This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Ta Quang Hung - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec International General Hospital Da Nang.Blood transfusion is one of the effective therapies for many anemic patients, especially those with acute blood loss. In the fields of internal medicine, obstetrics, surgery... we often encounter many patients who need a large amount of blood transfusion in a short time to hope to be saved.
1. What is Mass Blood Transfusion?
Mass transfusion is the operation of transferring large volumes of blood over a short period of time in a patient with severe or uncontrolled bleeding. In the past, adult bulk blood transfusion was defined as the transfusion of 10 units of red blood cells within 24 hours in response to heavy and uncontrolled bleeding. However, this definition has been changed in order to treat more quickly and effectively such as transfusion of 3 units of erythrocyte sedimentation rate over 1 hour due to uncontrolled blood lossThere are also some other definitions such as mass transfusion Massive blood transfusion is blood that is transfused 50%-100% of the recipient's blood volume within 12-24 hours or 8 units over 30 minutes.
2. Benefits of Mass Blood Transfusion

3. Selection of blood and blood products in mass transfusion
First of all, it is necessary to ensure optimal ABO and Rh blood group matching between the donor and recipient and to perform a matching test on each unit of blood transfused.In the absence of co-type blood, group O blood with low antibody titres, also known as non-dangerous O blood, can be used for transfusion for patients with blood groups A and B; or use group A blood or group B blood for transfusion for patients with blood group AB or group O red blood cells for transfusion for patients with blood group A, B, AB.
In case a whole blood of different types has been used to transfuse the patient and there is no group O red blood cell mass, every effort must be made to ensure that blood group during the emergency period for the patient.
Transfusion blood must be maintained at 37 0C by means of blood warmer.
Blood used in bulk transfusion should be stored within 72 hours or not more than 5 days preferably. If blood is stored for a longer period of time, it is necessary to combine the use of fresh frozen plasma or a combination of red blood cells and fresh frozen plasma.
4. Possible complications
Acid-base imbalance: Mass transfusion can cause infection metabolic acidosis due to organizational hypoxia and the use of anticoagulants containing a lot of acid in the blood bag.
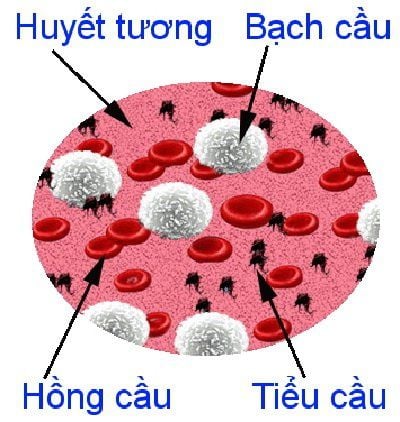
Potassium imbalance: The longer the blood is stored, the red blood cells will be destroyed and release potassium into the plasma, which is toxic to the heart and causes kidney failure.
NH4 infection: Normally, the body has about 140 mg/1 liter of blood. The longer the blood is stored, the more NH 4 increases, so when a large volume of blood is transfused, the liver can not remove NH 4 in time, leading to liver toxicity and coma.
Hypothermia : Blood is normally stored from 2 0C -8 0C , cold blood transfusion and too fast often cause thermoregulation and cause cardiac arrhythmia . If cold blood at 8 0C can cool the endocardium and cause endocardial paralysis, patients will die, especially children.
Reducing enzyme 2, 3 DPG (Diphosphoglycerate) is an enzyme that helps to release oxygen in the HbO 2 complex (Oxy Hemoglobin) because the longer the blood is stored for a long time, the lower the enzyme 2, 3 DPG decreases. If the patient transfuses a lot of blood stored for many days, the oxygen exchange in the cells will be lacking, leading to the patient's brain irritation, so the hypoxia becomes more severe.
Injury to red blood cells: The cause may be due to the blood suction pump, due to improper warming of the blood.
Blood clotting disorders: Because platelets and clotting substances are diluted in the circulation, in addition, blood stored for a long time increases the small adhesion in the blood unit, which will increase the coagulation activity leading to thrombocytopenia. and blood-clotting agents.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a high-quality medical facility in Vietnam with a team of highly qualified medical professionals, well-trained, domestic and foreign, and experienced.
A system of modern and advanced medical equipment, possessing many of the best machines in the world, helping to detect many difficult and dangerous diseases in a short time, supporting the diagnosis and treatment of doctors the most effective. The hospital space is designed according to 5-star hotel standards, giving patients comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Master. Doctor Ta Quang Hung has over 10 years of experience in teaching and practicing in the field of Anesthesia and Resuscitation. Currently, he is an Anesthesiologist, General Surgery Department - Vinmec International Hospital Da Nang.
If customers notice unusual problems, they should visit and consult with specialists.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.