This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Cao Thanh Tam - Cardiologist - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital. Master - Doctor Cao Thanh Tam has many years of experience in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseasesThrombosis can occur in any blood vessel in the body, but most often in the veins, especially those located deep inside the body such as the legs, causing deep vein thrombosis (Deep) Vein Thrombosis (DVT).
1. What is Thrombosis?
Thrombosis is the process by which blood cells gather to a torn blood vessel and stop bleeding when you are injured, for example, if you accidentally bleed yourself, at this time the clotting process will be activated. Platelets are summoned to the area of injury to create the initial stopper.The clotting factors in the blood cause a rapid chain reaction, leading to the formation of fibrin fibers that hold the platelets together. Many platelets release chemicals that attract other platelets to form a more stable clot and stop bleeding.
Proteins in the body help determine when to stop the clotting process when it is large enough. As the wound heals, the fibers dissolve on their own and the platelets return to normal blood tissue.
2. Mechanism of thrombus formation
Thrombosis or blood clot is defined as a pathological process due to the inappropriate initiation and spread of hemostatic reactions in the body leading to the formation of blood clots in the blood vessel lumen. Depending on the size of the thrombus, the diameter of the blood vessel, the thrombus can cause complete or partial embolism or embolism...Stages of thrombus formation
The process of forming a blood clot (thrombosis) ) is the clotting process with more than 30 factors involved in this process, going through the following stages:
2.1. Vascular phase When a blood vessel is injured, the vessel wall constricts by reflex mechanism. Platelets that are moving freely in the blood vessel will gather in the lesion to form a knot called a white blood clot or Hayem nail, the platelets will stick together and secrete some factors that initiate the process coagulation and this is called the hemostasis phase.
2.2. The plasma phase This phase is quite complicated. In the blood vessels with the participation of many factors; thromboplastin formation, thrombin formation acting on fibrinogen eventually forming fibrin fibers (fibrin).
2.3. Thrombolytic phase Includes the stage of blood clotting and clot dissolution. Clotting by plasmin degradation is regulated by a number of stimulants and inhibitors.
Classification of thrombosis
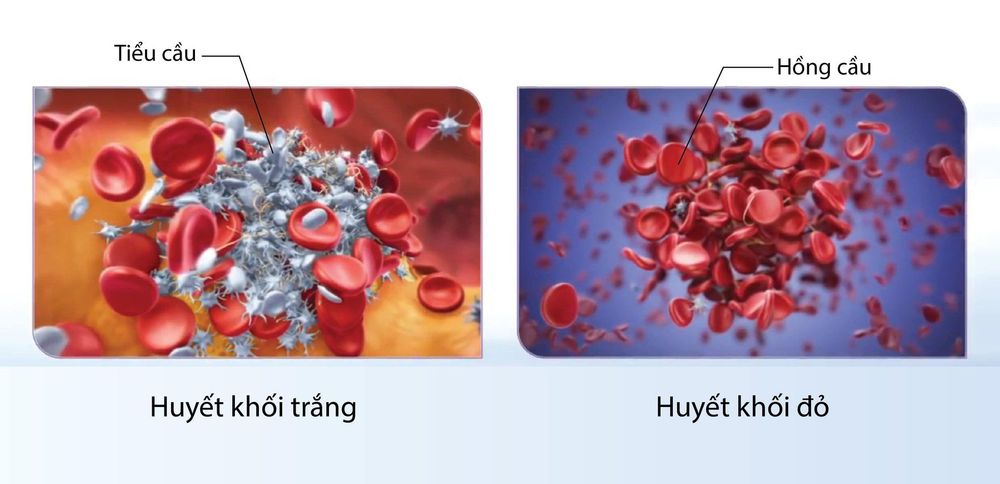
In terms of structure, thrombus usually has two types, white and red thrombus, and can also meet mixed type. White blood clots form when endothelial cells are damaged, platelets stick and aggregate, the main component is platelets; Common in arteries such as coronary vessels, cerebral vessels,...
Red blood clots form when the blood flow is slow with the main component being fibrin fibers that cover red blood cells, usually in veins.
In addition, thrombosis is also classified into arterial, venous and microvascular thrombosis.
Arterial thrombosis is composed mainly of platelets. Vascular damage and increased platelet activation are major factors in thrombosis. Common in people with cardiovascular disease such as high blood pressure, blood fat, diabetes...
3. Factors causing thromboembolism
3.1 Vascular Abnormalities The normal vessel wall structure consists of three layers: the pericardium, the mediastinum, and the endothelium. In it, the endothelium is in direct contact with the blood circulating in the vessel. Normally, the endothelium synthesizes and secretes substances that inhibit platelet activation and vasodilatation. Endothelial incompetence results in embolism by loss of anti-embolic properties and the expression of platelet-activated components in the subendothelial system. Common in patients with coronary atherosclerosis, hypertension,...3.2 Abnormal blood flow When blood flow increases, displacement is high or blood flow is decreased, displacement decreases or A steady increase in blood viscosity will activate platelets, leading to thrombus formation.
3.3 Abnormalities in blood components All abnormalities in platelets, coagulation factors, coagulation inhibitors as well as fibrinolytic system factors alone or in combination can lead to thrombosis (blood clot).
4. Signs of Thrombosis
4.1 Swelling of one leg In most cases, DVT will lead to swelling in the affected leg. It is usually noticeable below the knee and rarely occurs in both legs. This is because when a blood clot forms in a vein, blood cannot return to the heart and the pressure causes fluid to escape in the legs.4.2 Skin discoloration When blood flow is blocked in the veins, the skin over that area can begin to change color, like a bruise. Shades of blue, purple, or even red can be seen. If your skin is discolored and it's itchy or hot to the touch, you should see a doctor.
4.3 Shortness of breath Because blood circulation is affected, oxygen levels may begin to drop. As a result, you may feel an increased heart rate, dry cough, and shortness of breath.
This could be a sign that the blood clot has moved to the lungs, especially when accompanied by dizziness. Call 911 and seek medical attention as soon as possible in such cases.
4.4 Pain in one leg or arm This type of pain can occur alone or with signs of skin discoloration and swelling. Thrombotic pain can easily be confused with muscle cramps or tension, which is why the problem is often undiagnosed and especially dangerous.
4.5 Severe pain in the chest When a blood clot travels to the lungs, it can cause a pulmonary embolism and cause symptoms similar to a heart attack.
According to Dr. Thomas Maldonado of NYU Langone Medical Center, a dull ache that is felt in the center of the chest but radiates to surrounding areas is more likely a heart attack. A pulmonary embolism can feel like a sharp pain that increases with each breath.
5. Enemies of Cardiovascular Patients
Under normal conditions, thrombus formation is usually small and short-lived, these clots will be cleaned up by a fibrinolytic agent such as plasmin. It has a hemostatic effect when bleeding due to lacerations.However, when this process occurs in the blood vessel without rupture, it is called pathological thrombosis and harms the body, potentially causing death at any time. Pathological thrombus formation is the result of the interaction of three factors: hemodynamic changes, endothelial integrity, and an increase in platelets and coagulation proteins.
Blood clots that form at the wrong time in the right place in the blood vessel can stop at one place, grow bigger, cause a blockage or move anywhere along the flow of blood, to a blood vessel with sugar The glass is smaller than its size, it will cause embolism, it is really dangerous when it moves to the cerebral blood vessels, causing a stroke, to the heart, causing a heart attack, and can take the patient's life at any time. without any prior notice.
In people with cardiovascular disease, the risk of blood clot formation is very difficult to avoid. Therefore, it is said that thrombosis is the enemy of cardiovascular patients.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.