This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Van Huong - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.
Nowadays, kidney and urinary tract diseases are very common. Renal ultrasound is one of the most effective diagnostic methods for diagnosing nephropathy. Based on the large kidneys shown on ultrasound results, doctors can diagnose many serious diseases that affect the kidneys.
1. Working principle of the kidney
In the body, the kidney is an important organ in the urinary system, each person has 2 kidneys symmetrically on both sides of the lumbar spine. The kidneys are responsible for filtering waste and converting it into urine, maintaining acid-base stability, regulating electrolytes, and regulating blood pressure.
Kidneys act as the body's natural blood filter. It is estimated that every day 8 liters of the body's blood is filtered through the kidneys 20-25 times, respectively, these two parts filter about 180 liters / 24 hours. The composition of the blood is constantly changing as we digest food and drink, which means that the kidneys must work continuously without stopping.
Thận có vai trò lọc máu tự nhiên của cơ thể
2. What is renal ultrasound?
Ultrasound is a diagnostic technique that uses sound waves to create images of the size, structure, and pathological signs of many organs and organs in the body, including the kidneys. Renal ultrasound is especially useful in diagnosing kidney diseases such as: Kidney stones, kidney cysts, renal abscesses, hydronephrosis ... At the same time, it is also a non-invasive, painless method associated with kidney disease. High accuracy and safety for the patient.Doctors often prescribe renal ultrasound for patients with signs of: dysuria, urinary retention, hematuria, injury and pain in the kidney, ureter, kidney failure (acute and chronic), no Renal shadow on x-ray, sudden hypertension, or suspected polycystic kidney disease.
3. Signs and causes of enlarged kidneys
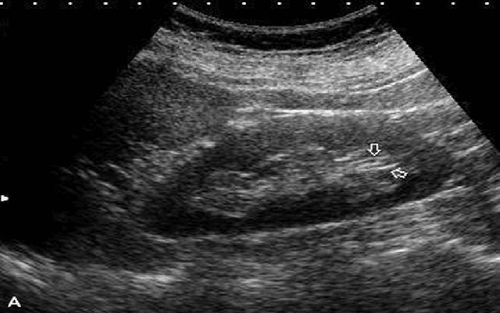
3.1 Normal kidney on ultrasound The kidney is oval in shape, the hilum is inside. In adults, the right kidney will tend to be lower than the left kidney. In terms of size, the average kidney length is from 9-12cm, width 4-8cm, thickness 3-5cm. If the size of the kidney is larger than the above, it is called an enlarged kidney. The size of the two kidneys can vary from 1-1.5cm and also varies by gender (men have larger kidneys than women), depending on age. On ultrasound of a healthy kidney, we can see that the border is even, the left side has pressure on the spleen, making the renal parenchyma look like a triangle, in addition, the renal arteries and veins can be clearly seen.
Hình ảnh thận bình thường trên siêu âm
● The organelles of the kidney are too hyperplastic, causing the kidneys to enlarge (eg, kidney cancer ...)
The kidneys are filled with water due to a blockage at the bottom like stones. ureters, ureteral stenosis ...
Specifically, enlarged kidneys can also be caused by diseases such as:
Water retention, pyelonephritis
Due to a certain cause, the urinary tract is blocked causing urine to flow. accumulates in the renal pelvis and enlarges the kidney. Urine stasis for a long time causes bacteria to grow and gradually become pus, causing fever, swelling, pain in the kidney area and pus urine. Causes of fluid retention and pus in the renal pelvis include:
● Kidney stones, ureteral stones.
● Tumors in the abdomen press on the ureter or because a branch of the iliac artery crosses the ureter...
● Tuberculosis of the ureter causes narrowing leading to narrowing of the ureter and pelvis.
● Prostate tumor, traumatic brain injury, myelitis causing urinary retention, urinary retention.
● Polycystic kidney: Is a congenital malformation with ultrasound results showing enlarged kidneys (usually on both sides, convex surface, convex convex border). Patients often have low back pain, sometimes kidney pain, if there is a bacterial infection, they will have fever or cloudy urine (protein urine, many red blood cells, white blood cells), chronic high blood urea. Renal ultrasonography also shows indirect images of "renal cysts" and elongated calyces. Polycystic kidney disease progresses quite slowly, can last for many years, but the patient still dies because of bacterial superinfection, kidney failure and high blood urea.
● Kidney cancer is an incurable disease that is more common in the elderly, men than women. When ultrasonography of patients with kidney cancer will show images of large, hard, lumpy kidneys, a mass occupying space in the kidney, in addition, it may be associated with varicocele. Patients will feel pain in the lower back, blood in the urine, urine containing many red blood cells.
● Enlarged kidney: If unfortunately there is only one kidney left in the body, making the other side work harder will cause that kidney to enlarge (sometimes 1.5 times normal). This compensatory nephropathy is not a pathology and when combined with the urine test, it will not show protein, white blood cells, red blood cells, as well as urea, blood creatinine is not high.
● Compensatory hypertrophy: Similar to compensatory enlargement, occurs when the opposite kidney is absent, has no function or has impaired function. In more active kidneys there is an increase in length and cross-sectional area by up to 30%, so that the volume can be increased by up to 80%. Meanwhile, the morphology of the kidney remained at the normal level.
● Acute pyelonephritis : A disease that can cause the kidneys to enlarge in both length and cross section. However, there are still cases of acute pyelonephritis showing very little or no apparent change in size.
● Renal vein thrombosis: It is also a disease that causes the kidney to enlarge. When ultrasound shows altered renal echogenicity with areas of hyperechoicity alternating with hypoechoic areas due to bleeding and swelling, perirenal serosa may appear.
● Acute Arterial Infarction: A fairly rare disease, but it can also cause an increase in kidney size. The hyperechoic and hypoechoic areas of edema and bleeding are similar to those commonly seen in trunk venous thrombosis.
Infiltrative causes. Starch infiltrates, lymphoma, and many other causes of infiltration are also the reason for the enlarged kidney, loss of cortical medullary differentiation. No difference was found between the infiltrative causes.
● Acute tubular necrosis: often causes renal enlargement in severe cases. The size of the kidney will change in the following direction: increase in cross-sectional area is more obvious than in length. The kidneys may appear normal if the primary cause is ischemia, but are cortical in tone if nephrotoxic, and the pyramids are enlarged in the presence of Tamm Horsfall protein.
Master Doctor Nguyen Van Huong used to be a Lecturer in Medical Imaging at Danang University of Medicine and Pharmacy, many years of experience working in hospitals such as Cancer Hospital; Da Nang Hospital; Da Nang Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital.
With his dedication to his work, dedication to the medical profession in general and the specialty of diagnostic imaging in particular, Dr. Huong is always loved and trusted by patients.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
Recommended video:
What should people with kidney stones eat?
SEE MORE
Children with nephrotic syndrome: Causes, symptoms, treatment Instructions on how to care & eat for people with kidney dysfunction What to eat with nephrotic syndrome?