This is an automatically translated article.
The article is written by Specialist Doctor II, MSc. Pham Tuyet Trinh - Head of Inpatient Unit, Cardiology Center - Vinmec Times City International HospitalDuring the test, the body is more active and requires more energy, so the heart has to pump more blood. The test can show whether the blood supply of the arteries that feed the heart is adequate. Stress testing also helps your doctor know what type and level of physical activity is right for you. Stress testing is done with a treadmill or a bicycle ergometry.
1. What is a stress test?
The exercise test or stress test is a non-bleeding exploratory test, also known as the wheelchair walk or bicycle test, in parallel with the ECG, therefore. This test helps your doctor determine whether symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and palpitations are cardiovascular causes that are not present at rest, and determine how well your heart is when your body exertion.In addition to the stress ECG, there are several types of stress tests: Stress echocardiography; stress echocardiography; stress magnetic resonance.
History of stress testing:
1928: Feil and Siegel noticed ST-T changes on the electrocardiogram during exercise Stress test 1956: Bruce introduces the process of doing a running mat stress test
2. Indication for exercise testing
Diagnose coronary artery disease Diagnose the cause of possible cardiovascular symptoms such as: chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations Determine the extent of some types of valvular disease Determine the safe level of exercise: determine the level of exertion of participants in a program of sports or physical activity, cardiac rehabilitation. Evaluating the effectiveness of some cardiovascular treatments: after coronary artery bypass graft surgery, after coronary revascularization stent placement. Predict the risk of cardiovascular events: stroke, angina pectoris. Diagnosis of exercise-related arrhythmias. Evaluation of physical activity of some congenital heart diseases, heart valve disease. Assess the function of pacemakers with frequency response. Some special professions: diver, pilot. Patients > 40 years of age, asymptomatic and with ≥ 2 cardiovascular risk factors or who plan to undergo severe physical activity. Assess the effectiveness of treatment in hypertension before engaging in high-intensity physical activity. Indications other than cardiovascular disease: assessment of post-exercise tolerance; diagnosis of bronchial asthma after exercise; assessment of respiratory failure and prognosis; preoperative assessment; measure V02 max.3. What to do before a stress test?

4. What activities will take place during the test?
Connect electrodes according to the diagram, fix electrodes and connect to equipment: electrocardiogram, sphygmomanometer, running mat or bicycle Walking slowly on the running mat The treadmill will be controlled gradually incline and change the speed Pre-installed phase-by-stage acceleration: there are usually 7 exercise phases and recovery phase - Recovery (3 minutes each). You will be monitored blood pressure, breathing, heart rate, clinical signs throughout the test: fatigue, shortness of breath, chest pain You can stop the test whenever you want or the doctor will stop. testing if there are some abnormal changes in blood pressure, or in the electrocardiogram. Before stopping the test, the machine will slow down and then stop completely. You will sit or lie down to continue monitoring your blood pressure and heart rate every 3 minutes until 12 minutes later.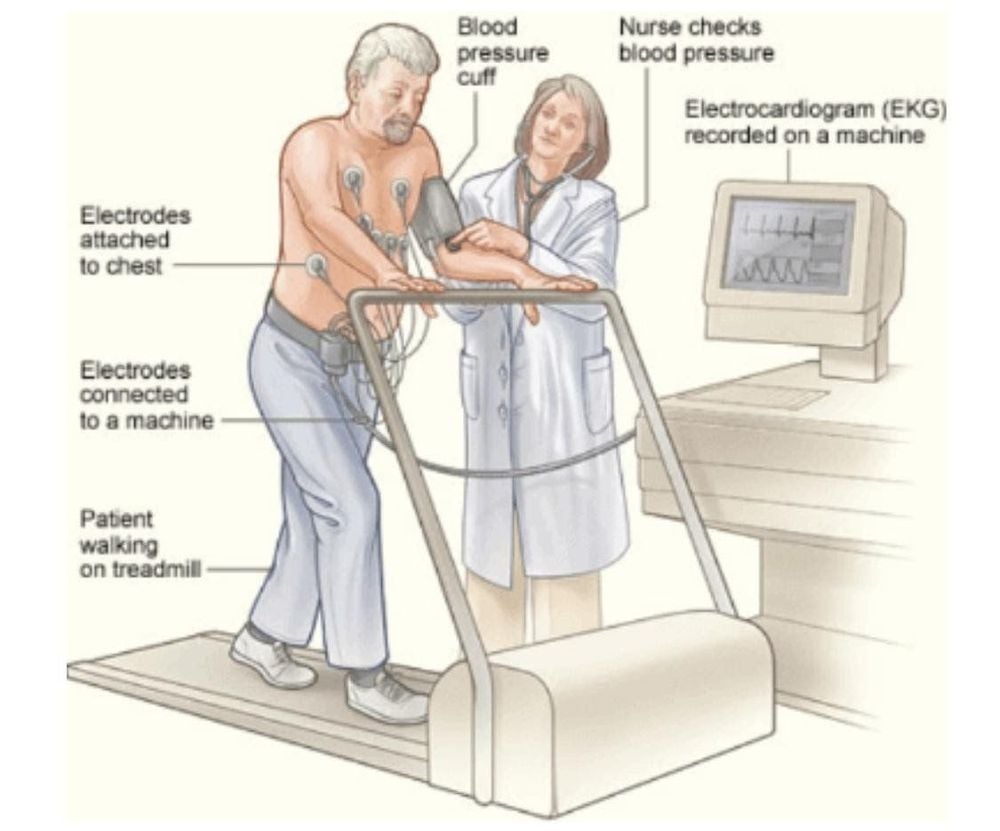
5. Parameters monitored during testing
Blood pressure: monitor blood pressure before the test, during the test every 3 minutes (set the program automatically) Heart rate, electrocardiogram: continuous monitoring on monitoring in basic ECG leads, monitoring Abnormal electrocardiogram changes and automatically recorded. Your breathing rate, fatigue, unusual signs such as: shortness of breath, sweating, cyanosis, chest pain, cramps... Monitor device activity: slope, running mat speed, bike speed according to a pre-selected procedure (Bruce or Modified Bruce procedure)6. When to stop testing?
Immediate when: New signs of myocardial infarction Moderate to severe chest pain systolic blood pressure drops of more than 10 mmHg despite increased exercise or electrocardiographic signs of ischemia Manifestations of decreased perfusion: cyanosis, cold, moist skin, dizziness, dizziness. Severe or unusual dyspnea Have a dangerous arrhythmia: atrioventricular block, ventricular tachycardia.. Consider stopping the test when: Any case of increased chest pain, dyspnea, fatigue Feet fatigue or otherwise responsive (cramps) Excessively high blood pressure (SBP > 260 mmHg, DBP > 115 mmHg) Diabetic changes: ST elevation ≥ 1mm in leads without prior Q waves (except V1 or aVR); ST depression > 2mm, lateral or descending, especially if accompanied by chest pain. Presence of exercise-induced bundle branch block that is indistinguishable from ventricular tachycardia. Less dangerous cardiac arrhythmias: HFMD, high number of NTT/T... Achieved 85% of maximum theoretical frequency: Astrand's formula: maximum theoretical frequency (MST) = 220 - Age
7. Assess the results of stress testing when investigating coronary artery disease?
Does the stress test reach the theoretical frequency? (Based on Astrand formula for age) Guaranteed exercise duration of at least 6 minutes and is age and gender dependent Heart rate and blood pressure response to exercise level. Stress test (+) or (-): according to the Duce treatmill score scale based on three parameters: duration of exertion (minutes); ST change relative to isoelectric (mm); Angina score: 0- No pain; 1- there is pain but no limitation of exertion; 2- Chest pain must stop testing Risk assessment: low risk when Duce score ≥ +5; Average (Medium) Score from -10 to +4; high risk when score ≤ - 11. Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical professionals, modern equipment and technology, but also outstanding with comprehensive and professional medical examination, consultation and treatment services; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
ReferenceACC/AHA Guidelines for Exercise Testing: Executive Summary. Circulation, 96(1), pp. 345–354 (1997) Stress testing to determine prognosis of coronary heart disease. Up to date (2019)