This is an automatically translated article.
Article by Resident Doctor Nguyen Thi Thuy Hang - Doctor of Microbiology - Laboratory Department - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
Aspergillus infection can spread by blood to many other organs, when reaching the brain can cause seizures, infarction or meningitis. Aspergillus galactomannan test has the advantage of early detection 5-8 days before clinical manifestations or X-ray signs.
1. What is Galactomannan?
Galactomannan is a polysaccharide antigen that exists mainly in the cell walls of Aspergillus species. Galactomannan can be released into the bloodstream and other body fluids even in the early stages of Aspergillus infection. The presence of galactomannan antigens may persist for 1 to 8 weeks. Therefore, the detection of galactomannan antigen levels through enzyme immunoassays (ELISA) may be useful in the early diagnosis of invasive Aspergillus infections.2. How dangerous is Aspergillus infection?
Invasive Aspergillus infections, mainly caused by Aspergillus fumigatus, are a severe, high mortality form of Aspergillus infections. Aspergillus species can directly invade the bronchi, trachea and lungs, leading to airway compression and serious sequelae, such as necrotizing pneumonia, and they can also affect other organs by spread by blood.
In the past, invasive Aspergillus infections have been reported to occur mainly in patients with neutropenia, particularly when neutrophils are less than 500 cells/mm3, such as in patients have hematologic malignancies, tissue transplants, hematopoietic stem cell transplants, and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection or are on long-term immunosuppressive therapy. However, it is increasingly being found that people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), bronchiectasis or pre-existing tuberculosis, are also susceptible to Aspergillus infection in the lungs.
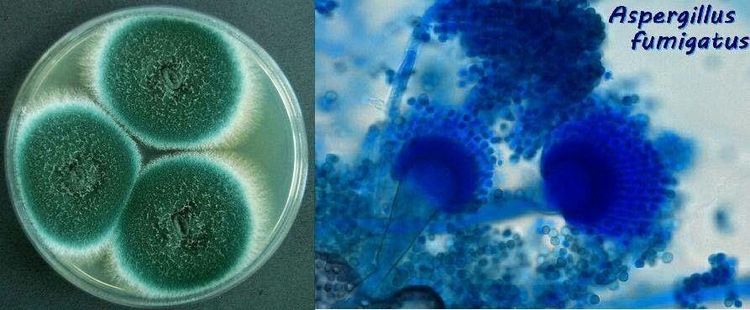
The clinical signs of this disease are nonspecific and are often confused with bronchopneumonia. Cough with expectoration, shortness of breath, fever unresponsive to antibiotics, chest pain, and hemoptysis are common symptoms. The fungus can spread by blood to many other organs, when reaching the brain can cause seizures, infarction or meningitis. Kidneys, pleura, liver... are places where fungi often cause disease but with a low rate.
3. Aspergillus Galactomannan Test
Early diagnosis of Aspergillus infection is important for prompt treatment as well as to avoid serious complications leading to death. However, due to the lack of specific clinical manifestations, moreover lung biopsy is an invasive and high-risk test while microbiological tests, such as fungal culture in sputum, have very low sensitivity. Therefore, early diagnosis of invasive Aspergillus infection remains challenging.
Aspergillus galactomannan test has the advantage of early detection 5-8 days before clinical manifestations or X-ray signs. Currently, the detection of galactomannan in serum is considered the microbiological diagnostic criterion for fungal infections in neutropenic patients, according to the guidelines of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Invasive Cancer/Fungal Infections. Europe. More recently, galactomannan-detecting bronchoalveolar lavage was also recommended in the Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines in 2016 as a test that provides high-quality evidence in neutropenic patients.
Regarding laboratory specimens, many studies have shown that detecting galactomannan in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid is 71-100% more sensitive than detecting in blood. Bronchoalveolar lavage specimens are obtained at the site of infection, where galactomannan antigens are likely to be much more abundant than in serum. In addition, serum neutrophils can remove galactomannan antigens via the mannan-binding receptor, reducing serum galactomannan levels.
However, the galactomannan test also has many limitations as follows:
A negative test result of serum and/or bronchoalveolar lavage fluid does not exclude the diagnosis of invasive Aspergillosis. Serum samples from patients at risk for invasive Aspergillosis should be tested twice weekly. For positive test results, the definitive diagnosis should be combined with clinical symptoms, other laboratory tests such as chest X-ray, sputum culture/PCR, bronchoalveolar lavage . In summary, Aspergillus fungi can directly invade the bronchi, trachea and lungs, leading to airway compression as well as leaving serious sequels, such as necrotizing pneumonia, and they can also affect organs other by blood-borne transmission. The aspergillus galactomannan test is still recognized as having an important role in the early diagnosis of invasive Aspergillus infection.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.