This is an automatically translated article.
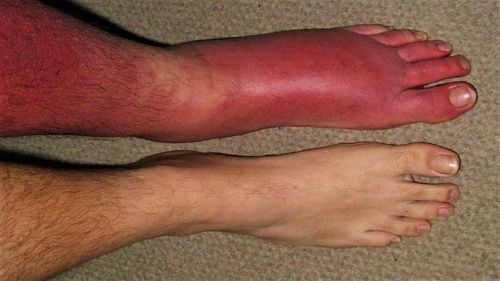
The article was written by Specialist II, Senior Doctor Doan Du Dat - Head of Medical Examination Unit and Doctor Hoang Thanh Nga, Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital.Potassium (K) is one of the electrolyte components of the blood. Normal blood K level is 3.5-5 mEq/L. Hypokalemia makes the body tired, weak limbs, muscle pain, cramps, constipation, can cause complications of bradycardia, decreased myocardial contractility or torsades de pointes tachycardia, is one of the causes of confusion. arrhythmia leading to cardiac arrest. Hypokalemia is very dangerous, especially for patients with pre-existing chronic diseases such as heart failure, obstructive pulmonary disease...
1. Symptoms of hypokalemia? How to deal with it?
Manifestations of hypokalemia are mainly in the cardiovascular and neuromuscular systems. Cardiovascular manifestations include weak pulse, decreased systolic blood pressure, orthostatic hypotension, and auscultation with a systolic murmur. Electrocardiogram shows U wave, flattened ST segment, extrasystoles of all kinds, especially when there is QT prolongation and torsades de pointes arrhythmia, which means severe hypokalemia, extremely dangerous for the patient's life if not treated. timely replacement of potassium.
In the case of hypokalaemia, it is necessary to replace the lost K in the body, to achieve normal blood K, in one of the following forms:
If hypokalemia is mild: Just by providing food rich in K such as bananas, oranges, or drink Oresol water, mix each pack with 1000ml of drinking water... If blood K is reduced moderately: Need to take K tablets, usually Kaleoride or Kaldyum 600mg a day 3 divided into 3 times after meals. If severely reduced (K < 2.5mmol/l) Blood K: Need to infusion of potassium in isotonic saline serum, the usual dose is 20-40mmol/1 liter, according to the following usual concoction:
| Lượng KCl | Lượng K+ | Thể tích tối thiểu sau khi đã pha loãng bằng NaCl 0.9% hoặc G5% | Thời gian truyền |
| 1 g | 13.4 mmol | 250 mL | 1 h |
| 2 g | 26.8 mmol | 500 mL | 2 h |
| 3 g | 40.2 mmol | 1.000 mL | 3 h |
| 4 g | 53.6 mmol | 1.000 mL | 4 h |
Note: K blood transfusion can only be done in privileged medical facilities, not at home or where K transfusion is not allowed.
2. Why is there a phenomenon of falsely high blood K?
Extracellular fluid accounts for only about one-third of the body's fluids, so most (about 98%) of potassium is in the cells, with only a small amount outside (1.5-2 percent).Therefore, disturbances in serum potassium levels are often the result of transmembrane potassium translocation which may not accurately reflect total body potassium deficiency or excess. Increased intracellular potassium migration may increase serum potassium levels or aggravate pre-existing hyperkalemia but not total body potassium. Pay attention to cases of pseudohyperkalemia due to:
Ischemia in the blood collection area: Garrot is too tight and prolonged. Hemolysis in vitro: Due to the technique of drawing blood (using a fine needle), leaving the blood tube for too long or during the transport of the blood tube causes the rupture of red blood cells. Leukocytosis (> 50 G/L) or thrombocytosis (> 1000 G/L) causes the blood sample to clot and release potassium from the cells.
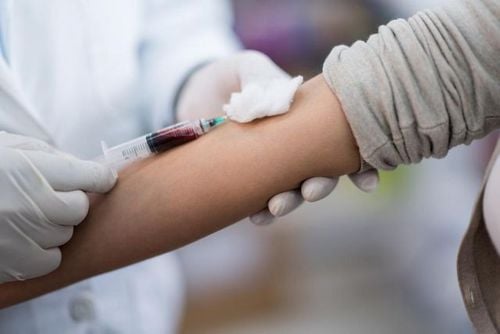
Xét nghiệm nồng độ kali máu
3. What happens to the body if there is a lack of K in the blood?
Manifestations of K deficiency: Body fatigue, muscle weakness, even lower limb paralysis, can cause complications of bradycardia, decreased myocardial contractility or torsades de pointes, is one of the causes of disorders heart rate leading to cardiac arrest. Effects of anemia on the body: The body will manifest the conditions due to hypokalemia (mentioned above) How if the body is hypokalemic: Need to compensate for blood potassium depending on the degree of hypokalemia It is up to us to decide how to compensate for K through oral administration or infusion of potassium-containing solutions. Need to compensate the body for the amount of K lost, in order to achieve normal blood K (as above).

Hạ Kali máu gây tình trạng mệt mỏi cho người bệnh
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
SEE ALSO:
What disease does hypokalemia warn of? Treatment and management of hypokalemia Causes and effects of hypokalemia