , dermatomyositis Treatment After breastbone biopsy, temporary heart rate implant, pericardial implant, or central line insertion Idiopathic pericarditis Complications of surgery at the esophageal junction such as antireflux Surgery Due to mechanical openings or holes gastrointestinal fistula)
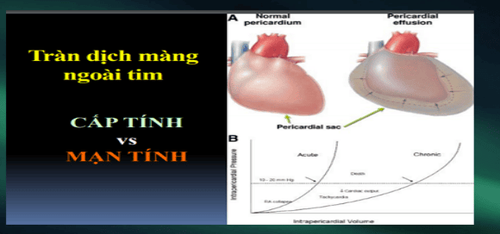
2. What is acute and chronic pericardial effusion?
Normally contains 10-20cc of fluid. Cardiac tamponade begins to appear when the fluid increases 150ml If the fluid increases, the pericardium can dilate up to 2 liters reported in chronic disease.
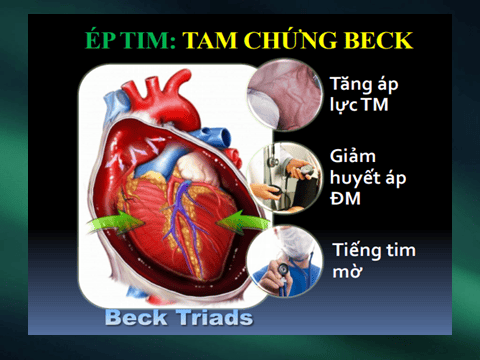
3. Symptoms
Shortness of breath, tachycardia, rapid breathing. Hunger, loss of appetite, fatigue, difficulty swallowing Cold chi. Malignancy - weight loss, fatigue, anorexia Chest pain - pericarditis, after myocardial infarction. Joint pain - connective tissue. Renal failure - blood urea increased. Drugs - drug-related lupus. Recent procedure - pacemaker, central line. Tuberculosis - night sweats, fever. Irradiation - history of cancer.

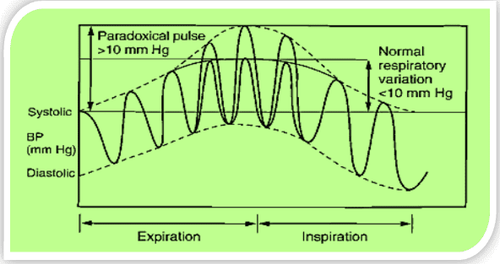

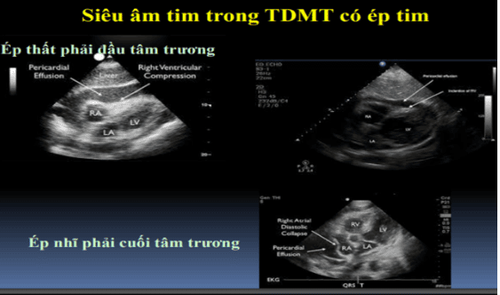
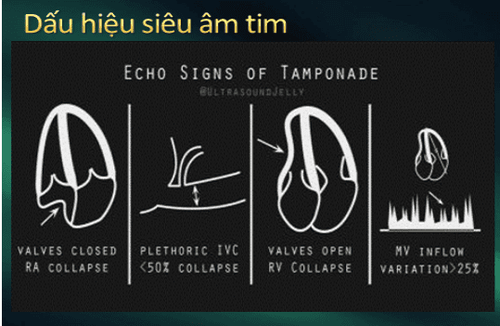
Estimate volume: When echocardiography
<1cm 100cc 1-2cm 100-500cc > 2cm > 500cc
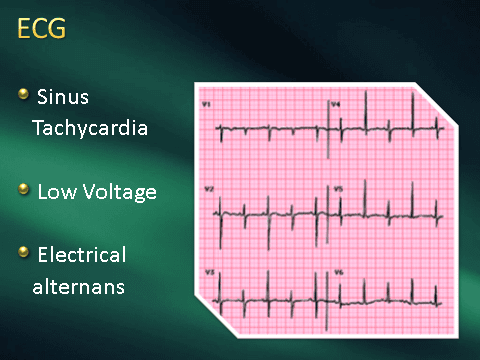
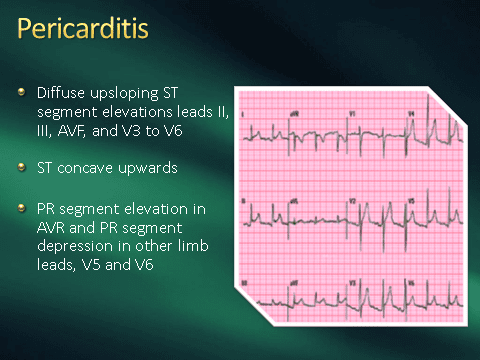
About electrocardiogram:
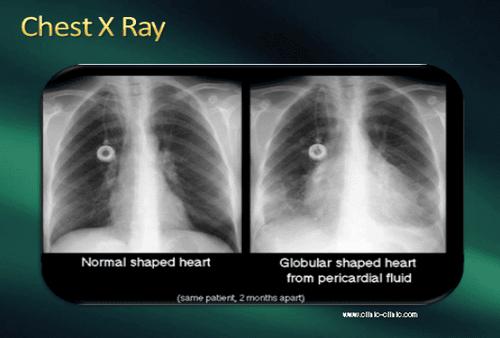
Chest X-ray:
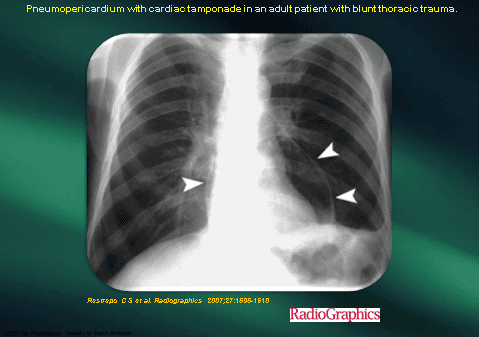
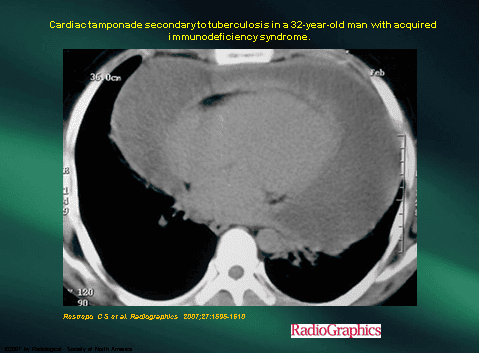
4. Treatment
Oxygen Infusion Transfusion of blood, plasma or saline to maintain adequate intravascular volume. Bed rest elevates the legs, which can help increase venous return. Inotropes (Dobutamine) Choose inotropes that do not increase systemic vascular resistance while increasing cardiac output.
5.Treatment of acute cardiac epoch
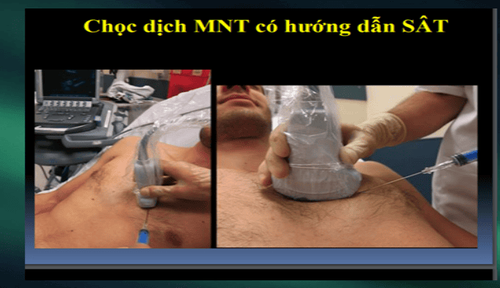
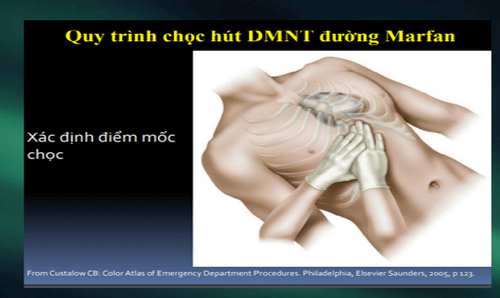
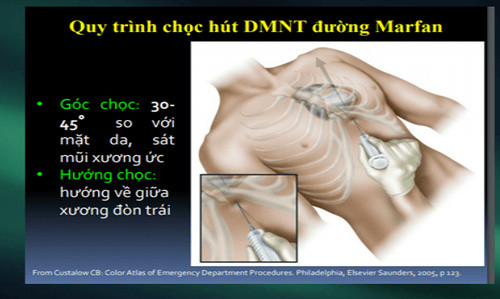
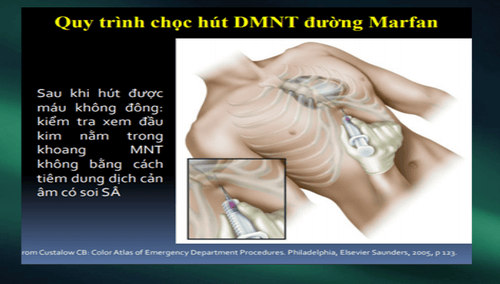
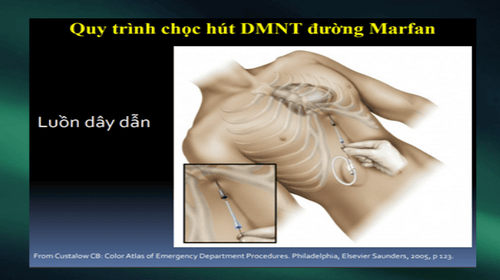
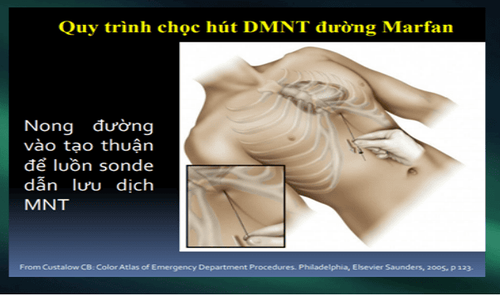
Emergency blind drainage Or ultrasound-guided puncture. Surgical excision: If the pericardial cavity cannot be reached by needle/catheter. Indicated in patients with intrapericardial bleeding, or blood clots. Positive airway pressure should be avoided because it reduces cardiac output.

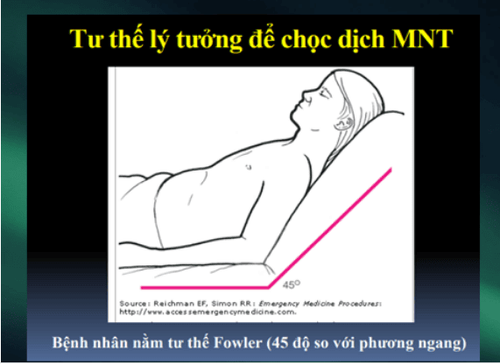
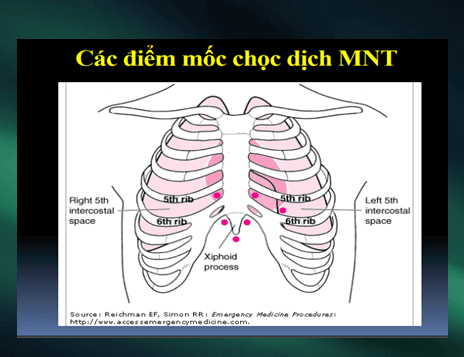
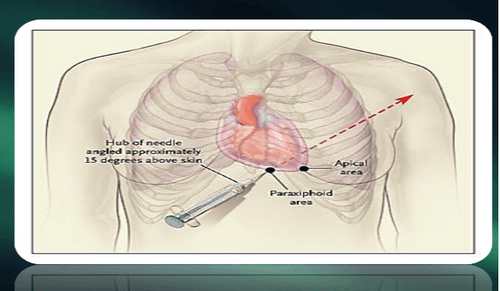

Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.