This is an automatically translated article.
Cupping is a rather unique non-drug therapy that brings certain benefits. So what is cupping and what does the cupping method do?
1. What is cupping?
Cupping is a method of therapy originating from China, also known as fire therapy. The mechanism of cupping is to use specialized cups to place on the patient's skin. The purpose is to create negative pressure in these cups and cause local blood vessel congestion, help relieve pain, reduce inflammation, detoxify or prevent and treat certain diseases.
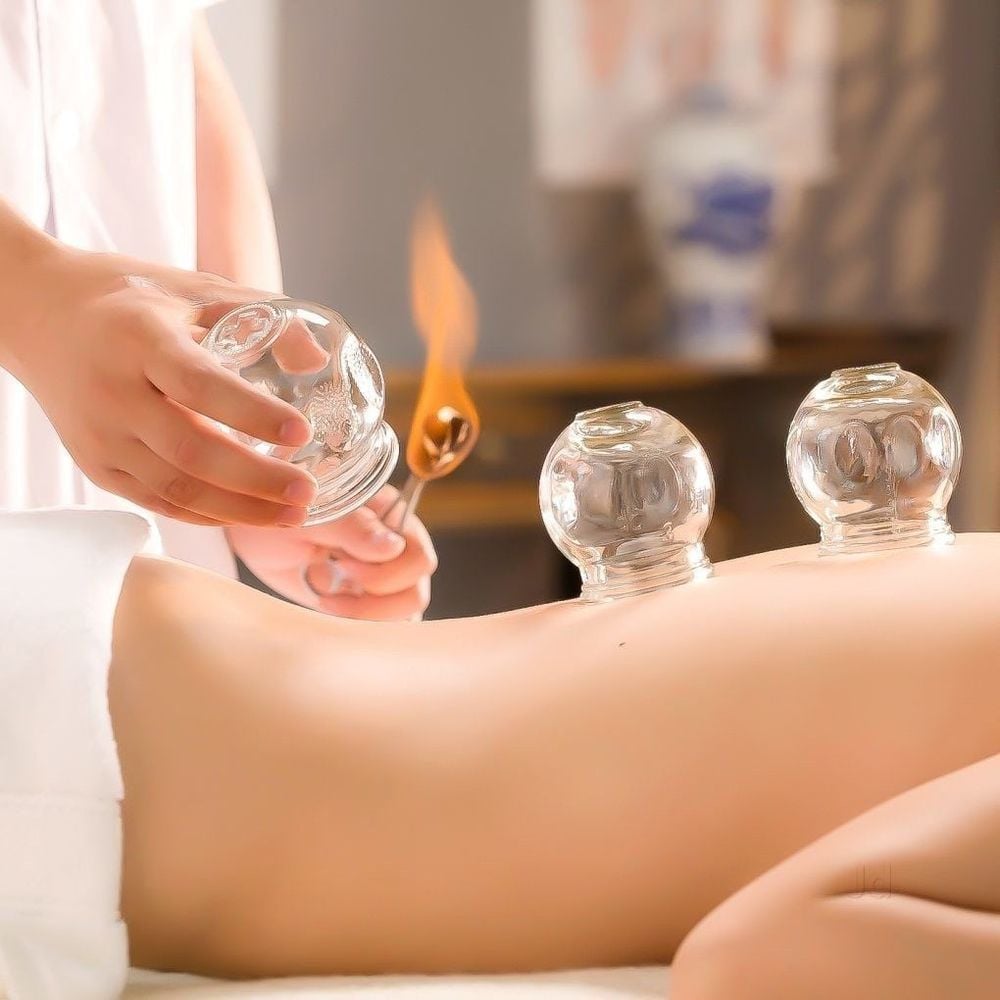

Phương pháp giác hơi hay còn được gọi là hỏa liệu pháp
2. Classification of cupping
Current cupping methods include the following:
"Dry" cupping: This method is done by heating the inside of the cup with a fire stick, burning alcohol, herbs, paper. When the fire goes out, the cup holder quickly puts the cup against the patient's skin, when the air inside cools, it will create negative pressure to pull the skin inside the cup. "Air" cupping: This is a cupping method that instead of using a flame to burn, the cup is pressed to the skin and sucks in the air in the cup with a dedicated pump to create a vacuum. Cupping "wet": Cupping in this way will combine pricking the skin before placing the cup. When the cup is pressed against the skin and the skin is aspirated, a small amount of blood may flow from the injection site to help remove toxins from the body.
3. What does the cupping method do?
3.1 According to Traditional Medicine
According to Traditional Medicine, cupping has the effect of regulating yin and yang, the first channel of communication, edema, eliminating evil, activating blood, eliminating stasis, and eliminating pain.
Through the mechanical side effects of temperature stimulation, cupping leads to local and systemic reactions, thereby regulating the body's functions, eliminating pathological factors.

Giác hơi có tác dụng giả trừ mệt mỏi, đau nhức cơ thể
3.2 According to modern medicine
According to modern medicine, the negative pressure inside the cup has the effect of pulling the skin into the area inside the cup, helping the pores to open, stimulating the circulation of blood in the vessel, and also creating Open a hole to eliminate toxins in the body.
Besides, the vacuum environment inside the cup also helps the tissues to expand locally, which facilitates the dilation of blood vessels and increases blood flow to the pathological tissues, increases oxygen supply, and increases blood flow. Cell metabolism and effective anti-inflammatory and pain relief.
4. Indications and contraindications of cupping
Some diseases can be treated by cupping method including:
Colds, bronchitis, asthma Bone and joint pain such as back pain, knee pain... or muscle and joint pain Stomach pain, gastritis High blood pressure Colds, coughs, obesity Treatment of dermatological problems such as herpes, acne. Cases need contraindications to cupping
Patients with skin lesions in the cupping area such as scratches, dermatitis, dermatological diseases such as tinea versicolor, ringworm, eczema, psoriasis... Patient has fever tall or convulsing

Người bệnh đang bị sốt không được chỉ định giác hơi
Patients with a history of heart, kidney, lung disease Patients with bleeding disorders, bleeding, low platelet counts, blood cancers or taking anticoagulants Patients with systemic edema Mental diseases neurological disorders such as epilepsy, neurasthenia... History of deep vein thrombosis Children under 4 years of age Elderly people when the skin and muscle layers are too thin, complications can occur when cupping Patients with metastatic cancer People who are drunk, too tired, too full or too hungry...
5. How does the cupping process take place?
Cupping can be done at home through the following steps:
5.1 Preparation for cupping
The surrounding environment when cupping should be airtight, with adequate air circulation. Before cupping, you should clean the cupping device with medical alcohol to avoid infection.
5.2 Choosing the cupping position
There is no mandatory position, the patient just needs to choose the position that is most comfortable and convenient.
Sitting position: Selected when cupping the neck, arms, shoulders, back waist. prone position: Choose this position when cupping is in the back, waist or back of the leg. Supine position: When cupping is in the chest, abdomen, front legs. Side lying position: This position when you need to cup your back, shoulders, buttocks and outside of the legs.

Giác hơi có thể được thực hiện ở tư thế ngồi
5.3 Selection of cupping position
The cupping sites should be where the muscles are thick and the subcutaneous fat is moderate. Absolutely do not perform in areas with superficial blood vessels, areas of the heart, areas of skin that are too thin, scarred or flabby skin with many wrinkles. An important note is that the previous cupping position should not be repeated if there are still traces of the old cup.
5.4 Performing cupping
First of all, it is necessary to choose the size of the kit suitable for each patient from small, medium to large. Each time placing 1 cup of steam lasts from 5 to 10 minutes, avoid using too strong suction.
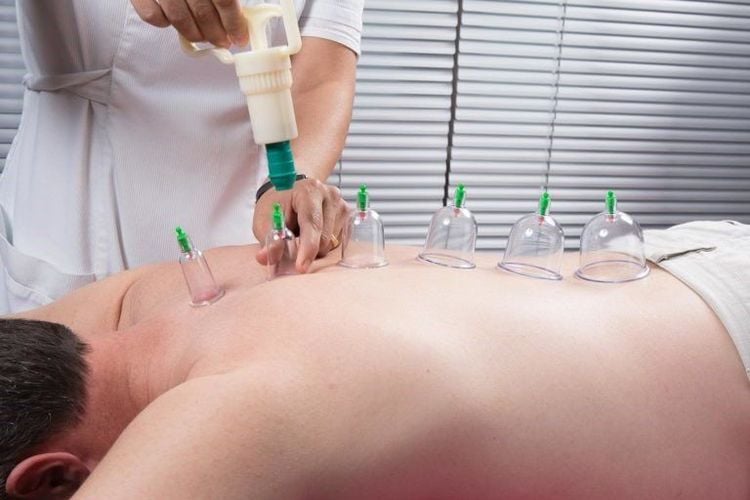
Giác hơi - sự kì diệu của y học cổ truyền
5.5 End of cupping
Wipe or oil the cup skin after removing the cup. Clean the cupping kit with medical alcohol.
6. Some complications can occur when cupping
Some side effects: Skin discoloration, scarring, burns, skin infections or aggravation of eczema or psoriasis. Some serious side effects are less common such as internal bleeding when cupping the scalp or causing blood loss when cupping is injected. Transmission of infectious diseases through blood-stained cupping equipment and use by many different people without proper hygiene. Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consulting services. and comprehensive, professional medical treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Recommended videos:
SEE MORE
Find out how to cure diseases by affecting the spine What is shoulder pain, numbness in hands and feet? Where should I check? Neck pain, leg numbness with a history of cervical spondylosis and nerve root compression?













