This is an automatically translated article.
This article is expertly consulted by Master, Doctor Bui Ngoc Phuong Hoa - General Internal Medicine - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.If after a while since the onset of the migraine, the patient's eye muscles gradually weaken, endure more pain around the eye area, it is a sign of a new disease, related to damage to the cranial nerve - ophthalmology.
1. Migraine near the eye socket
A migraine near the orbit is a nervous system problem that affects the eyes and head. People with this rare condition will experience headaches and pain around the eyeballs. The muscles around their eyes become weak and tired, causing double vision (also known as double vision).Many people still confuse this disease with a common migraine condition (Migraine). Despite many similar symptoms, proximal orbital migraine is a distinct neurological disorder. This symptom involves the oculomotor nerves – most typically the third cranial nerve, which helps us move our eyes and eyelids. In some cases, it also affects the sixth cranial nerve, which controls side vision, and the fourth cranial nerve, which causes our eyes to move up and down.
Migraines around the eyes often appear in children and adolescents. The majority of people who experience this eye pain headache are women.
2. Symptoms of migraine near the eye socket
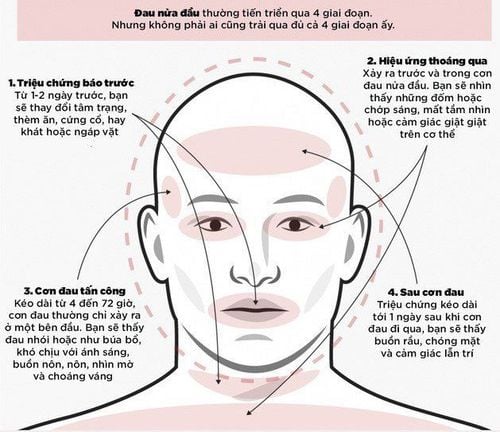
The most common symptoms include :
Muscles around one or both eyes are weak or even paralyzed. Pain around the eyeballs The irises are misaligned, out of alignment (crossed eyes) Diplopia (one-to-two vision) Irregular pupils, large, small Sensitivity to light May be painful throbbing on the same side of the head as in a migraine before the eye muscles weaken a few days or even weeks. Upper eyelid drooping (drooping eyelid) Nausea or vomiting.
3. Causes of migraine around the eye socket area
Doctors don't know why some people get migraines near the eye sockets. But it's usually due to the effects of stress, alcohol, or certain foods.It is theorized that Myelin - the name for the coating that surrounds the axons of some nerve cells, breaks down for some reason and causes the nerve to become inflamed. Myelin then heals on its own, allowing symptoms to subside within a few days or weeks. But a short time later, this eye pain will reappear.
Problems in the blood vessels that prevent the eyes from being supplied with an adequate amount of blood is also a cause of the above fatigue.
Recently, some experts in the field have suggested that migraines cause a sudden narrowing of the arteries that send blood to the optic nerve in the skull (third nerve). , IV, and VI) causes them not to receive enough blood, leading to weakness or paralysis of the eye muscles.
However, more in-depth studies are needed to fully understand why proximal migraines occur.
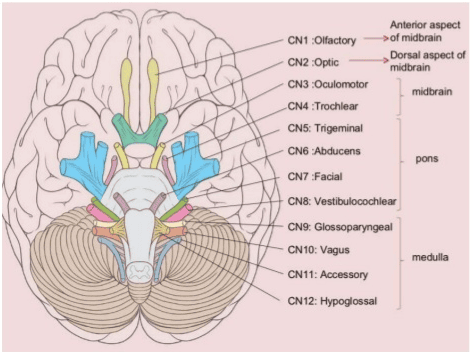
4. Diagnose headache and eye pain
Currently, because medical professionals have not yet found a test to detect periocular migraine, it is only possible to use a method to rule out other possible disorders in the patient first. when diagnosing.After asking about the patient's symptoms and medical history, the doctor will conduct an eye exam. The eye may be dilated with specialized eye drops to help the ophthalmologist see the patient's pupils better.
In addition to migraines near the orbit, lymphoma, meningitis, granulomatous disease (sarcoidosis) or blood clots can also cause the eye muscles to be weak or paralyzed. Therefore, doctors need to suggest patients to do tests for the above diseases to ensure accuracy before making a diagnosis.
Additional tests needed include:
Blood tests to check for blood clots or infections Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) - a method of obtaining detailed images of organs, which helps doctors diagnose tumor (if any) in the cranial nerve. Lumbar puncture to check for meningitis, lymphoma, leukemia, or infectious disorder Chest X-ray and blood tests help detect Granulomatogram Angioplasty (DSA) helps find whether or not there is a weak (narrowed) blood vessel or aneurysm. If the above conditions have been ruled out, accompanied by the onset of migraine symptoms and then the patient's previously reported weakness or paralysis of the eye muscles, doctors may diagnose migraines. near the eye socket.
5. How to treat migraine near the eye socket
Doctors will usually prescribe several medications that are suitable and can help the patient. Patients need to work closely with their doctor to find the best treatment.Intravenous (IV) pain relievers, such as Methylprednisolone or prednisone, are helpful in certain groups of patients.
Several different blood pressure medications, such as beta-blockers and calcium antagonists, also offer some positive results. However, there is no evidence that these medications can help treat or prevent migraines.
Like other migraines, finding the cause of eye pain and proactively preventing it is the best solution. Saying no to alcohol, toxic foods and reducing stress are very important notes that patients need to keep in mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Articles refer to the source Webmd.com